Chapter 6
Quadratic Functions and Factoring
By Boundless
Quadratic equations are second order polynomials, and have the form
The zeros of a quadratic equation can be found by solving what is known as the quadratic formula.
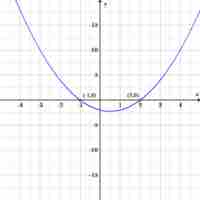
The discriminant of a polynomial is a function of its coefficients that reveals information about the polynomial's roots.
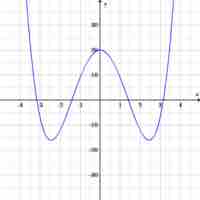
Many equations with no odd-degree terms can be reduced to quadratics and solved with the same methods as quadratics.
The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola, and its parts provide valuable information about the function.
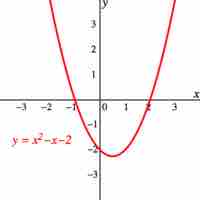
The roots of a quadratic function can be found algebraically or graphically.
The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola whose axis of symmetry is parallel to the
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of the form
A quadratic equation of the form
When a trinomial is a perfect square, it can be factored into two equal binomials.
When a quadratic is a difference of squares, there is a helpful formula for factoring it.
Polynomials of the form
Completing the square is a common method for solving quadratic equations, and takes the form of
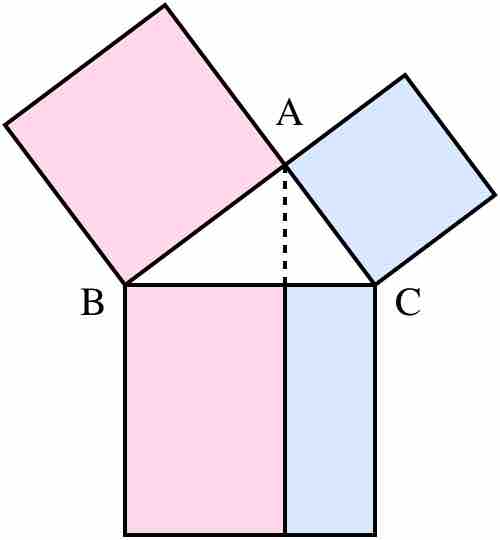
Quadratic relationships between variables are commonly found in physical sciences, engineering, and elsewhere.
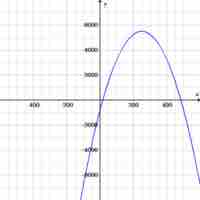
For problems involving quadratics in finance, it is useful to graph the equation. From these, one can easily find critical values of the function by inspection.