Intensive forms of animal husbandry often involve the problem of excessive water consumption for
cleaning, which leads to large quantities of wastewater, dilute substrate and unnecessarily large
biogas plants (cf. chapter 6). In areas where water is scarce, the digester drain-water can be used
for scrubbing down the pens and diluting the fresh substrate, thus reducing the water requirement
by 30-40%.
Stables
Differentiation is generally made between:
- stabling systems with litter and
- stabling systems without litter, with the design details of the stalls appropriate to the type of
animal kept.
For use in a biogas plant, any straw used as litter must be reduced in size to 2-6 cm. Sawdust has
poor fermenting properties and should therefore not be used.
Cattle shelter
Variants suitable for connection to a biogas plant include:
- Stanchion barns with a slurry-flush or floating removal system (no litter) or dung collecting
(with litter),
- Cow-cubicle barns with collecting channel (no litter).
Piggeries
The following options are well-suited for combination with a biogas plant:
- barns with fully or partially slotted floors (no litter),
- lying bays with manure gutter (no litter),
- group bays (with or without litter).
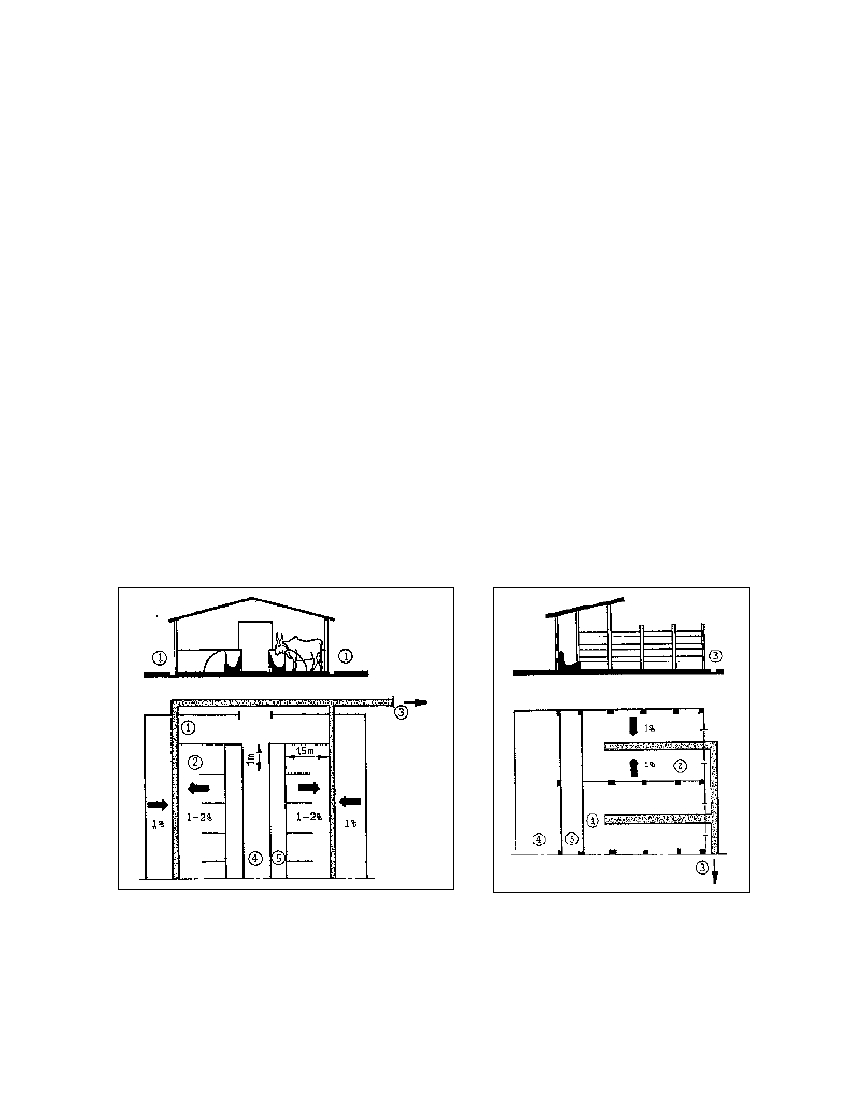
Fig. 3.4: Stanchion barn with floating gutter.
Collecting channel, 2 Stable,
3 Floating gutter leading to the biogas plant,
feeding aisle, 5 Feeding trough
(Source: OEKOTOP)
23
Fig. 3.5: Cow-cubicle barn with 1
floating gutter. 1 Collecting
channel, 2 Cubicle, 3 Floating 4
gutter leading to the biogas plant,
4 Feeding aisle, 5 Feeding trough
(Source: OEKOTOP)