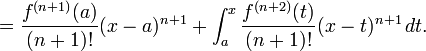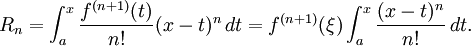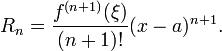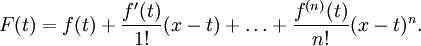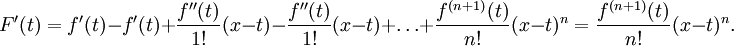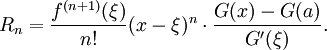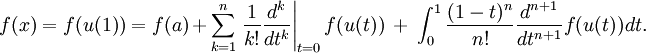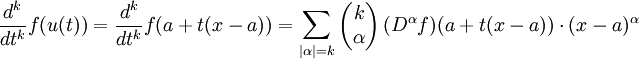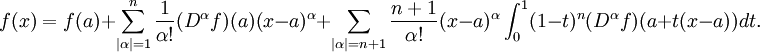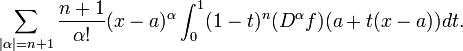Taylor's theorem
Did you know...
SOS Children made this Wikipedia selection alongside other schools resources. Sponsoring children helps children in the developing world to learn too.
In calculus, Taylor's theorem gives a sequence of approximations of a differentiable function near a given point by polynomials (the Taylor polynomials of that function) whose coefficients depend only on the derivatives of the function at that point. The theorem also gives precise estimates on the size of the error in the approximation. The theorem is named after the mathematician Brook Taylor, who stated it in 1712, even though the result was first discovered 41 years earlier in 1671 by James Gregory.
Taylor's theorem in one variable
A simple example of Taylor's theorem is the approximation of the exponential function 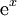 near x = 0:
near x = 0:
The precise statement of the theorem is as follows: If n ≥ 0 is an integer and f is a function which is n times continuously differentiable on the closed interval [a, x] and n + 1 times differentiable on the open interval (a, x), then we have
Here, n! denotes the factorial of n, and Rn(x) is a remainder term, denoting the difference between the Taylor polynomial of degree n and the original function. The remainder term Rn(x) depends on x and is small if x is close enough to a. Several expressions are available for it.
The Lagrange form of the remainder term states that there exists a number ξ between a and x such that
This exposes Taylor's theorem as a generalization of the mean value theorem. In fact, the mean value theorem is used to prove Taylor's theorem with the Lagrange remainder term.
The Cauchy form of the remainder term states that there exists a number ξ between a and x such that
More generally, if G(t) is a continuous function on [a,x] which is differentiable with non-vanishing derivative on (a,x), then there exists a number ξ between a and x such that
This exposes Taylor's theorem as a generalization of the Cauchy mean value theorem.
The integral form of the remainder term is
provided, as is often the case, f(n) is absolutely continuous on [a,x]. This shows the theorem to be a generalization of the fundamental theorem of calculus.
For some functions f(x), one can show that the remainder term Rn approaches zero as n approaches ∞; those functions can be expressed as a Taylor series in a neighbourhood of the point a and are called analytic.
Taylor's theorem (with the integral formulation of the remainder term) is also valid if the function f has complex values or vector values. Furthermore, there is a version of Taylor's theorem for functions in several variables.
For complex functions analytic in a region containing a circle C surrounding a and its interior, we have a contour integral expression for the remainder
valid inside of C.
Estimates of the remainder
Another common version of Taylor's theorem holds on an interval (a-r,a+r) where the variable x is assumed to take its values. This formulation of the theorem has the advantage that it is often possible to explicitly control the size of the remainder terms, and thus arrive at an approximation of a function valid in a whole interval with precise bounds on the quality of the approximation.
A precise version of Taylor's theorem in this form is as follows. Suppose f is a function which is n times continuously differentiable on the closed interval [a-r, a+r] and n + 1 times differentiable on the open interval (a-r, a+r). If there exists a positive real constant Mn such that |f(n+1)(x)| ≤ Mn for all x ∈ (a-r,a+r), then
where the remainder function Rn satisfies the inequality (known as Cauchy's estimate):
for all x ∈ (a-r,a+r). This is called a uniform estimate of the error in the Taylor polynomial centered at a, because it holds uniformly for all x in the interval.
If, in addition, f is infinitely differentiable on [a-r,a+r] and
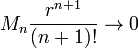 as
as 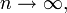
then f is analytic on (a-r,a+r). In other words, an analytic function is the uniform limit of its Taylor polynomials on an interval. This makes precise the idea that analytic functions are those which are equal to their Taylor series.
Taylor's theorem for several variables
Taylor's theorem can be generalized to several variables as follows. Let B be a ball in RN centered at a point a, and f be a real-valued function defined on the closure 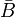 having n+1 continuous partial derivatives at every point. Taylor's theorem asserts that for any
having n+1 continuous partial derivatives at every point. Taylor's theorem asserts that for any 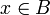 ,
,
where the summation extends over multi-indices α (this formula uses the multi-index notation).
The remainder terms satisfy the inequality
for all α with |α|=n+1. As was the case with one variable, the remainder terms can be described explicitly. See the proof for details.
Proof: Taylor's theorem in one variable
Integral version
We first prove Taylor's theorem with the integral remainder term.
The fundamental theorem of calculus states that
which can be rearranged to:
Now we can see that an application of Integration by parts yields:
(The first equation is arrived at by letting 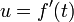 and
and 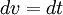 ; the second equation by noting that
; the second equation by noting that 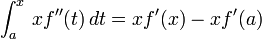 ; the third just factors out some common terms.)
; the third just factors out some common terms.)
Another application yields:
By repeating this process, we may derive Taylor's theorem for higher values of n.
This can be formalized by applying the technique of induction. So, suppose that Taylor's theorem holds for a particular n, that is, suppose that
We can rewrite the integral using integration by parts. An antiderivative of (x − t)n as a function of t is given by −(x−t)n+1 / (n + 1), so
Substituting this in (*) proves Taylor's theorem for n + 1, and hence for all nonnegative integers n.
The remainder term in the Lagrange form can be derived by the mean value theorem in the following way:
The last integral can be solved immediately, which leads to
Mean value theorem
An alternative proof, which holds under milder technical assumptions on the function f, can be supplied using the Cauchy mean value theorem. Let G be a real-valued function continuous on [a,x] and differentiable with non-vanishing derivative on (a,x). Let
By Cauchy's mean value theorem,
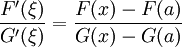 (1)
(1)
for some ξ ∈ (a,x). Note that the numerator F(x) - F(a) = Rn is the remainder of the Taylor polynomial for f(x). On the other hand, computing F′(t),
Putting these two facts together and rearranging the terms of (1) yields
which was to be shown.
Note that the Lagrange form of the remainder comes from taking G(t) = (t-a)n+1, and the given Cauchy form of the remainder comes from taking G(t) = (t-a).
Proof: several variables
Let x=(x1,...,xN) lie in the ball B with centre a. Parametrize the line segment between a and x by u(t)=a+t(x-a). We apply the one-variable version of Taylor's theorem to the function f(u(t)):
By the chain rule for several variables,
where  is the multinomial coefficient for the multi-index α. Since
is the multinomial coefficient for the multi-index α. Since 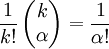 , we get
, we get
The remainder term is given by
The terms of this summation are explicit forms for the Rα in the statement of the theorem. These are easily seen to satisfy the required estimate.

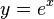 (continuous red line) and the corresponding Taylor polynomial of degree four around the origin (dashed green line).
(continuous red line) and the corresponding Taylor polynomial of degree four around the origin (dashed green line).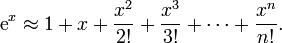
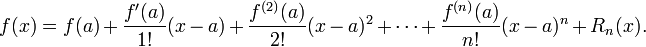
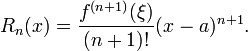
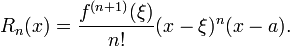
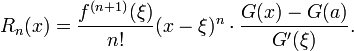
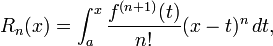
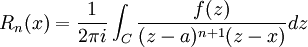
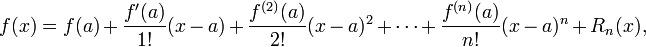
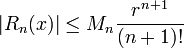
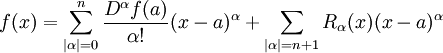
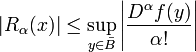
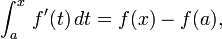
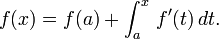
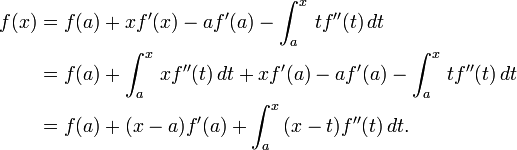
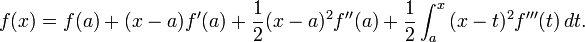
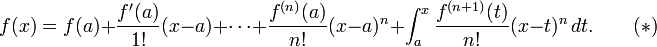
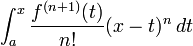
![{} = - \left[ \frac{f^{(n+1)} (t)}{(n+1)n!} (x - t)^{n+1} \right]_a^x + \int_a^x \frac{f^{(n+2)} (t)}{(n+1)n!} (x - t)^{n+1} \, dt](../../images/127/12701.png)