Chapter 6
Metabolism
By Boundless
All organisms require energy to complete tasks; metabolism is the set of the chemical reactions that release energy for cellular processes.

The various types of energy include kinetic, potential, and chemical energy.
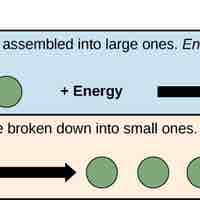
An anabolic pathway requires energy and builds molecules while a catabolic pathway produces energy and breaks down molecules.

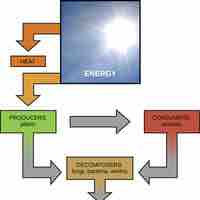
Organisms break down carbohydrates to produce energy for cellular processes, and photosynthetic plants product carbohydrates.
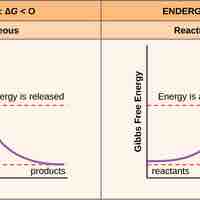
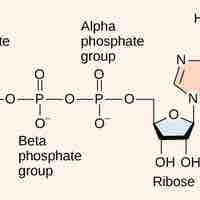
Free energy, called Gibbs free energy (G), is usable energy or energy that is available to do work.

The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can be transferred or transformed, but cannot be created or destroyed.
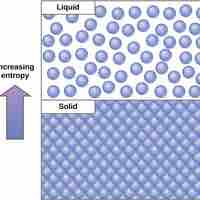
The second law of thermodynamics states that every energy transfer increases the entropy of the universe due to the loss of usable energy.
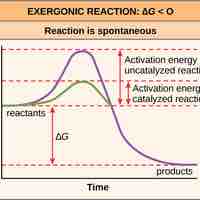
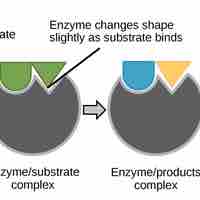
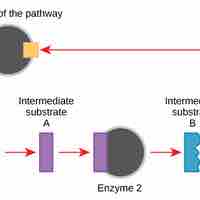
Activation energy is the energy required for a reaction to occur, and determines its rate.