GRAVITY GOODS ROPEWAY
on the adopted mixing method. There are usually
two methods of concrete mixing mechanical
mixing and manual mixing. As mechanical mixing
is not possible in remote ropeway sites, concrete
mixing is done manually. Concrete may be mixed
using ordinary hand shovels. The consistency and
uniformity of the concrete mix will depend on the
degree of control and experience of the labour
force. Hand mixing method is very unlikely to
produce uniform quality concrete but this method
is satisfactory for gravity ropeway as the concrete
volume required is less.
7.5.4 Casting of concrete
Casting of concrete has to be done immediately
after mixing but in unavoidable situation it can
be casted within two hours of mixing to avoid
setting of the concrete mix. Before casting the
concrete, the formwork should be thoroughly
cleaned. In construction joints, the previously
concreted surfaces must also be cleaned with
water. Loose stones and debris must be removed.
Ideally, the surface should be rough, clean and
damp. The concrete can be transferred from
the mixing place manually in steel dishes and
should be placed in the excavations in such a
way that the concrete does not fall freely from
heights of more than one and a half metre.
Concrete falling from greater heights leads to
the segregation of the aggregates and a loss in
consistency of the concrete mix. Guiding chutes
should be used when it has to be poured from
higher than recommended levels. The concrete
should be vibrated during the placing. Usually
a electric vibrator is used, but in remote places
where basic infrastructures like electricity, fuel
and generators lack, uniform hand tamping can
be done using pieces of timber or steel rods.
To attain good compaction and an acceptable
concrete quality, a high degree of control is
required. While compacting, the thickness
of the concrete layers should be 150 to 200
mm and the layers be tamped until an air tight
surface is achieved.
7.5.5 Curing concrete
When concrete sets, it releases a lot of heat. The
chemical reactions take place when concrete
sets are exothermic, where the concrete dries
quickly and may develop shrinkage cracks. The
concrete therefore needs to be kept wet until the
setting is complete.
7.5.6 Prescribed concrete mixes
In most of the cases, there is a lack of expertise
in the rural areas to calculate a proper concrete
mix design in which case prescribed mixes
commonly used in the construction industry
may be adopted. The mixes do not give an
accurate grade of concrete but the results are
generally accepted being within the reasonable
target strengths. The commonly used mixes are
specified in terms of fixed volumes.
The grades of concrete and mix prescribed for
the ropeway are given in table 5:
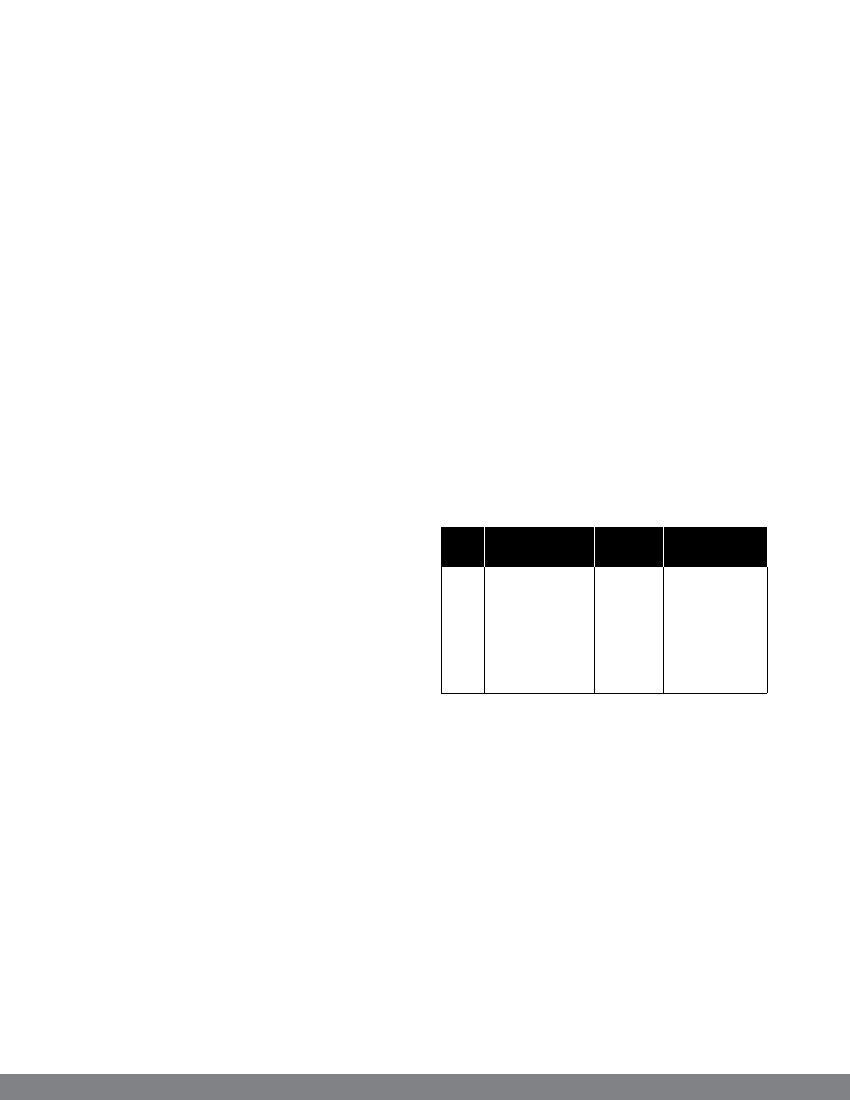
Table 5: Grades of concrete and its proportions
Grade Classification
Mix
Use
proportions
M10 Low strength 1:3:6
M15 Standard concrete 1:2:4
Plumb
concrete,
floor
Tower,
Column, Post,
and sheave
anchorage
Concrete should comply with the following IS
codes:
IS 456-1978 Plain and reinforced concrete
IS 269-1989 Ordinary Portland cement
IS 383-1970 Coarse and fine aggregate
36