• Deenbandhu, the successor of the
Janata plant in India, with improved
design, was more crack-proof and
consumed less building material than
the Janata plant. with a hemisphere
digester
• CAMARTEC model has a simplified
structure of a hemispherical dome
shell based on a rigid foundation ring
only and a calculated joint of fraction,
the so-called weak / strong ring. It was
developed in the late 80s in Tanzania.
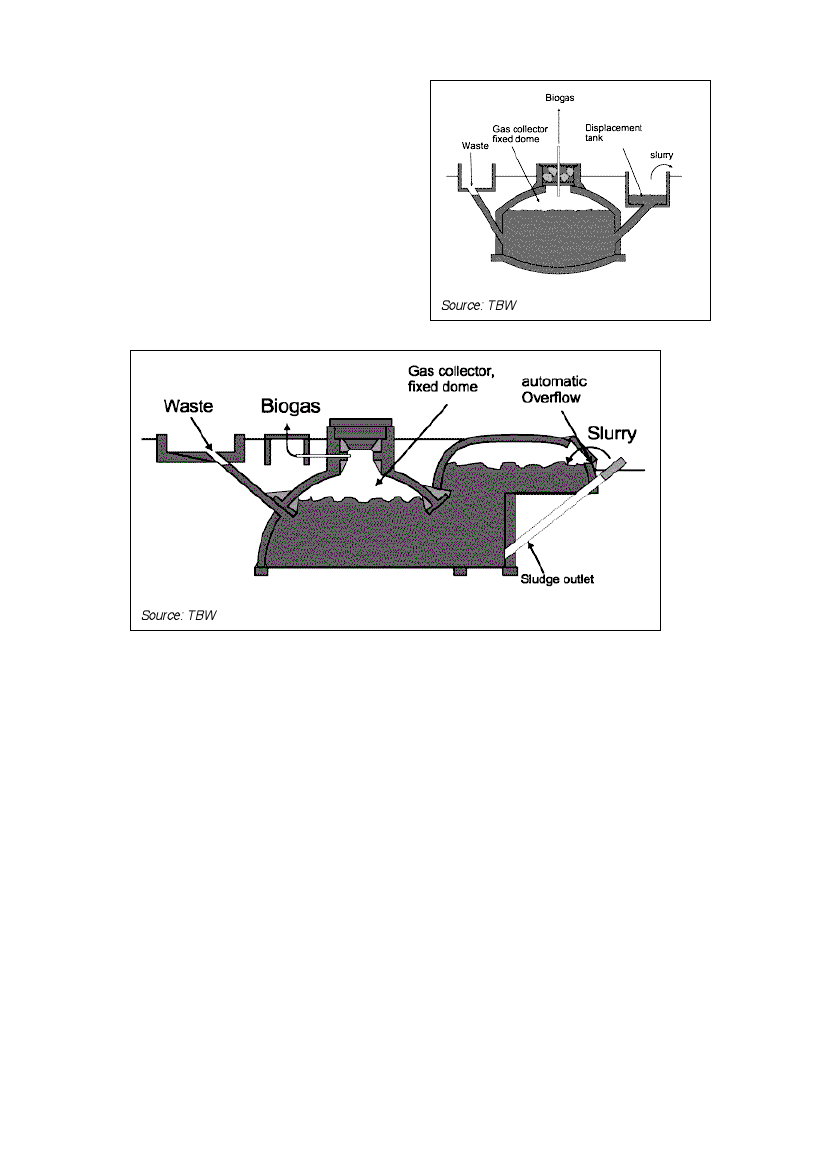
Figure 4: Chinese fixed dome plant
Source: TBW
Figure 5: Fixed dome plant CAMARTEC design
Source: TBW
Climate and size
Fixed-dome plants must be covered with earth up to the top of the gas-filled space to
counteract the internal pressure (up to 0,15 bar). The earth cover insulation and the option
for internal heating makes them suitable for colder climates. Due to economic parameters,
the recommended minimum size of a fixed-dome plant is 5 m3. Digester volumes up to 200
m3 are known and possible.
Advantages: Low initial costs and long useful life-span; no moving or rusting parts
involved; basic design is compact, saves space and is well insulated; construction
creates local employment.
Disadvantages: Masonry gas-holders require special sealants and high technical skills
for gas-tight construction; gas leaks occur quite frequently; fluctuating gas pressure
complicates gas utilization; amount of gas produced is not immediately visible, plant
operation not readily understandable; fixed dome plants need exact planning of levels;
excavation can be difficult and expensive in bedrock.
Fixed dome plants can be recommended only where construction can be supervised by
experienced biogas technicians.
10