Chapter 7
Introduction to Quantum Theory
By Boundless
In many cases, the properties of light can be explained as a wave, as was shown in Young's double-slit experiment.
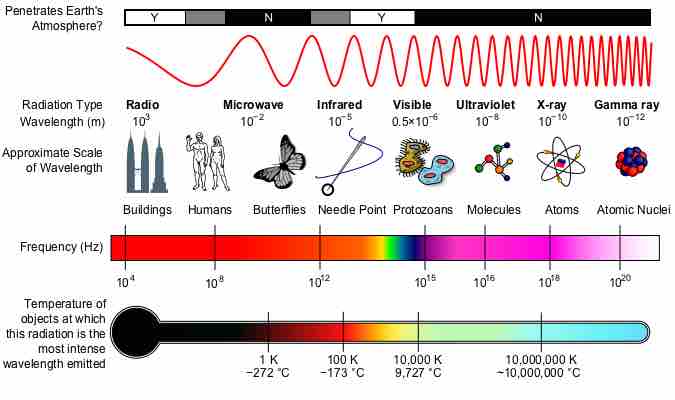
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation.
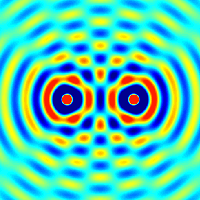
Interference and diffraction are terms that describe a wave interacting with something that changes its amplitude, such as another wave.
Max Planck suggested that the energy of light is proportional to its frequency, also showing that light exists in discrete quanta of energy.
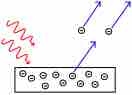
The photoelectric effect is the propensity of high-energy electromagnetic radiation to eject electrons from a given material.
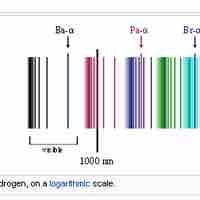
The emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen is divided into a number of spectral series.
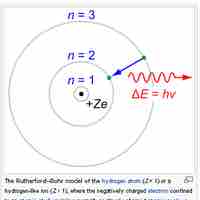
The Bohr model depicts atoms as small, positively charged nuclei surrounded by electrons in circular orbits.
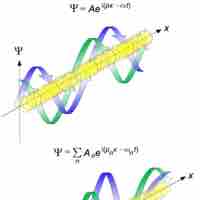
The de Broglie wavelength is inversely proportional to the momentum of a particle.
Only partial knowledge of the momentum and position of a particle may be known at the same time.
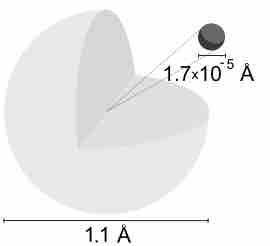
A hydrogen atom is electrically neutral, containing a single proton and a single electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force.
Quantum indeterminacy refers to the necessary incompleteness in the description of a physical system.
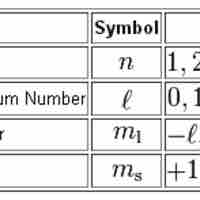
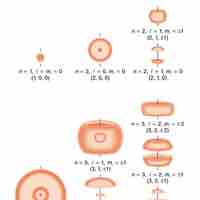
Quantum numbers provide a numerical description of the orbitals in which electrons reside.
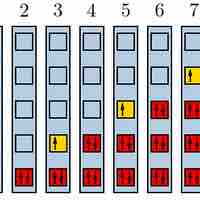
The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two fermions can have identical wavefunctions.
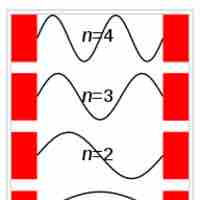
The particle in a box model provides one of the very few problems in quantum mechanics which can be solved analytically.
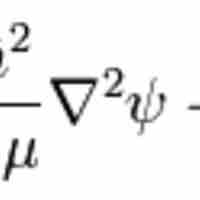
The hydrogen atom is the simplest one-electron atom and has analytical solutions to the Schrödinger equation.
- Energy
- Introduction to Thermodynamics
- Enthalpy
- Calorimetry
- Standard Enthalpy of Formation and Reaction