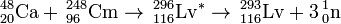Livermorium
About this schools Wikipedia selection
This Schools selection was originally chosen by SOS Children for schools in the developing world without internet access. It is available as a intranet download. To compare sponsorship charities this is the best sponsorship link.
| Livermorium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
116Lv
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| unknown | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name, symbol, number | livermorium, Lv, 116 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pronunciation | / ˌ l ɪ v ər ˈ m ɔər i ə m / LIV-ər-MOHR-ee-əm |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Element category | unknown | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group, period, block | 16 (chalcogens), 7, p | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight | [293] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p4 (predicted) 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 6 (predicted) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Joint Institute for Nuclear Research and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (2000) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 12.9 (predicted) g·cm−3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | 2, 4 (prediction) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies | 1st: 723.6 (prediction) kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 175 (estimated) pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellanea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS registry number | 54100-71-9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most stable isotopes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main article: Isotopes of livermorium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Livermorium is the synthetic superheavy element with the symbol Lv and atomic number 116. The name was adopted by IUPAC on May 31, 2012.
It is placed as the heaviest member of group 16 (VIA) although a sufficiently stable isotope is not known at this time to allow chemical experiments to confirm its position as a heavier homologue to polonium.
It was first detected in 2000. Since then, about 35 atoms of livermorium have been produced, either directly or as a decay product of ununoctium, belonging to the four neighbouring isotopes with masses 290–293. The most stable isotope known is livermorium-293 with a half-life of ~60 ms.
History
Unsuccessful synthesis attempts
In late 1998, Polish physicist Robert Smolańczuk published calculations on the fusion of atomic nuclei towards the synthesis of superheavy atoms, including ununoctium. His calculations suggested that it might be possible to make ununoctium and livermorium by fusing lead with krypton under carefully controlled conditions.
In 1999, researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory made use of these predictions and announced the discovery of livermorium and ununoctium, in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, and very soon after the results were reported in Science. The researchers reported to have performed the reaction
- 86
36Kr + 208
82Pb → 293
118Uuo + n.
The following year, they published a retraction after researchers at other laboratories were unable to duplicate the results and the Berkeley lab itself was unable to duplicate them as well. In June 2002, the director of the lab announced that the original claim of the discovery of these two elements had been based on data fabricated by principal author Victor Ninov.
Discovery
On July 19, 2000, scientists at Dubna ( JINR) detected a single decay from an atom of livermorium following the irradiation of a Cm-248 target with Ca-48 ions. The results were published in December 2000. This 10.54 MeV alpha-emitting activity was originally assigned to 292Lv due to the correlation of the daughter to previously assigned 288Fl. That assignment was later altered to 289Fl, and hence this activity was correspondingly changed to 293Lv. Two further atoms were reported by the institute during their second experiment between April–May 2001.
In the same experiment they also detected a decay chain which corresponded to the first observed decay of flerovium and assigned to 289Fl. This activity has not been observed again in a repeat of the same reaction. However, its detection in this series of experiments indicates the possibility of the decay of an isomer of livermorium, namely 293bLv, or a rare decay branch of the already discovered isomer,293aLv, in which the first alpha particle was missed. Further research is required to positively assign this activity.
The team repeated the experiment in April–May 2005 and detected 8 atoms of livermorium. The measured decay data confirmed the assignment of the discovery isotope as 293Lv. In this run, the team also observed 292Lv in the 4n channel for the first time.
In May 2009, the Joint Working Party reported on the discovery of copernicium and acknowledged the discovery of the isotope 283Cn. This implied the de facto discovery of livermorium, as 291Lv (see below), from the acknowledgment of the data relating to the granddaughter 283Cn, although the actual discovery experiment may be determined as that above.
In 2011, the IUPAC evaluated the Dubna team results and accepted them as a reliable identification of element 116.
Naming
Livermorium is historically known as eka-polonium. Ununhexium (Uuh) was the temporary IUPAC systematic element name. Scientists usually refer to the element simply as element 116 (or E116). According to IUPAC recommendations, the discoverer(s) of a new element has the right to suggest a name.
The discovery of livermorium was recognized by JWG of IUPAC on 1 June 2011, along with that of flerovium. According to the vice-director of JINR, the Dubna team wanted to name element 116 moscovium, after the Moscow Oblast in which Dubna is located. However, the name livermorium and the symbol Lv were adopted on May 31, 2012 after an approval process by the IUPAC. The name recognises the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, within the city of Livermore, California, USA, which collaborated with JINR on the discovery. The city in turn is named after the American rancher Robert Livermore, a naturalized Mexican citizen of English birth.
Current and future experiments
The team at Dubna have indicated plans to synthesize livermorium using the reaction between plutonium-244 and titanium-50. This experiment will allow them to assess the feasibility of using projectiles with Z > 20 required in the synthesis of superheavy elements in the eighth period (Z > 118). Although initially scheduled for 2008, the reaction looking at the synthesis of evaporation residues has not been conducted to date.
There are also plans to repeat the Cm-248 reaction at different projectile energies in order to probe the 2n channel, leading to the new isotope 294Lv. In addition, they have future plans to complete the excitation function of the 4n channel product, 292Lv, which will allow them to assess the stabilizing effect of the N=184 shell on the yield of evaporation residues.
Nucleosynthesis
- Target-projectile combinations leading to Z=116 compound nuclei
The below table contains various combinations of targets and projectiles which could be used to form compound nuclei with atomic number 116. The table below provides cross-sections and excitation energies for hot fusion reactions producing livermorium isotopes directly. Data in bold represent maxima derived from excitation function measurements. The below table contains various targets-projectile combinations for which calculations have provided estimates for cross section yields from various neutron evaporation channels.
| Target | Projectile | CN | Attempt result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 208Pb | 82Se | 290Lv | Failure to date |
| 232Th | 58Fe | 290Lv | Reaction yet to be attempted |
| 238U | 54Cr | 292Lv | Failure to date |
| 244Pu | 50Ti | 294Lv | Reaction yet to be attempted |
| 248Cm | 48Ca | 296Lv | Successful reaction |
| 246Cm | 48Ca | 294Lv | Reaction yet to be attempted |
| 245Cm | 48Ca | 293Lv | Successful reaction |
| 249Cf | 40Ar | 289Lv | Reaction yet to be attempted |
Cold fusion
- 208Pb(82Se,xn)290−xLv
In 1998, the team at GSI attempted the synthesis of 290Lv as a radiative capture (x=0) product. No atoms were detected providing a cross section limit of 4.8 pb.
Hot fusion
This section deals with the synthesis of nuclei of livermorium by so-called "hot" fusion reactions. These are processes which create compound nuclei at high excitation energy (~40–50 MeV, hence "hot"), leading to a reduced probability of survival from fission. The excited nucleus then decays to the ground state via the emission of 3–5 neutrons. Fusion reactions utilizing 48Ca nuclei usually produce compound nuclei with intermediate excitation energies (~30–35 MeV) and are sometimes referred to as "warm" fusion reactions. This leads, in part, to relatively high yields from these reactions.
- 238U(54Cr,xn)292−xLv
There are sketchy indications that this reaction was attempted by the team at GSI in 2006. There are no published results on the outcome, presumably indicating that no atoms were detected. This is expected from a study of the systematics of cross sections for 238U targets.
- 248Cm(48Ca,xn)296−xLv (x=3,4)
The first attempt to synthesise livermorium was performed in 1977 by Ken Hulet and his team at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). They were unable to detect any atoms of livermorium. Yuri Oganessian and his team at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions (FLNR) subsequently attempted the reaction in 1978 and were met by failure. In 1985, a joint experiment between Berkeley and Peter Armbruster's team at GSI, the result was again negative with a calculated cross-section limit of 10–100 pb.
In 2000, Russian scientists at Dubna finally succeeded in detecting a single atom of livermorium, assigned to the isotope 292Lv. In 2001, they repeated the reaction and formed a further 2 atoms in a confirmation of their discovery experiment. A third atom was tentatively assigned to 293Lv on the basis of a missed parental alpha decay. In April 2004, the team ran the experiment again at higher energy and were able to detect a new decay chain, assigned to 292Lv. On this basis, the original data were reassigned to 293Lv. The tentative chain is therefore possibly associated with a rare decay branch of this isotope. In this reaction, 2 further atoms of 293Lv were detected.
In an experiment run at the GSI between June-July 2010, scientists detected six atoms of livermorium; two atoms of 293116 and four atoms of 292116. They were able to confirm both the decay data and cross sections for the fusion reaction.
- 245Cm(48Ca,xn)293−x116 (x=2,3)
In order to assist in the assignment of isotope mass numbers for livermorium, in March–May 2003 the Dubna team bombarded a 245Cm target with 48Ca ions. They were able to observe two new isotopes, assigned to 291Lv and 290Lv. This experiment was successfully repeated in Feb–March 2005 where 10 atoms were created with identical decay data to those reported in the 2003 experiment.
As decay product
Livermorium has also been observed in the decay of ununoctium. In October 2006 it was announced that 3 atoms of ununoctium had been detected by the bombardment of californium-249 with calcium-48 ions, which then rapidly decayed into livermorium.
The observation of 290Lv allowed the assignment of the product to 294Uuo and proved the synthesis of ununoctium.
Fission of compound nuclei with Z=116
Several experiments have been performed between 2000–2006 at the Flerov laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Dubna studying the fission characteristics of the compound nuclei 296,294,290Lv. Four nuclear reactions have been used, namely 248Cm+48Ca, 246Cm+48Ca, 244Pu+50Ti and 232Th+58Fe. The results have revealed how nuclei such as this fission predominantly by expelling closed shell nuclei such as 132Sn (Z=50, N=82). It was also found that the yield for the fusion-fission pathway was similar between 48Ca and 58Fe projectiles, indicating a possible future use of 58Fe projectiles in superheavy element formation. In addition, in comparative experiments synthesizing 294Lv using 48Ca and 50Ti projectiles, the yield from fusion-fission was ~3x less for 50Ti, also suggesting a future use in SHE production.
Isotopes and nuclear properties
- Chronology of isotope discovery
| Isotope | Year discovered | Discovery reaction |
|---|---|---|
| 290Lv | 2002 | 249Cf(48Ca,3n) |
| 291Lv | 2003 | 245Cm(48Ca,2n) |
| 292Lv | 2004 | 248Cm(48Ca,4n) |
| 293Lv | 2000 | 248Cm(48Ca,3n) |
Theoretical calculation in a quantum tunneling model supports the experimental data relating to the synthesis of 293,292Lv.
- Retracted isotope
- 289Lv
In 1999, researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory announced the synthesis of 293Uuo (see ununoctium), in a paper published in Physical Review Letters. The claimed isotope 289Lv decayed by 11.63 MeV alpha emission with a half-life of 0.64 ms. The following year, they published a retraction after other researchers were unable to duplicate the results. In June 2002, the director of the lab announced that the original claim of the discovery of these two elements had been based on data fabricated by the principal author Victor Ninov. As such, this isotope of livermorium is currently unknown.
Chemical properties
Extrapolated chemical properties
Oxidation states
Livermorium is projected to be the fourth member of the 7p series of non-metals and the heaviest member of group 16 (VIA) in the Periodic Table, below polonium. The group oxidation state of +6 is known for all the members apart from oxygen which lacks available d- orbitals for expansion and is limited to a maximum +2 state, exhibited in the fluoride OF2. The +4 is known for sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and polonium, undergoing a shift in stability from reducing for S(IV) and Se(IV) to oxidizing in Po(IV). Tellurium(IV) is the most stable for this element. This suggests a decreasing stability for the higher oxidation states as the group is descended and livermorium should portray an oxidizing +4 state and a more stable +2 state. The lighter members are also known to form a −2 state as oxide, sulfide, selenide, telluride, and polonide.
Chemistry
The possible chemistry of livermorium can be extrapolated from that of polonium. It should therefore undergo oxidation to a dioxide, LvO2, although a trioxide, LvO3 is plausible, but unlikely. The stability of a +2 state should manifest itself in the formation of a simple monoxide, LvO. Fluorination will likely result in a tetrafluoride, LvF4 and/or a difluoride, LvF2; a hexafluoride, LvF6, is possible but unlikely. Chlorination and bromination may well stop at the corresponding dihalides, LvCl2 and LvBr2. Oxidation by iodine should certainly stop at LvI2 and may even be inert to this element. The heavier livermorium dihalides are predicted to be linear, but the lighter ones are predicted to be bent.