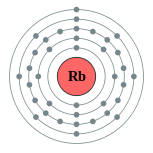
Rubidium
Background to the schools Wikipedia
SOS Children volunteers helped choose articles and made other curriculum material SOS Child sponsorship is cool!
| Rubidium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
37Rb
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
grey white |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name, symbol, number | rubidium, Rb, 37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pronunciation | / r ʉ ˈ b ɪ d i ə m / roo-BID-ee-əm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Element category | alkali metal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group, period, block | 1 (alkali metals), 5, s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight | 85.4678(3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 5s1 2, 8, 18, 8, 1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff (1861) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | George de Hevesy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 1.532 g·cm−3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Liquid density at m.p. | 1.46 g·cm−3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 312.46 K, 39.31 °C, 102.76 °F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 961 K, 688 °C, 1270 °F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | (extrapolated) 2093 K, 16 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 2.19 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 75.77 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 31.060 J·mol−1·K−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | 1 (strongly basic oxide) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | 0.82 (Pauling scale) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies | 1st: 403 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2nd: 2632.1 kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd: 3859.4 kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | 248 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 220±9 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 303 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellanea | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | body-centered cubic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | (20 °C) 128 nΩ·m | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 58.2 W·m−1·K−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound (thin rod) | (20 °C) 1300 m·s−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 2.4 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 2.5 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 0.216 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS registry number | 7440-17-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most stable isotopes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main article: Isotopes of rubidium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rubidium is a chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. Rubidium is a soft, silvery-white metallic element of the alkali metal group, with an atomic mass of 85.4678. Elemental rubidium is highly reactive, with properties similar to those of other elements in Group 1, such as very rapid oxidation in air. Rubidium has only one stable isotope, 85Rb, with the isotope 87Rb, which composes almost 28% of naturally occurring rubidium, being slightly radioactive with a half-life of 49 billion years—more than three times longer than the estimated age of the universe.
German chemists Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff discovered rubidium in 1861 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy.
Rubidium's compounds have various chemical and electronic applications. Rubidium metal is easily vaporized and has a convenient spectral absorption range, making it a frequent target for laser manipulation of atoms.
Rubidium is not known to be necessary for any living organisms. However, like caesium, rubidium ions are handled by living organisms in a manner similar to potassium ions, being actively taken up by plants and by animal cells.
Characteristics
Rubidium is a very soft, ductile, silvery-white metal. It is the second most electropositive of the non-radioactive alkali metals and melts at a temperature of 39.3 °C (102.7 °F). Similar to other alkali metals, rubidium metal reacts violently with water, forms amalgams with mercury and alloys with gold, iron, caesium, sodium, and potassium, but not lithium (despite the fact that rubidium and lithium are in the same group). As with potassium (which is slightly less reactive) and caesium (which is slightly more reactive), rubidium's reaction with water is usually vigorous enough to ignite the hydrogen gas it liberates. Rubidium has also been reported to ignite spontaneously in air. Rubidium has a very low ionization energy of only 406 kJ/mol. Rubidium and potassium show a very similar purple colour in the flame test, which makes spectroscopy methods necessary to distinguish the two elements.
Compounds
Rubidium chloride (RbCl) is probably the most used rubidium compound; it is used in biochemistry to induce cells to take up DNA, and as a biomarker since it is readily taken up to replace potassium, and occurs in only small quantities in living organisms. Other common rubidium compounds are the corrosive rubidium hydroxide (RbOH), the starting material for most rubidium-based chemical processes; rubidium carbonate (Rb2CO3), which is used in some optical glasses, and rubidium copper sulfate, Rb2SO4·CuSO4·6H2O. Rubidium silver iodide (RbAg4I5) has the highest room temperature conductivity of any known ionic crystal, a property that is being exploited in thin film batteries and other applications.
Rubidium has a number of oxides, including rubidium monoxide (Rb2O), Rb6O and Rb9O2, which form if rubidium metal is exposed to air; rubidium in excess oxygen gives the superoxide RbO2. Rubidium forms salts with halides, making rubidium fluoride, rubidium chloride, rubidium bromide, and rubidium iodide.
Isotopes
Although rubidium is monoisotopic, naturally occurring rubidium is composed of two isotopes: the stable 85Rb (72.2%) and the radioactive 87Rb (27.8%). Natural rubidium is radioactive with specific activity of about 670 Bq/g, enough to significantly expose a photographic film in 110 days. Aside from 85Rb and 87Rb, another 24 synthetically produced isotopes or rubidium are known, with half times of under 3 months; most of these are highly radioactive and have few uses.
Rubidium-87 has a half-life of 48.8×109 years, which is more than three times the age of the universe of 13.75±0.11×109 years, making it a primordial nuclide. It readily substitutes for potassium in minerals, and is therefore fairly widespread. Rb has been used extensively in dating rocks; 87Rb decays to stable 87Sr by emission of a negative beta particle. During fractional crystallization, Sr tends to become concentrated in plagioclase, leaving Rb in the liquid phase. Hence, the Rb/Sr ratio in residual magma may increase over time, resulting in rocks with elevated Rb/Sr ratios due to progressing differentiation. The highest ratios (10 or more) occur in pegmatites. If the initial amount of Sr is known or can be extrapolated, then the age can be determined by measurement of the Rb and Sr concentrations and of the 87Sr/86Sr ratio. The dates indicate the true age of the minerals only if the rocks have not been subsequently altered (see rubidium-strontium dating).
Rubidium-82, one of the element's non-natural isotopes, is produced by electron-capture decay of strontium-82 with a half-life of 25.36 days. The subsequent decay of rubidium-82 with a half-life of 76 seconds to stable krypton-82 happens by positron emission.
Occurrence
Rubidium is the twenty-third most abundant element in the Earth's crust, roughly as abundant as zinc and rather more common than copper. It occurs naturally in the minerals leucite, pollucite, carnallite, and zinnwaldite, which contain up to 1% of its oxide. Lepidolite contains between 0.3% and 3.5% rubidium, and is the commercial source of the element. Some potassium minerals and potassium chlorides also contain the element in commercially significant amounts.
Seawater contains an average of 125 µg/L of rubidium compared to the much higher value for potassium of 408 mg/L and the much lower value of 0.3 µg/L for caesium
Because of its large ionic radius, rubidium is one of the " incompatible elements." During magma crystallization, rubidium is concentrated together with its heavier analogue caesium in the liquid phase and crystallizes last. Therefore the largest deposits of rubidium and caesium are zone pegmatite ore bodies formed by this enrichment process. Because rubidium substitutes for potassium in the crystallization of magma, the enrichment is far less effective than in the case of caesium. Zone pegmatite ore bodies containing mineable quantities of caesium as pollucite or the lithium minerals lepidolite are also a source for rubidium as a by-product.
Two notable sources of rubidium are the rich deposits of pollucite at Bernic Lake, Manitoba, Canada, and the rubicline ((Rb,K)AlSi3O8) found as impurities in pollucite on the Italian island of Elba, with a rubidium content of 17.5%. Both of these deposits are also sources of caesium.
Production
Although rubidium is more abundant in Earth's crust than caesium, the limited applications and the lack of a mineral rich in rubidium limits the production of rubidium compounds to 2 to 4 tonnes per year. Several methods are available for separating potassium, rubidium, and caesium. The fractional crystallization of a rubidium and caesium alum (Cs,Rb)Al(SO4)2·12H2O yields after 30 subsequent steps pure rubidium alum. Two other methods are reported, the chlorostannate process and the ferrocyanide process.
For several years in the 1950s and 1960s, a by-product of potassium production called Alkarb was a main source for rubidium. Alkarb contained 21% rubidium, with the rest being potassium and a small fraction of caesium. Today the largest producers of caesium, such as the Tanco Mine, Manitoba, Canada, produce rubidium as by-product from pollucite.
History
Rubidium was discovered in 1861 by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff, in Heidelberg, Germany, in the mineral lepidolite through the use of a spectroscope. Because of the bright red lines in its emission spectrum, they chose a name derived from the Latin word rubidus, meaning "dark red".
Rubidium is present as a minor component in lepidolite. Kirchhoff and Bunsen processed 150 kg of a lepidolite containing only 0.24% rubidium oxide (Rb2O). Both potassium and rubidium form insoluble salts with chloroplatinic acid, but these salts show a slight difference in solubility in hot water. Therefore, the less-soluble rubidium hexachloroplatinate (Rb2PtCl6) could be obtained by fractional crystallization. After reduction of the hexachloroplatinate with hydrogen. This process yielded 0.51 grams of rubidium chloride for further studies. The first large scale isolation of caesium and rubidium compounds, performed from 44,000 liters of mineral water by Bunsen and Kirchhoff, yielded, besides 7.3 grams of caesium chloride, also 9.2 grams of rubidium chloride. Rubidium was the second element, shortly after caesium, to be discovered spectroscopically, only one year after the invention of the spectroscope by Bunsen and Kirchhoff.
The two scientists used the rubidium chloride thus obtained to estimate the atomic weight of the new element as 85.36 (the currently accepted value is 85.47). They tried to generate elemental rubidium by electrolysis of molten rubidium chloride, but instead of a metal, they obtained a blue homogeneous substance which "neither under the naked eye nor under the microscope showed the slightest trace of metallic substance." They assigned it as a subchloride (Rb2Cl); however, the product was probably a colloidal mixture of the metal and rubidium chloride. In a second attempt to produce metallic rubidium, Bunsen was able to reduce rubidium by heating charred rubidium tartrate. Although the distilled rubidium was pyrophoric, it was possible to determine the density and the melting point of rubidium. The quality of the research done in the 1860s can be appraised by the fact that their determined density differs less than 0.1 g/cm3 and the melting point by less than 1 °C from the presently accepted values.
The slight radioactivity of rubidium was discovered in 1908 but before the theory of isotopes was established in the 1910s and the low activity due to the long half-life of above 1010 years made interpretation complicated. The now proven decay of 87Rb to stable 87Sr through beta decay was still under discussion in the late 1940s.
Rubidium had minimal industrial value before the 1920s. Since then, the most important use of rubidium has been in research and development, primarily in chemical and electronic applications. In 1995, rubidium-87 was used to produce a Bose–Einstein condensate, for which the discoverers, Eric Allin Cornell, Carl Edwin Wieman and Wolfgang Ketterle, won the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Applications
Rubidium compounds are sometimes used in fireworks to give them a purple colour. Rubidium has also been considered for use in a thermoelectric generator using the magnetohydrodynamic principle, where rubidium ions are formed by heat at high temperature and passed through a magnetic field. These conduct electricity and act like an armature of a generator thereby generating an electric current. Rubidium, particularly vaporized 87Rb, is one of the most commonly used atomic species employed for laser cooling and Bose-Einstein condensation. Its desirable features for this application include the ready availability of inexpensive diode laser light at the relevant wavelength, and the moderate temperatures required to obtain substantial vapor pressures.
Rubidium has been used for polarizing 3He, producing volumes of magnetized 3He gas, with the nuclear spins aligned toward a particular direction in space, rather than randomly.
Rubidium vapor is optically pumped by a laser and the polarized Rb polarizes 3He through the hyperfine interaction.
Such spin-polarized 3He cells are becoming popular for neutron polarization measurements and for producing polarized neutron beams for other purposes.
The resonant element in atomic clocks utilizes the hyperfine structure of rubidium's energy levels, making rubidium useful for high-precision timing, and is used as the main component of secondary frequency references (rubidium oscillators) to maintain frequency accuracy in cell site transmitters and other electronic transmitting, networking, and test equipment. These rubidium standards are often used with GPS to produce a "primary frequency standard" that has greater accuracy and is less expensive than caesium standards. Such rubidium standards are often mass-produced for the telecommunication industry.
Other potential or current uses of rubidium include a working fluid in vapor turbines, as a getter in vacuum tubes, and as a photocell component. Rubidium is also used as an ingredient in special types of glass, in the production of superoxide by burning in oxygen, in the study of potassium ion channels in biology, and as the vapor to make atomic magnetometers. In particular, 87Rb is currently being used, with other alkali metals, in the development of spin-exchange relaxation-free (SERF) magnetometers.
Rubidium-82 is used for positron emission tomography. Rubidium is very similar to potassium and therefore tissue with high potassium content will also accumulate the radioactive rubidium. One of the main uses is in myocardial perfusion imaging. The very short half-life of 76 seconds makes it necessary to produce the rubidium-82 from decay of strontium-82 close to the patient. As a result of changes in the blood brain barrier in brain tumors, rubidium collects more in brain tumors than normal brain tissue, allowing the use of radioisotope rubidium-82 in nuclear medicine to locate and image brain tumors.
Rubidium was tested for the influence on manic depression and depression. Dialysis patients suffering from depression show a depletion in rubidium and therefore a supplementation may help during depression. In some tests the rubidium was administered as rubidium chloride with up to 720 mg per day for 60 days.
Precautions and biological effects
Rubidium reacts violently with water and can cause fires. To ensure safety and purity, this metal is usually kept under a dry mineral oil or sealed in glass ampoules in an inert atmosphere. Rubidium forms peroxides on exposure even to small amount of air diffusing into oil, and is thus subject to similar peroxide precautions as storage of metallic potassium.
Rubidium, like sodium and potassium, almost always has +1 oxidation state when dissolved in water, including its presence in all biological systems. The human body tends to treat Rb+ ions as if they were potassium ions, and therefore concentrates rubidium in the body's intracellular fluid (i.e., inside cells). The ions are not particularly toxic; a 70 kg person contains on average 0.36 g of rubidium, and an increase in this value by 50 to 100 times did not show negative effects in test persons. The biological half-life of rubidium in humans was measured as 31–46 days. Although a partial substitution of potassium by rubidium is possible, rats with more than 50% of their potassium substituted in the muscle tissue died.