GRAVITY GOODS ROPEWAY
6.1 Types of Planning
Mostly three types of planning are involved in
gravity ropeway construction.
a) Time planning
b) Resource planning and
c) Technical planning
6.1.1 Time planning
Time planning simply means to manage the time
effectively to get more work done in less time. It
means utilising minimum time to accomplish the
goals. More time consumption means more cost.
Time planning involves preparation of project
activities schedule using bar chart. Preparation
of project implementation schedule in the initial
stage is always helpful. A typical Critical Path
Network (CPN) diagram will be very useful to
know what activities are in critical path and
allows for effective time planning of activities
ahead. Additionally, the chart can be used for
optimising resources (labour, equipment and
material) by distributing them in a balanced way.
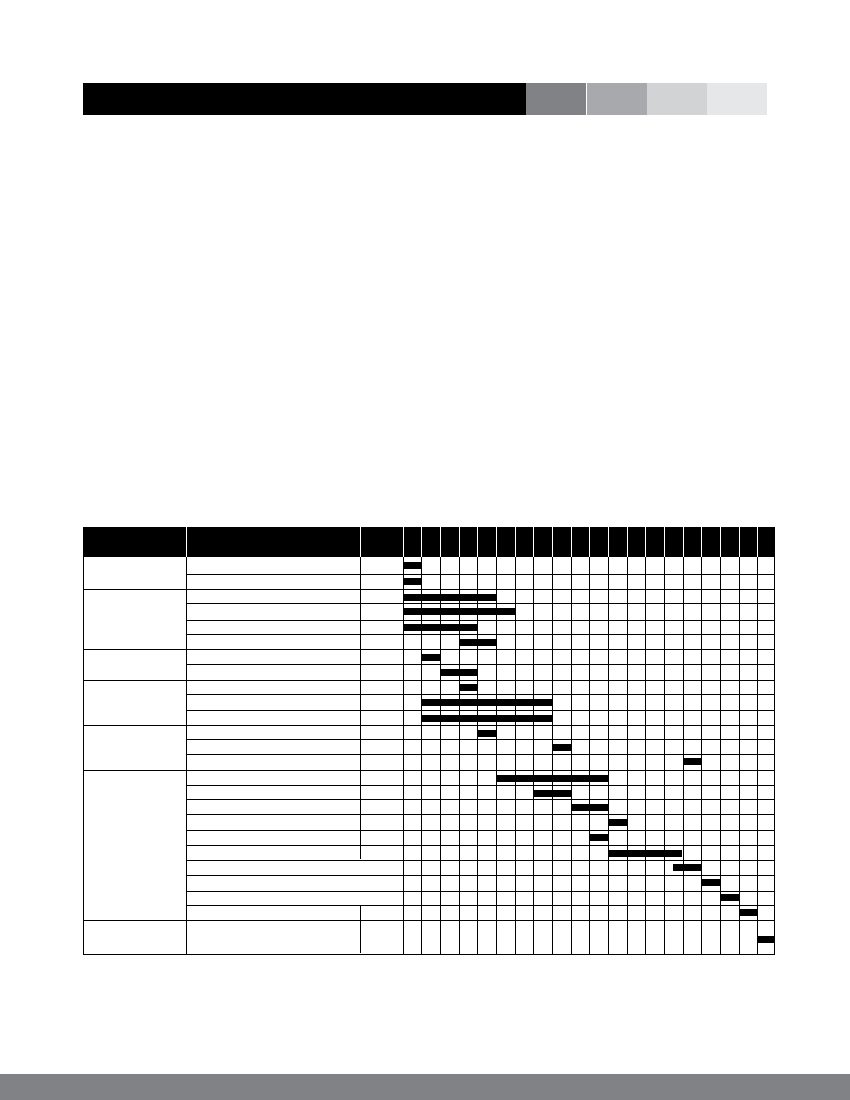
A typical time planning chart is shown in table 3.
Furthermore, this will also be a key tool for
monitoring progress by tracking the planned
versus actual milestones reached - both for
particular activities and for the overall project
implementation activities. If required such chart
may require revision as construction progresses.
Table 3: A typical time planning chart
scheduling
Time Planing
Items
Details
Time/
weeks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
A) Agreement MOU Signing
Project Management training
B) Local materials Sand
collection and Gravel
preparation
Stones
Wood
C) Excavation
Site clearance and layout
Excavation
D)Procurement Cement and reinforcement rod
Fabrication and supply of steel parts
Wire ropes
E) Transportation Cement and reinforcement rod
Structural steel
Wire ropes
F) Execution
Masonray work
Plumb concrete
RCC work
Roofing
Sheave anchoragefixing
Curing and finishing works
Alignment clearance for cable laying
Cable laying and hoisting
Shave fixing and trolley installation
Test operation
G) Testing and Operation and maintenance
Commissioning training and commissioning
Source: Access for Opportunities Project, Practical Action Nepal Office
30