Section 2
Applications of Differentiation
By Boundless
A linear approximation is an approximation of a general function using a linear function.
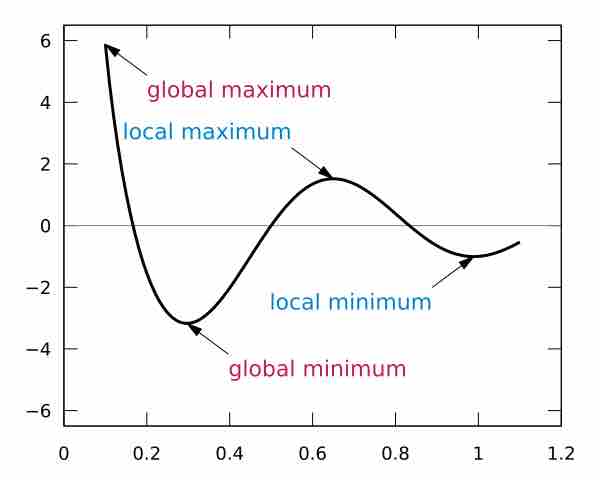
Maxima and minima are critical points on graphs and can be found by the first derivative and the second derivative.
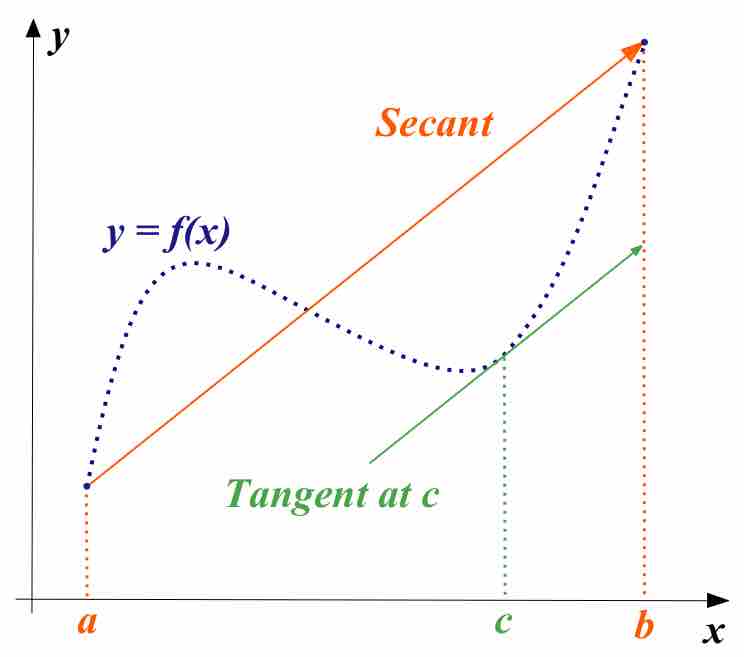
The MVT states that for a function continuous on an interval, the mean value of the function on the interval is a value of the function.
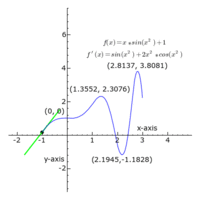
The shape of a graph may be found by taking derivatives to tell you the slope and concavity.

The asymptotes are computed using limits and are classified into horizontal, vertical and oblique depending on the orientation.
Curve sketching is used to produce a rough idea of overall shape of a curve given its equation without computing a detailed plot.

Graphics can be created by hand, using computer programs, and with graphing calculators.
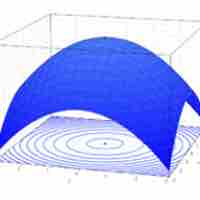
Mathematical optimization is the selection of a best element (with regard to some criteria) from some set of available alternatives.
Newton's Method is a method for finding successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function.
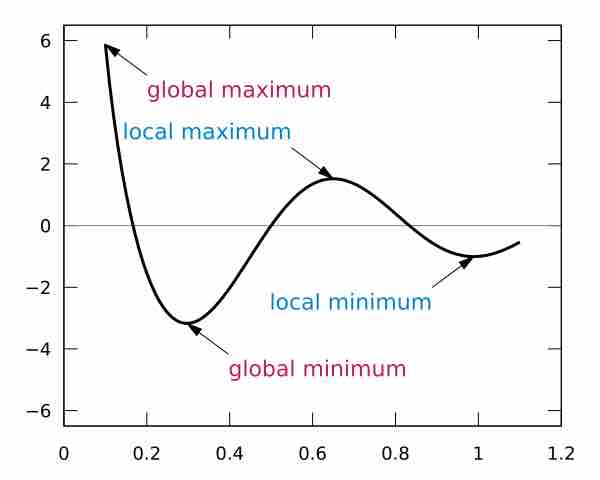
The second derivative test is a criterion for determining whether a given critical point is a local maximum or a local minimum.
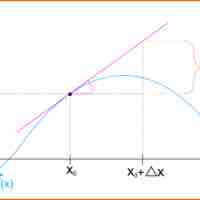
Differentials are the principal part of the change in a function