Chapter 2
Derivatives and Integrals
By Boundless
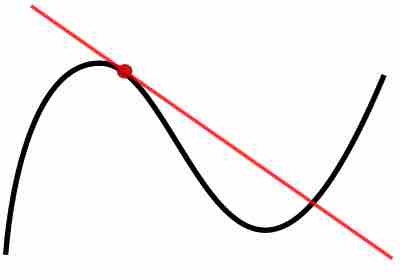
The use of differentiation makes it possible to solve the tangent line problem by finding the slope
Differentiation is a way to calculate the rate of change of one variable with respect to another.
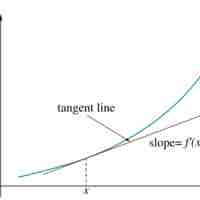
If every point of a function has a derivative, there is a derivative function sending the point

The rules of differentiation can simplify derivatives by eliminating the need for complicated limit calculations.
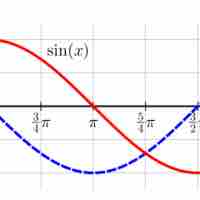
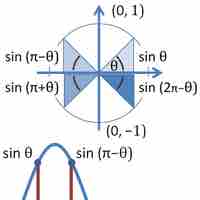
Derivatives of trigonometric functions can be found using the standard derivative formula.

The chain rule is a formula for computing the derivative of the composition of two or more functions.
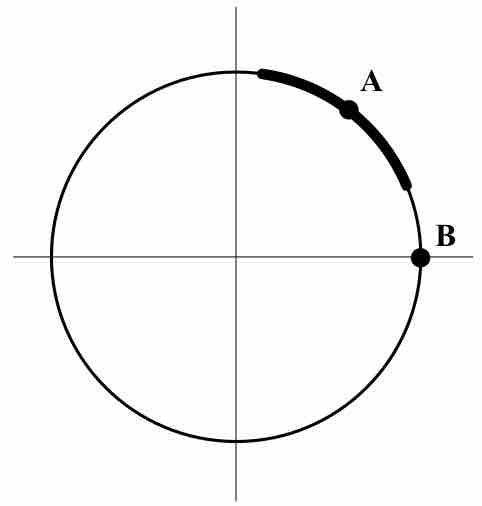
Implicit differentiation makes use of the chain rule to differentiate implicitly defined functions.
Differentiation, in essence calculating the rate of change, is important in all quantitative sciences.
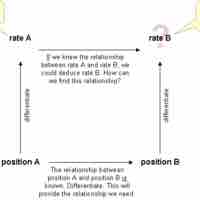
Related rates problems involve finding a rate by relating that quantity to other quantities whose rates of change are known.
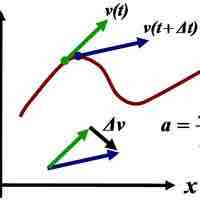
The derivative of an already-differentiated expression is called a higher-order derivative.
A linear approximation is an approximation of a general function using a linear function.
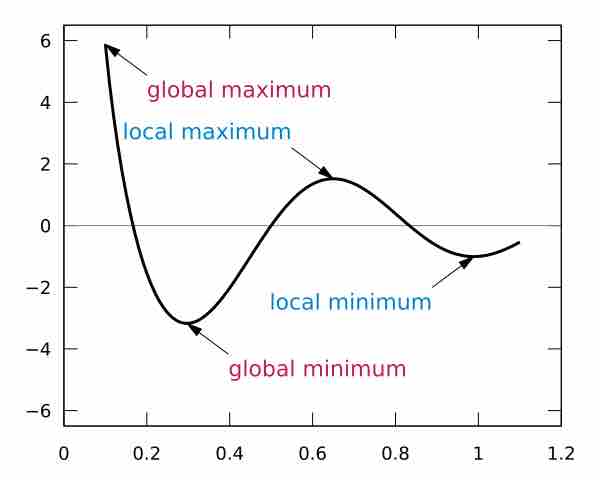
Maxima and minima are critical points on graphs and can be found by the first derivative and the second derivative.
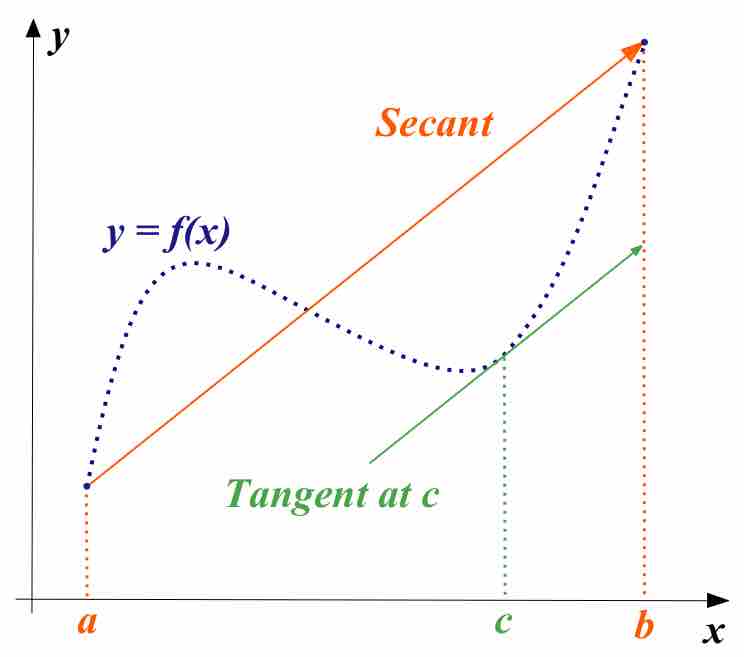
The MVT states that for a function continuous on an interval, the mean value of the function on the interval is a value of the function.
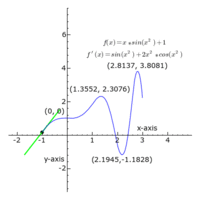
The shape of a graph may be found by taking derivatives to tell you the slope and concavity.

The asymptotes are computed using limits and are classified into horizontal, vertical and oblique depending on the orientation.
Curve sketching is used to produce a rough idea of overall shape of a curve given its equation without computing a detailed plot.

Graphics can be created by hand, using computer programs, and with graphing calculators.
Mathematical optimization is the selection of a best element (with regard to some criteria) from some set of available alternatives.
Newton's Method is a method for finding successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function.
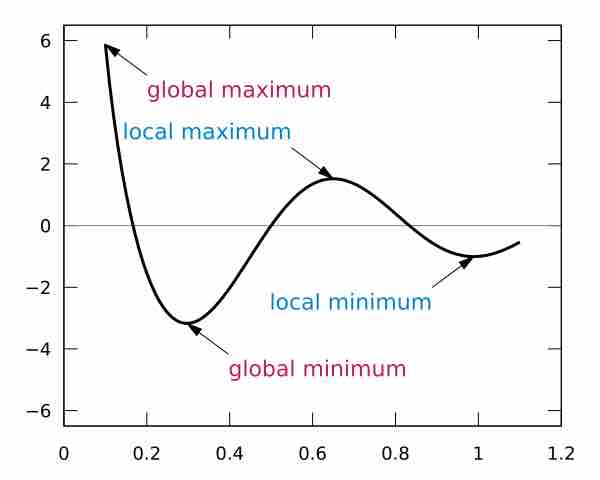
The second derivative test is a criterion for determining whether a given critical point is a local maximum or a local minimum.
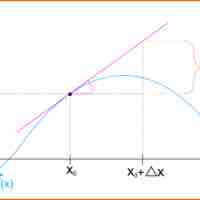
Differentials are the principal part of the change in a function
An antiderivative is a differentiable function
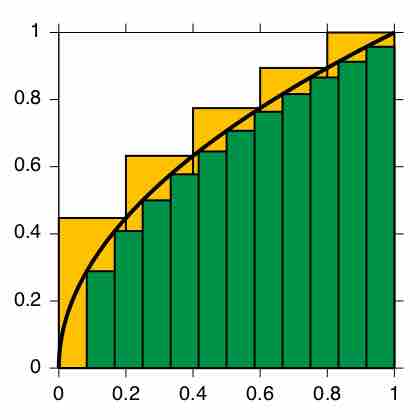
Defined integrals are used in many practical situations that require distance, area, and volume calculations.
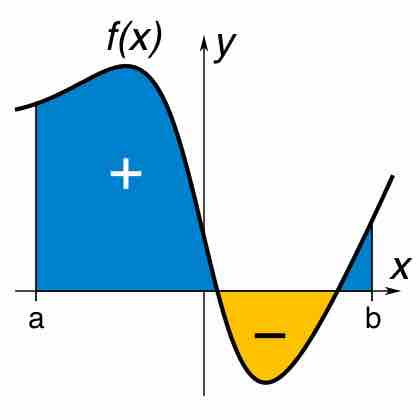
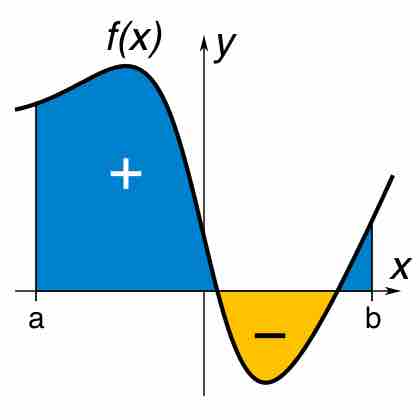
A definite integral is the area of the region in the
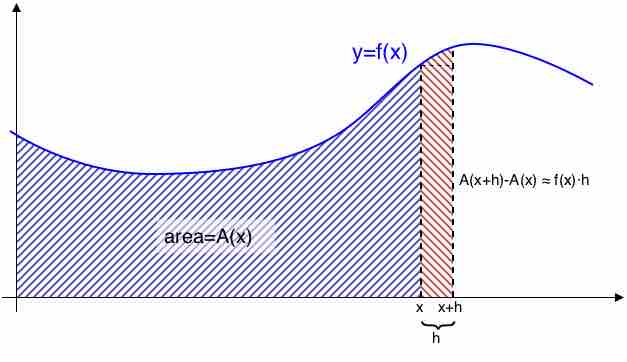
The fundamental theorem of calculus is a theorem that links the concept of the derivative of a function to the concept of the integral.
An indefinite integral is defined as
Integration by substitution is an important tool for mathematicians used to find integrals and antiderivatives.
A transcendental function is a function that is not algebraic.
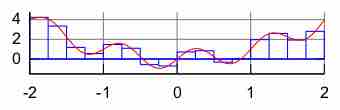
Numerical integration is a method of approximating the value of a definite integral.
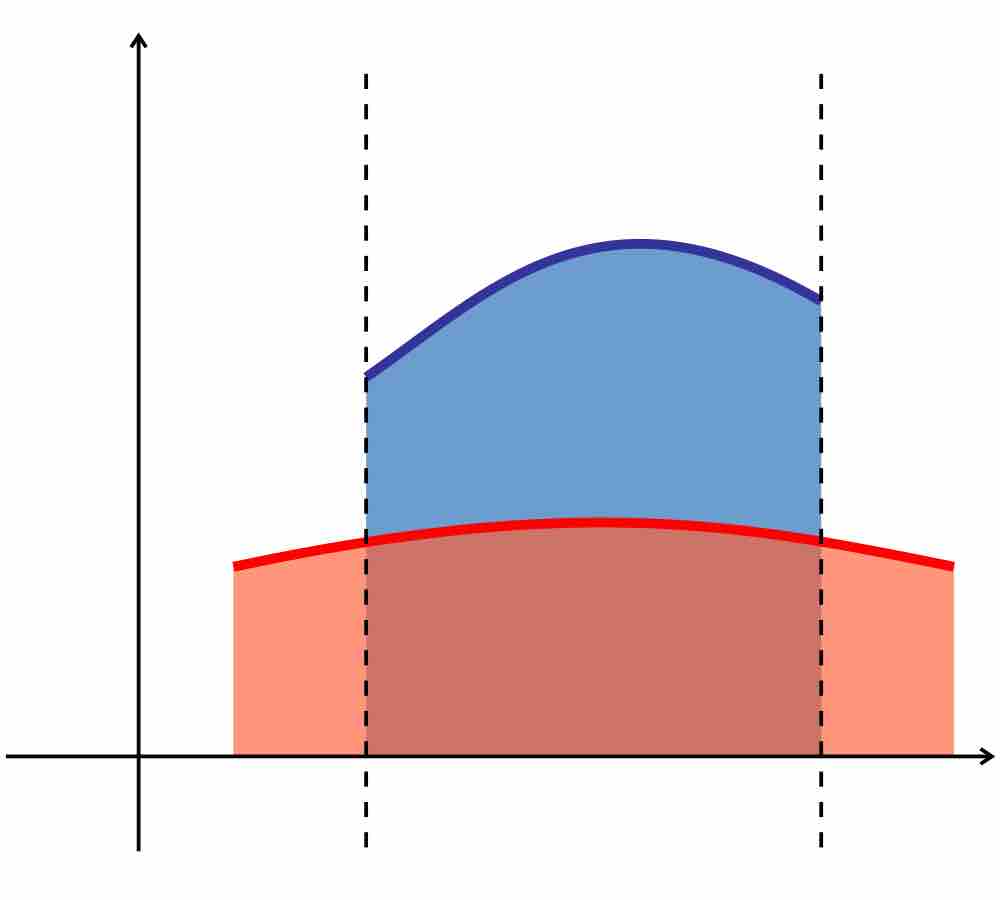
The area between the graphs of two functions is equal to the integral of a function,
Volumes of complicated shapes can be calculated using integral calculus if a formula exists for the shape's boundary.
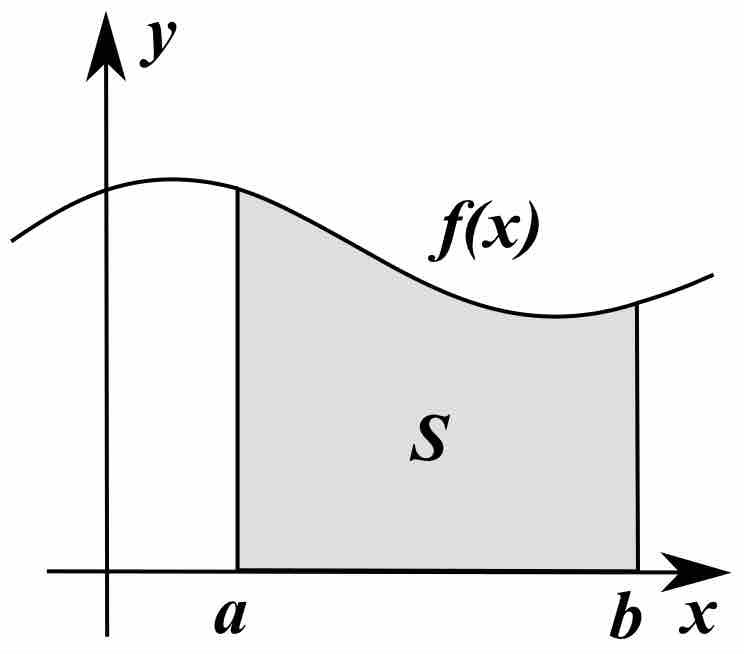
The average of a function
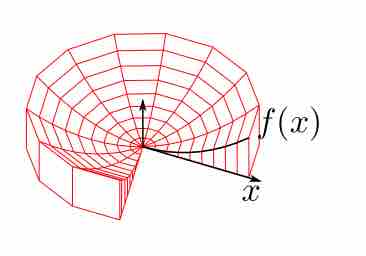
In the shell method, a function is rotated around an axis and modeled by an infinite number of cylindrical shells, all infinitely thin.
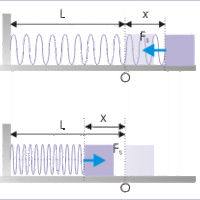
Forces may do work on a system. Work done by a force (
Disc and shell methods of integration can be used to find the volume of a solid produced by revolution.