Procedure
- measuring the gas consumption through daily checking of the calibration marks on the
gasholder
- measuring the daily input quantities via defined-volume vessels
- measuring the air/slurry temperature with a thermometer.
Documentation
Daily notation of measured values.
Interpretation/results
Daily gas production as a function of substrate input and temperature.
Field testing by the extension officer
Procedure
- installation and daily reading of a dry gas meter to determine the rate of gas production
- random sampling of the CO2 and H2S contents of the biogas
- determination of quantities added by weighing the moist mass and water on a spring scale
- random sampling to determine the total solids content of the substrate
- measuring the digester temperature with the aid of a remote electronic thermometer
- measuring the ambient temperature with a mini-max thermometer
- determining pH levels via litmus paper
- laboratory testing to determine the C/Nratio, volatile solids content and manurial quality of
digested slurry.
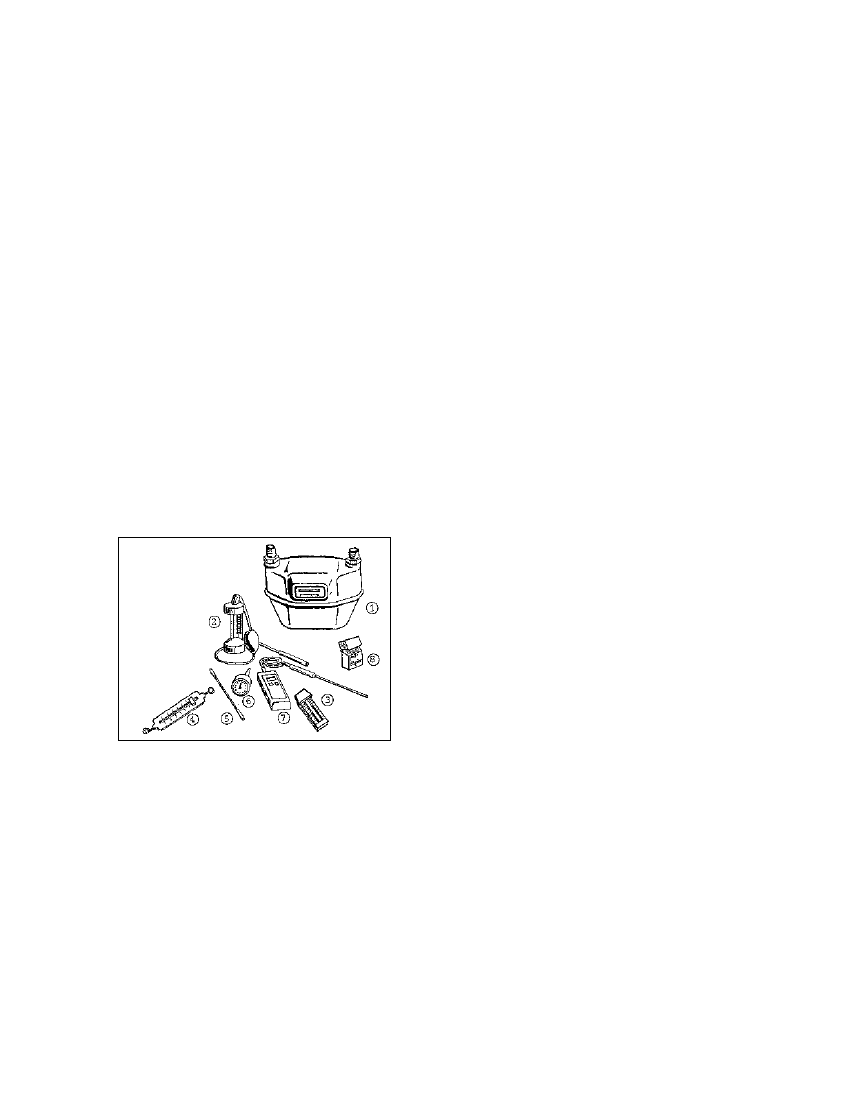
Fig. 5.38: Measuring instruments for biogas field
tests. 1 Gas meter, 2 CO2 tester, 3 Mini-max
thermometer, 4 Spring scale, 5 Stem thermometer, 6
Insertable thermometer, 7 Electric remote
thermometer, 8 Litmus paper (Source: OEKOTOP)
Documentation
Daily entry of measured values in a log book.
Interpretation of results
- time history of daily gas production as a function of temperature and substrate input
- time history of specific gas yield (Gy = m³ gas/kg TS) and of specific gas production (m³
gas/m³ Vd) as a function of temperature
- time history of pH
- time history of maximum and minimum ambient temperatures, i.e. mean monthly and
annual temperatures, plus extremes.
81