Principal Sponsors
Makes grants to address the most serious social and environmental problems facing society, where risk capital, responsibly invested, may make a difference over time.
An independent federal agency created by Congress in 1950 to promote the progress of science.
King Saud University seeks to become a leader in educational and technological innovation, scientific discovery and creativity through fostering an atmosphere of intellectual inspiration and partnership for the prosperity of society.
The O'Donnell Foundation is devoted to building model programs to enhance the quality of education.
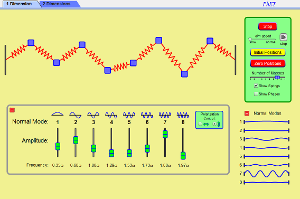
Normal Modes
 Download
Run Now!
542 kB
Version: 1.01 (change log)
Download
Run Now!
542 kB
Version: 1.01 (change log)
Embed a running copy of this simulation Use this HTML to embed a running copy of this simulation. You can change the width and height of the embedded simulation by changing the "width" and "height" attributes in the HTML. Embed an image that will launch the simulation when clicked Use this HTML code to display a screenshot with the words "Click to Run". |
Play with a 1D or 2D system of coupled mass-spring oscillators. Vary the number of masses, set the initial conditions, and watch the system evolve. See the spectrum of normal modes for arbitrary motion. See longitudinal or transverse modes in the 1D system. |
Teaching Resources
Main Topics
- Oscillator
- Normal Modes
- Polarization
- Mass Spring System
- Frequency
- Amplitude
- Phase
Sample Learning Goals
- Explain what a normal mode is.
- Explain what are the frequency, the amplitude, and the phase of a normal mode.
- Explain why different normal modes have different frequencies and why higher-numbered modes have higher frequencies.
- Identify how many normal modes a given system has and be able to sketch the individual modes qualitatively, for both 1D and 2D systems.
- Explain the distinction between transverse and longitudinal normal modes in a 1D system.
- Explain how adjusting the phase of a normal mode affects the motion of the system.
- Explain qualitatively how any arbitrary state of the system can be written as a sum of normal modes; that is, explain the superposition principle.
- Explain which properties of the system are set by the initial conditions, which properties are time-independent, and which properties are time-dependent.
- Explain why striking a metal plate in one spot raises the temperature of the plate.
Tips for Teachers
The teacher's guide (pdf) contains tips created by the PhET team.
Teaching Ideas
You can submit your own ideas and activities.
Related Simulations
Translated Versions:
Software Requirements
| Windows | Macintosh | Linux |
|---|---|---|
|
Microsoft Windows
XP/Vista/7 Macromedia Flash 9 or later |
OS 10.5 or later
Macromedia Flash 9 or later |
Macromedia Flash 9 or later |
Credits
| Design Team | Third-party Libraries | Thanks To |
|---|---|---|
|
© 2013 University of Colorado.
Some rights reserved.