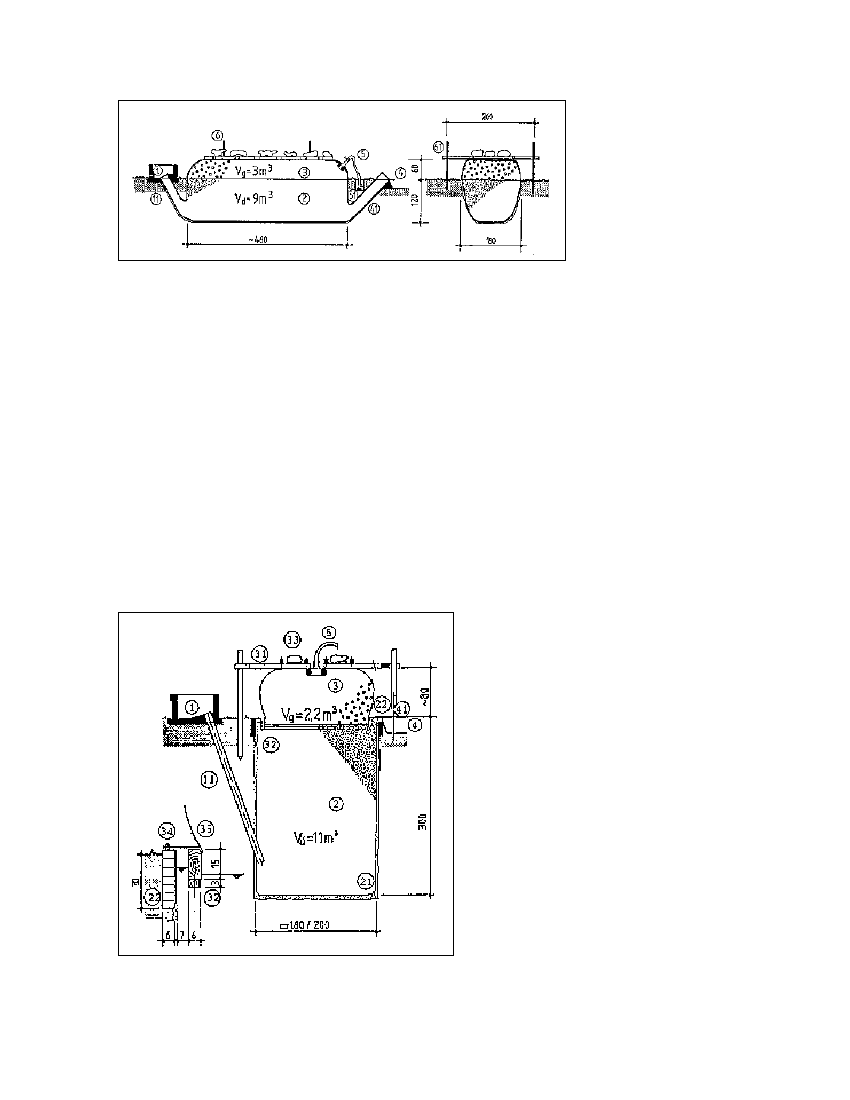
Fig. 5.12: Horizontal
balloon-type
biogas
plant. 1 Mixing pit, 11
Fill pipe, 2 Digester, 3
Gasholder, 4 Slurry
store, 41 Outlet pipe, 5
Gas pipe, 51 Water trap,
6 Burden, 61 Guide
frame
(Source:
OEKOTOP)
Inflatable balloon plants (cf. fig. 5.12)
Inflatable biogas plants consist of a heatsealed plastic or rubber bag (balloon), the top and bottom
parts of which serve as the gasholder and digester, respectively. The requisite gas pressure is
achieved by weighting down the bag. Since the material has to be weather-resistant, specially
stabilized, reinforced plastic or synthetic caoutchouc is given preference. The useful life amounts to
2 - 5 years.
Advantages: Standardized prefabrication at low cost; shallow installation suitable for use in areas
with a high groundwater table.
Drawbacks: Low gas pressure requires extra weight burden, scum cannot be removed. The plastic
balloon has a relatively short useful life, is susceptible to damage by mechanical means, and
usually not available locally. In addition, local craftsmen are rarely in a position to repair a damaged
balloon.
Inflatable biogas plants are recommended, if local repair is or can be made possible and the cost
advantage is substantial.
Fig. 5.13: Earth-pit plant with plastic-sheet
gasholder. 1 Mixing pit, ll Fill pipe, 2
Digester, 21 Rendering, 22 Peripheral
masonry, 3 Plastic-sheet gasholder, 31
Cuide frame, 32 Wooden frame, 33
Weight, 34 Frame anchorage, 35 Plastic
sheeting, 4 Slurry store, 41 Overflow, 5
Gas pipe (Source: OEKOTOP)
49