Chapter 4
The Laws of Motion
By Boundless
Newton’s first law of motion describes inertia. According to this law, a body at rest tends to stay at rest, and a body in motion tends to stay in motion, unless acted on by a net external force.

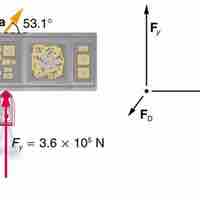
The second law states that the net force on an object is equal to the rate of change, or derivative, of its linear momentum.
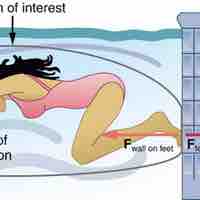
The third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
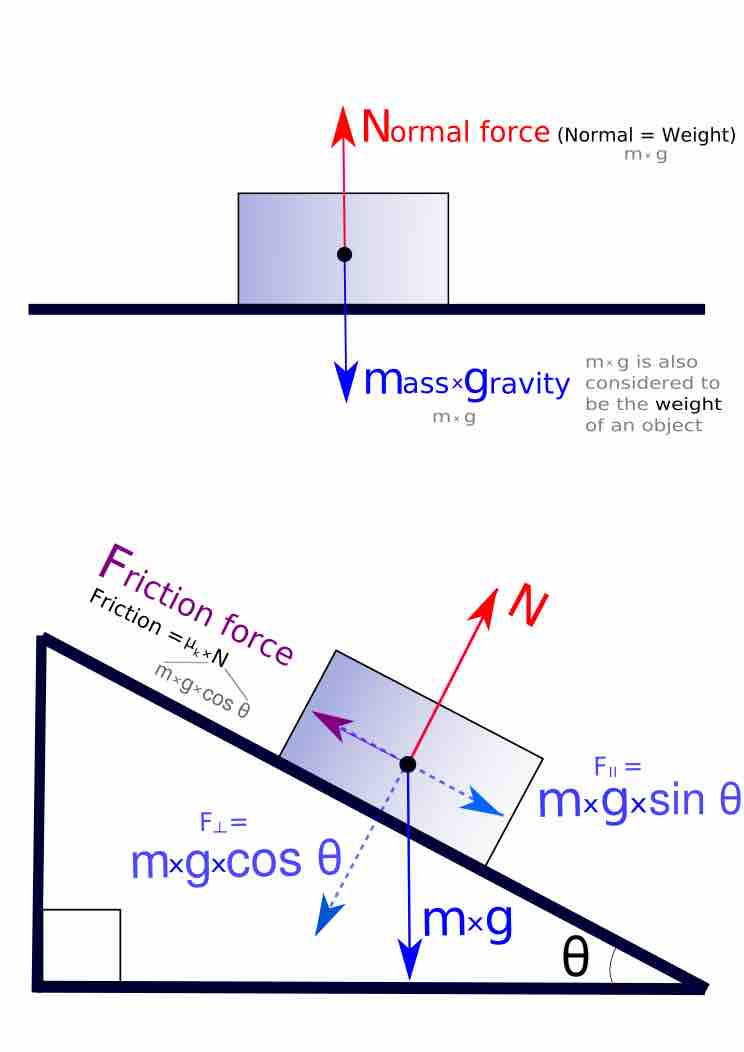
Net force affects the motion, postion and/or shape of objects (some important and commonly used forces are friction, drag and deformation).
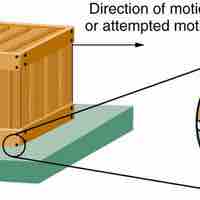
If two systems are in contact and moving relative to one another, then the friction between them is called kinetic friction.
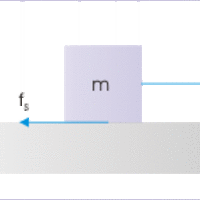
Static friction is a type of friction that occurs to resist motion when two objects are at rest against each other.
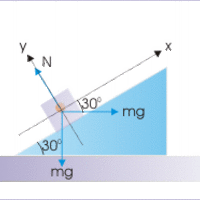
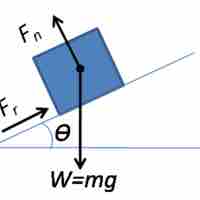
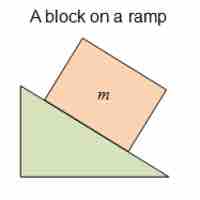
Combining motion on inclines with friction uses such concepts as equilibrium and contact force on an incline.

The drag force is the resistive force felt by objects moving through fluids and is proportional to the square of the object's speed.
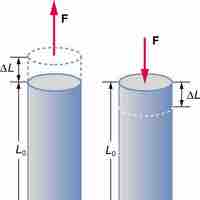
The ratio of force to area
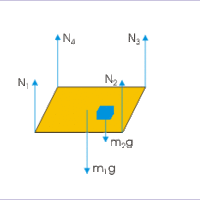
An object is said to be in equilibrium when there is no external net force acting on it.
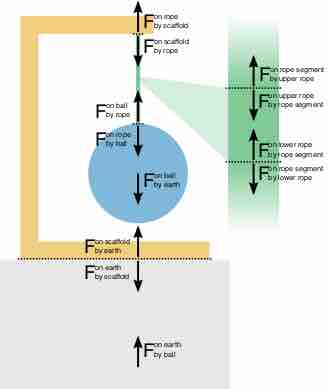
Forces can be transferred from one object to another through connections.
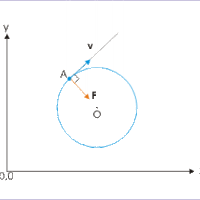
An object in circular motion undergoes acceleration due to centripetal force in the direction of the center of rotation.