Section 3
Newton's Laws
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Physics
Physics
by Boundless
3 concepts
The First Law: Inertia
Newton’s first law of motion describes inertia. According to this law, a body at rest tends to stay at rest, and a body in motion tends to stay in motion, unless acted on by a net external force.

The Second Law: Force and Acceleration
The second law states that the net force on an object is equal to the rate of change, or derivative, of its linear momentum.
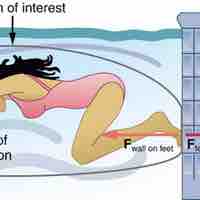
The Third Law: Symmetry in Forces
The third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.