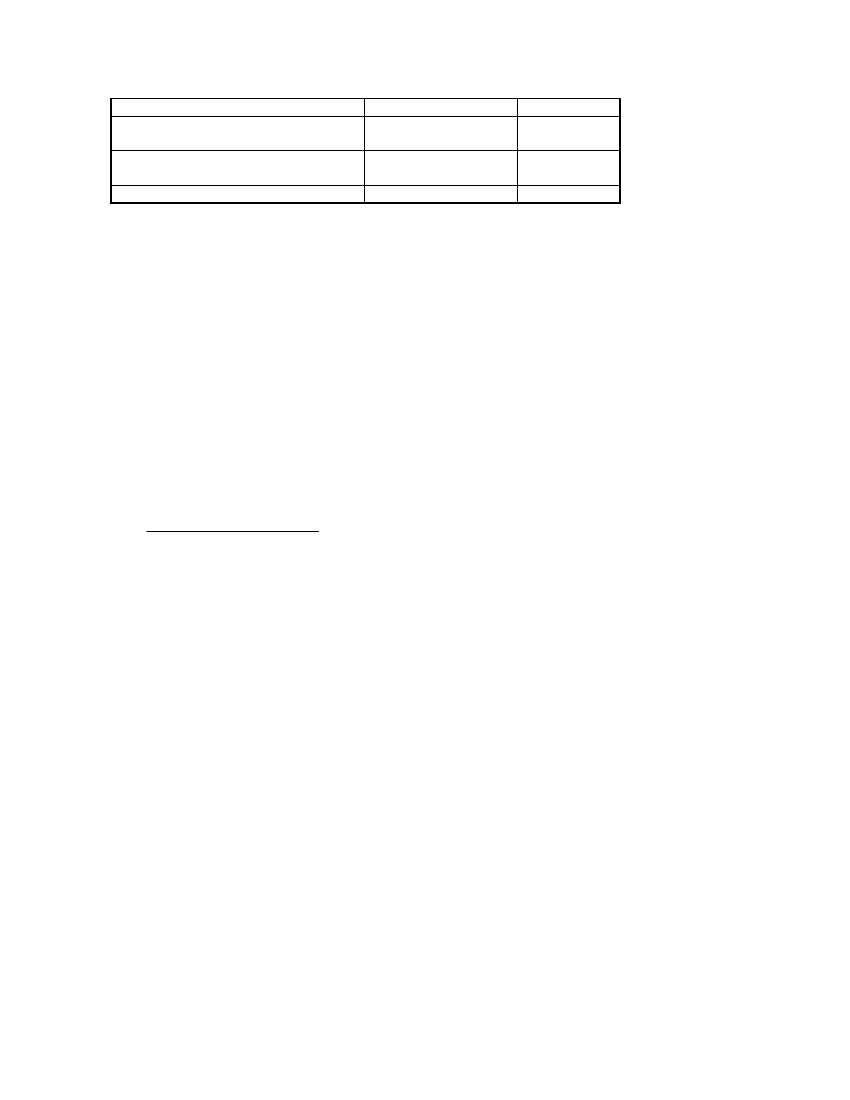
1 tortilla(fried)
Gas consumption per person and
meal
Gas consumption per 5-member
family
(2 cooked meals)
10-20 l
150-300 l/d
1500 -2400 l/d
~3 min
Single-flame burners and lightweight cookstoves tend to be regarded as stop-gap solutions for want
of suitable alternatives.
Biogas cookers require purposive installation with adequate protection from the wind. Before any
cooker is used, the burner must be carefully adjusted, i.e.:
- for a compact, bluish flame,
- the pot should be cupped by the outer cone of the flame without being touched by the inner
cone,
- the flame should be self-stabilizing, i.e. flameless zones must re-ignite automatically within
2 to 3 seconds.
Test measurements should be performed to optimize the burner setting and minimize consumption.
The physical efficiency of a typical gas burner ranges from 0.6 to 0.8.
1. Measuring the efficiency with water
QW ⋅ (T1 − T2) ⋅ cW + EW ⋅ L
η=
n. c. v ⋅ Q
η =- burner efficiency ( - )
QW = quantity of heated water (kg)
T1,T2 = initial and final temperature (°C)
cW = spec. heat capacity = 4.2 kJ/kg
EW = quantity of evaporated water (kg)
L = evaporation heat loss = 2260 kJ/kg
n.c.v. = net cal. value of biogas (kJ/m3 )
Q = quantity of biogas (m3)
——————————————————————————————————————————
2. Gas consumption for holding the temperature at boiling point (simmering temperature -95 °C), i.e.
the amount of gas needed per unit of time to maintain a water temperature of 95 °C
——————————————————————————————————————————
3. Standard cooking test
This test determines how much gas is- needed to cook a standard meal, e.g. 500 g rice and 1000 g
water; the standard meal is specified according to the regional staple diet
——————————————————————————————————————————
4. Complete-meal tests
Everything belonging to a complete meal is cooked by a native person.
——————————————————————————————————————————
69