Chapter 4
Organization at the Tissue Level
By Boundless
The human body consists of four types of tissue: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous. Epithelial tissue covers the body, lines all cavities, and composes the glands.
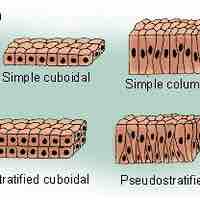
Epithelial tissue is classified by cell shape and the number of cell layers.

Connective tissue is incredibly diverse and contributes to energy storage, the protection of organs, and the body's structural integrity.
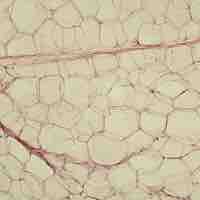
Connective tissues encompass a diverse array of tissue types that are involved in binding and supporting body structure and tissues.
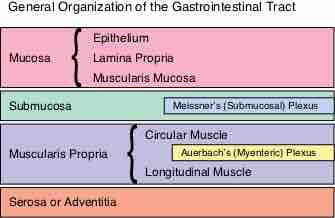
The mucous membranes are linings of mostly endodermal origin, covered in epithelium, which are involved in absorption and secretion.
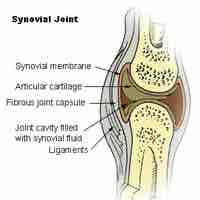
A synovial membrane is the soft tissue found between the articular capsule (joint capsule) and the joint cavity of synovial joints.