Central Europe
Background Information
SOS Children, which runs nearly 200 sos schools in the developing world, organised this selection. SOS Children is the world's largest charity giving orphaned and abandoned children the chance of family life.
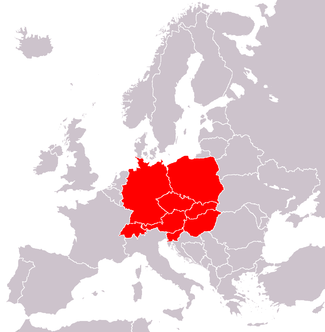
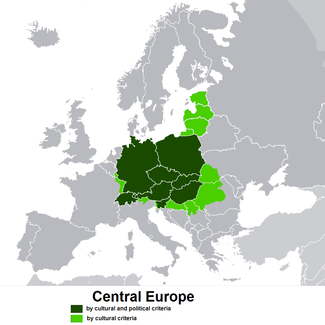
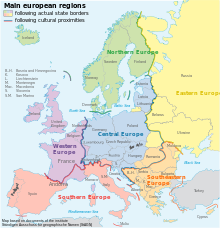
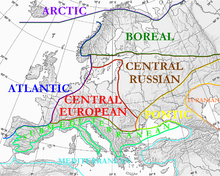
Central Europe, sometimes referred to as Middle Europe, is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe. Widespread interest in the region and the term itself resurfaced by the end of the Cold War, which had divided Europe and the West politically into Eastern Bloc and Western Bloc, splitting Central Europe in half.
The concept of Central Europe, and that of a common identity, is somewhat elusive. However, scholars assert that a distinct "Central European culture, as controversial and debated the notion may be, exists." It is based on "similarities emanating from historical, social and cultural characteristics", and it is identified as having been "one of the world's richest sources of creative talent" between the 17th and 20th centuries. Cross Currents: A Yearbook of Central European Culture characterizes Central Europe "as an abandoned West or a place where East and West collide". Germany's Permanent Committee on Geographical Names defines Central Europe both as a distinct cultural area and a political region. George Schöpflin and others argue that Central Europe is defined by being "a part of Western Christianity", and Samuel P. Huntington places the region firmly within Western culture.
From the 2000s on, Central Europe has been going through a phase of "strategic awakening", with initiatives like the CEI, Centrope or V4. While the region's economy shows high disparities with regard to income, all Central European countries are listed by the Human Development Index as "very high development" countries.
States
The comprehension of the concept of Central Europe is an ongoing source of controversy, though the Visegrád Group constituents are generally included as de facto C.E. countries.
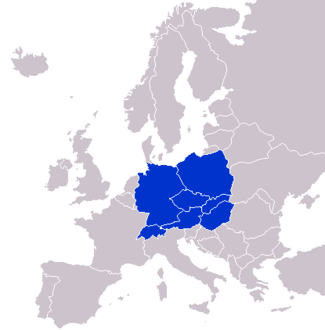
Countries classified as Central European
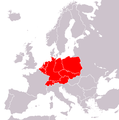
According to the majority of sources (see section Current views on Central Europe for some) the region includes:
 Austria
Austria Czech Republic
Czech Republic Germany
Germany Hungary
Hungary Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein Poland
Poland Slovakia
Slovakia Slovenia it is most often placed in Central Europe but sometimes in Southeastern Europe
Slovenia it is most often placed in Central Europe but sometimes in Southeastern Europe Switzerland
Switzerland
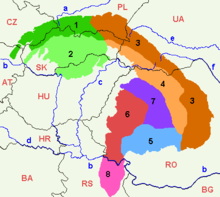
Countries (regions) occasionally included in Central Europe
Some sources also add neighbouring countries for historical (the former Habsburg Empire and German Empire, and modern Baltic states), geographical and/or cultural reasons:
 Croatia
Croatia Romania (geographical regions of Transylvania and southern Bukovina )
Romania (geographical regions of Transylvania and southern Bukovina ) Serbia ( Northern Serbia- Vojvodina, Mačva and Belgrade historically also Raška (Sandžak), Šumadija and Braničevo, and at various times Central Serbia
Serbia ( Northern Serbia- Vojvodina, Mačva and Belgrade historically also Raška (Sandžak), Šumadija and Braničevo, and at various times Central Serbia
The Baltic states, geographically located in Northern Europe, have been considered part of Central Europe in the German tradition.
Smaller parts of the following states may sometimes be included:
 Ukraine ( Zakarpatska Oblast, Galicia and northern Bukovina)
Ukraine ( Zakarpatska Oblast, Galicia and northern Bukovina) Belarus ( Hrodna and Brest Voblast)
Belarus ( Hrodna and Brest Voblast) Russia ( Kaliningrad Oblast)
Russia ( Kaliningrad Oblast) France ( Alsace and portions of Lorraine)
France ( Alsace and portions of Lorraine) Italy ( South Tyrol, Trentino, Trieste and Gorizia, Friuli, occasionally all of Northern Italy)
Italy ( South Tyrol, Trentino, Trieste and Gorizia, Friuli, occasionally all of Northern Italy)
Regional data
- Area: 1.036.370 km2 (2012)

- Population: (calculated data) 163.518.571 (July 2012)

- Population Density: (calculated data) 157.78/km2 (2012)

- GDP (PPP) per capita: USD $34.444 (2012)

- Life expectancy: (calculated data) 78.32 year (2012)

- Unemployment rate: 8.2% (2012)

- Fertility rate: 1.41 births/woman (2012)

- Human Development Index: 0.874 (2012) (very high)

- Globalization Index: 80.09 (2013)

Countries in descending order of Human Development Index (2012 data):
 Germany: 0.920 (ranked 4)
Germany: 0.920 (ranked 4) Switzerland: 0.913 (ranked 9)
Switzerland: 0.913 (ranked 9) Austria: 0.895 (ranked 18)
Austria: 0.895 (ranked 18) Slovenia: 0.892 (ranked 22)
Slovenia: 0.892 (ranked 22) Liechtenstein: 0.883 (ranked 24)
Liechtenstein: 0.883 (ranked 24) Czechia: 0.873 (ranked 28)
Czechia: 0.873 (ranked 28) Slovakia: 0.840 (ranked 35)
Slovakia: 0.840 (ranked 35) Hungary: 0.831 (ranked 37)
Hungary: 0.831 (ranked 37) Poland: 0.821 (ranked 39)
Poland: 0.821 (ranked 39)
The index of globalization in Central European countries (2013 data)
 Austria: 89.48 (ranked 4)
Austria: 89.48 (ranked 4) Hungary: 86.85 (ranked 9)
Hungary: 86.85 (ranked 9) Switzerland: 86.28 (ranked 10)
Switzerland: 86.28 (ranked 10) Czechia: 84.86 (ranked 15)
Czechia: 84.86 (ranked 15) Slovakia: 83.49 (ranked 19)
Slovakia: 83.49 (ranked 19) Germany: 81.08 (ranked 22)
Germany: 81.08 (ranked 22) Poland: 79.10 (ranked 26)
Poland: 79.10 (ranked 26) Slovenia: 76.85 (ranked 30)
Slovenia: 76.85 (ranked 30) Liechtenstein: 52,88 (ranked 101)
Liechtenstein: 52,88 (ranked 101)
Physical geography
Between the Alps and the Baltics
Geography strongly defines Central Europe's borders with its neighbouring regions to the North and South, namely Northern Europe (or Scandinavia) across the Baltic Sea, the Apennine peninsula (or Italy) across the Alps and the Balkan peninsula across the Soča-Krka-Sava-Danube line. The borders to Western Europe and Eastern Europe are geographically less defined and for this reason the cultural and historical boundaries migrate more easily West-East than South-North. The Rhine river which runs South-North through Western Germany is an exception.
Pannonian Plain and Carpathian Mountains
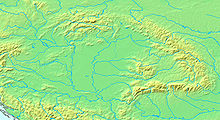
Southwards, the Pannonian Plain is bounded by the rivers Sava and Danube- and their respective floodplains. The Pannonian Plain stretches over the following countries: Austria, Croatia, Hungary, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia and Slovenia, and touches borders of Bosnia and Herzegovina ( Republika Srpska) and Ukraine ("peri- Pannonian states").
Dinaric Alps
As southeastern division of the Eastern Alps, the Dinaric Alps extend for 650 kilometres along the coast of the Adriatic Sea (northwest-southeast), from the Julian Alps in the northwest down to the Šar-Korab massif, north-south. According to the Freie Universitaet Berlin this mountain chain is classified as South Central European.
Current views on Central Europe
Rather than a physical entity, Central Europe is a concept of shared history which contrasts with that of the surrounding regions. The issue of how to name and define the Central European region is subject to debates. Very often, the definition depends on the nationality and historical perspective of its author.
Main propositions, gathered by Jerzy Kłoczowski, include:
- West-Central and East-Central Europe – this conception, presented in 1950, distinguishes two regions in Central Europe: German West-Centre, with imperial tradition of the Reich, and the East-Centre covered by variety of nations from Finland to Greece, placed between great empires of Scandinavia, Germany, Italy and the Soviet Union.
- Central Europe as the area of cultural heritage of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth – Ukrainian, Belarusian and Lithuanian historians, in cooperation (since 1990) with Polish historians, insist on the importance of the concept.
- Central Europe as a region connected to the Western civilisation for a very long time, including countries like the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Holy Roman Empire, later German Empire and the Habsburg Monarchy, the Kingdom of Hungary and Bohemia. Central Europe understood in this way borders on Russia and South-Eastern Europe, but the exact frontier of the region is difficult to determine.
- Central Europe as the area of cultural heritage of the Habsburg Empire – a concept which is popular in the region of Danube River.
- A concept underlining the links connecting Ukraine and Belarus with Russia and treating the Russian Empire together with the whole Slavic Orthodox population as one entity – this position is taken by the Russian historiography.
- A concept putting an accent on the links with the West, especially from the 19th century and the grand period of liberation and formation of Nation-states – this idea is represented by in the South-Eastern states, which prefer the enlarged concept of the “East Centre” expressing their links with the Western culture.
According to Ronald Tiersky, the 1991 summit held in Visegrád, Hungary and attended by the Polish, Hungarian and Czechoslovak presidents was hailed at the time as a major breakthrough in Central European cooperation, but the Visegrád Group became a vehicle for coordinating Central Europe's road to the European Union, while development of closer ties within the region languished.
Peter J. Katzenstein described Central Europe as a way station in a Europeanization process that marks the transformation process of the Visegrád Group countries in different, though comparable ways. According to him, in Germany's contemporary public discourse "Central European identity" refers to the civilizational divide between Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. He says there's no precise, uncontestable way to decide whether the Baltic states, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, Romania, and Bulgaria are parts of Central Europe or not.
Lonnie R. Johnson points out criteria to distinguish Central Europe from Western, Eastern and Southeast Europe:
- One criterion for defining Central Europe is the frontiers of medieval empires and kingdoms that largely correspond to the religious frontiers between the Roman Catholic West and the Orthodox East. The pagans of Central Europe were converted to Roman Catholicism while in Southeastern and Eastern Europe they were brought into the fold of the Eastern Orthodox Church.
- Multinational empires were a characteristic of Central Europe. Hungary and Poland, small and medium-size states today, were empires during their early histories. The historical Kingdom of Hungary was until 1918 three times larger than Hungary is today, while Poland was the largest state in Europe in the 16th century. Both these kingdoms housed a wide variety of different peoples.
He also thinks that Central Europe is a dynamical historical concept, not a static spatial one. For example, Lithuania, a fair share of Belarus and western Ukraine are in Eastern Europe today, but 250 years ago they were in Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Johnson's study on Central Europe received acclaim and positive reviews in the scientific community. However, according to Romanian researcher Maria Bucur this very ambitious project suffers from the weaknesses imposed by its scope (almost 1600 years of history).
The Columbia Encyclopedia defines Central Europe as: Germany, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Austria, Poland, Czechia, Slovakia, and Hungary. The World Factbook Encyclopedia Britannica and Brockhaus Enzyklopädie use the same definition adding Slovenia too. Encarta Encyclopedia does not clearly define the region, but places the same countries into Central Europe in its individual articles on countries, adding Slovenia in "south central Europe".
The German Encyclopaedia Meyers Grosses Taschenlexikon (English: Meyers Big Pocket Encyclopedia), 1999, defines Central Europe as the central part of Europe with no precise borders to the East and West. The term is mostly used to denominate the territory between the Schelde to Vistula and from the Danube to the Moravian Gate. Usually the countries considered to be Central European are Germany, Switzerland, Austria, Poland, Czechia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Hungary; in the broader sense Romania too, the northern, eastern and central part of Croatia, northern Serbia, occasionally also the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg.
Demographics
Central Europe is one of continent’s most populous regions. It includes countries of varied sizes, ranging from tiny Liechtenstein to Germany, the largest European country (that is entirely placed in Europe). Demographic figures for countries entirely located within notion of Central Europe (“the core countries”) number around 165 million people, out of which around 82 million are residents of Germany. Other populations include: Poland with around 39 million residents, Czech republic at 10.5 million, Hungary - 10 million, Austria with 8.5 million, Switzerland with its 8 million inhabitants, Slovakia at 5.5 million, Slovenia at 2 million and Liechtenstein at 0,03 million.
If the countries which are occasionally included in Central Europe were counted in, partially or in whole - Romania (7 - 19 million people), Serbia (3,6 – 7 million), Croatia (2,3 – 4,3 million), Lithuania (3.5 million), Latvia (2.5 million), Estonia (1.5 million) – it would contribute to the rise of between 20 - 37.5 million, depending on whether regional or integral approach was used. If smaller, western and eastern historical parts of Central Europe would be included in the demographic corpus, further 20 million people of different nationalities would also be added in the overall count, it would surpass the 200 million people figure.
History of the concept
Middle Ages
As elements of unity for Western and Central Europe were considered the Roman Catholicism and Latin. Eastern Europe that remained Orthodox Christian, was the area of Byzantine cultural influence, and after the schism will develop cultural unity and protection against the Catholic and Protestant (Western) world, within the framework of Slavonic language and the Cyrillic alphabet.
According to Hungarian historian Jenő Szűcs, foundations of Central European history at the first millennium were in close connection with Western European development. He explained that between the 11th and 15th centuries not only Christianization and its cultural consequences were implemented, but well-defined social features emerged in Central Europe based on Western characteristics. The keyword of Western social development after millennium was the spread of liberties and autonomies in Western Europe. These phenomena appeared in the middle of the 13th century in Central European countries. There were self-governments of towns, counties and parliaments.
In 1335 under the rule of the King Charles I of Hungary, the castle of Visegrád, the seat of the Hungarian monarchs was the scene of the royal summit of the Kings of Poland, Bohemia and Hungary. They agreed to cooperate closely in the field of politics and commerce, inspiring their late successors to launch a successful Central European initiative.
In the Middle Ages, countries in Central Europe adopted Magdeburg rights.
Before World War I
Before 1870, the industrialization that had developed in Western and Central Europe and the United States did not extend in any significant way to the rest of the world. Even in Eastern Europe, industrialization lagged far behind. Russia, for example, remained largely rural and agricultural, and its autocratic rulers kept the peasants in serfdom.
The concept of Central Europe was already known at the beginning of the 19th century, but its real life began in the 20th century and immediately became an object of intensive interest. However, the very first concept mixed science, politics and economy – it was strictly connected with intensively growing German economy and its aspirations to dominate a part of European continent called Mitteleuropa. The German term denoting Central Europe was so fashionable that other languages started referring to it when indicating territories from Rhine to Vistula, or even Dnieper, and from the Baltic Sea to the Balkans. An example of that-time vision of Central Europe may be seen in J. Partsch’s book of 1903.
On 21 January 1904 – Mitteleuropäischer Wirtschaftsverein (Central European Economic Association) was established in Berlin with economic integration of Germany and Austria–Hungary (with eventual extension to Switzerland, Belgium and the Netherlands) as its main aim. Another time, the term Central Europe became connected to the German plans of political, economic and cultural domination. The “bible” of the concept was Friedrich Naumann’s book Mitteleuropa in which he called for an economic federation to be established after the war. Naumann's idea was that the federation would have at its centre Germany and the Austro-Hungarian Empire but would also include all European nations outside the Anglo-French alliance, on one side, and Russia, on the other. The concept failed after the German defeat in World War I and the dissolution of Austria–Hungary. The revival of the idea may be observed during the Hitler era.
Interwar period
According to Emmanuel de Martonne, in 1927 the Central European countries included: Germany, Switzerland, Austria, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary and Romania. Italy and Yugoslavia are not considered by the author to be Central European because they are located mostly outside Central Europe. The author use both Human and Physical Geographical features to define Central Europe.
The interwar period (1918–1939) brought new geopolitical system and economic and political problems, and the concept of Central Europe took a different character. The centre of interest was moved to its eastern part – the countries that have reappeared on the map of Europe: Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia. Central Europe ceased to be the area of German aspiration to lead or dominate and became a territory of various integration movements aiming at resolving political, economic and national problems of "new" states, being a way to face German and Soviet pressures. However, the conflict of interests was too big and neither Little Entente nor Międzymorze ideas succeeded.
The interwar period brought new elements to the concept of Central Europe. Before World War I, it embraced mainly German states (Germany, Austria), non-German territories being an area of intended German penetration and domination – German leadership position was to be the natural result of economic dominance. After the war, the Eastern part of Central Europe was placed at the centre of the concept. At that time the scientists took interest in the idea: the International Historical Congress in Brussels in 1923 was committed to Central Europe, and the 1933 Congress continued the discussions.
Magda Adam, in the Versailles System and Central Europe, published in the Oxford journals: "Today we know that the bane of Central Europe was the Little Entente, military alliance of Czechoslovakia, Romania and Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (later Yugoslavia), created in 1921 not for Central Europe's cooperation nor to fight German expansion, but in a wrong perceived notion that a completely powerless Hungary must be kept down".
The avant-garde movements of Central Europe were an essential part of modernism’s evolution, reaching its peak throughout the continent during the 1920s. The Sourcebook of Central European avantgards (Los Angeles County Museum of Art) contains primary documents of the avant-gardes in Austria, Czechoslovakia, Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Yugoslavia from 1910 to 1930. The manifestos and magazines of Western European radical art circles are well known to Western scholars and are being taught at primary universities of their kind in the western world.
Central Europe behind the Iron Curtain
Following World War II, large parts of Europe that were culturally and historically Western became part of the Eastern bloc. Czech author Milan Kundera (emigrant to France) thus wrote in 1984 about the "Tragedy of Central Europe" in the New York Review of Books. Consequently, the English term Central Europe was increasingly applied only to the westernmost former Warsaw Pact countries (East Germany, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary) to specify them as communist states that were culturally tied to Western Europe. This usage continued after the end of the Warsaw Pact when these countries started to undergo transition.
The post-World War II period brought blocking of the research on Central Europe in the Eastern Bloc countries, as its every result proved the dissimilarity of Central Europe, which was inconsistent with the Stalinist doctrine. On the other hand, the topic became popular in Western Europe and the United States, much of the research being carried out by immigrants from Central Europe. At the end of the communism, publicists and historians in Central Europe, especially anti-communist opposition, came back to their research.
According to Meyers Enzyklopädisches Lexikon, Central Europe is a part of Europe composed by the surface of the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Poland, Switzerland, Austria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary and Romania, northern marginal regions of Italy and Yugoslavia (northern states- Slovenia, Croatia and Serbia) as well as northeastern France.
Mitteleuropa, the German term
The German term Mitteleuropa (or alternatively its literal translation into English, Middle Europe) is an ambiguous German concept. It is sometimes used in English to refer to an area somewhat larger than most conceptions of 'Central Europe'; it refers to territories under German(ic) cultural hegemony until World War I (encompassing Austria–Hungary and Germany in their pre-war formations but usually excluding the Baltic countries north of East Prussia). According to Fritz Fischer Mitteleuropa was a scheme in the era of the Reich of 1871–1918 by which the old imperial elites had allegedly sought to build a system of German economic, military and political domination from the northern seas to the Near East and from the Low Countries through the steppes of Russia to the Caucasus. Professor Fritz Epstein argued the threat of a Slavic "Drang nach Westen" (Western expansion) had been a major factor in the emergence of a Mitteleuropa ideology before the Reich of 1871 ever came into being.
In Germany the connotation is also sometimes linked to the pre-war German provinces east of the Oder-Neisse line which were lost as the result of World War II, annexed by People's Republic of Poland and the Soviet Union, and ethnically cleansed of Germans by communist authorities and forces (see expulsion of Germans after World War II) due to Yalta Conference and Potsdam Conference decisions. In this view Bohemia and Moravia, with its dual Western Slavic and Germanic heritage, combined with the historic element of the " Sudetenland", is a core region illustrating the problems and features of the entire Central European region.
The term Mitteleuropa conjures up negative historical associations, although the Germans have not played an exclusively negative role in the region. Most Central European Jews embraced the enlightened German humanistic culture of the 19th century. German-speaking Jews from turn of the 20th century Vienna, Budapest and Prague became representatives of what many consider to be Central European culture at its best, though the Nazi version of "Mitteleuropa" destroyed this kind of culture. Some German speakers are sensitive enough to the pejorative connotations of the term Mitteleuropa to use Zentraleuropa instead. Adolf Hitler was obsessed by the idea of Lebensraum and many non-German Central Europeans identify Mitteleuropa with the instruments he employed to acquire it: war, deportations, genocide.
Central European Flora region
The Central European Flora region stretches from Central France (Massif Central) to Central Romania ( Carpathians) and Southern Scandinavia.