Dutch language
Did you know...
This Schools selection was originally chosen by SOS Children for schools in the developing world without internet access. It is available as a intranet download. A good way to help other children is by sponsoring a child
| Dutch | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flemish Nederlands, Vlaams |
||||
| Pronunciation | [ˈneːdərlɑnts] | |||
| Native to | mainly the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, also in Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten, as well as France ( French Flanders). | |||
| Region | mainly Western Europe, today also in South America and the Caribbean. Afrikaans is spoken in Southern Africa. |
|||
| Native speakers | 23 million (2006) Total: 28 million (not including speakers of closely related Afrikaans) |
|||
| Language family |
Indo-European
|
|||
| Early forms: |
Old Dutch
|
|||
| Writing system | Latin ( Dutch alphabet) Dutch Braille |
|||
| Official status | ||||
| Official language in | ||||
| Regulated by | Nederlandse Taalunie ( Dutch Language Union) |
|||
| Language codes | ||||
| ISO 639-1 | nl | |||
| ISO 639-2 | dut (B) nld (T) |
|||
| ISO 639-3 | Variously: nld – Dutch/ Flemish vls – West Flemish (Vlaams) zea – Zealandic (Zeeuws) lim – Limburgish |
|||
| Linguasphere | 52-ACB-a (varieties: 52-ACB-aa to -an) |
|||
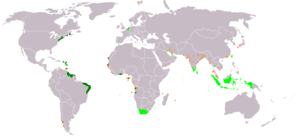
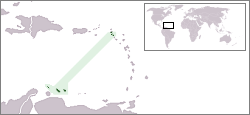
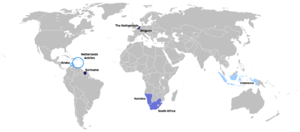 Dutch-speaking world. Dutch is also one of the official languages of the European Union and the Union of South American Nations.
|
||||
|
||||
Dutch (Nederlands) is a West Germanic language and the native language of most of the population of the Netherlands, and about sixty percent of the populations of Belgium and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second language for another 5 million people. It also holds official status in the Caribbean island nations of Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten, while historical minorities remain in parts of France and Germany, and to a lesser extent, in Indonesia, and up to half a million native Dutch speakers may be living in the United States, Canada, and Australia. The Cape Dutch dialects of Southern Africa have been standardised into Afrikaans, a mutually intelligible daughter language of Dutch which today is spoken to some degree by an estimated total of 15 to 23 million people in South Africa and Namibia.
Dutch is closely related to German and English and is said to be between them. Apart from not having undergone the High German consonant shift, Dutch—like English—has mostly abandoned the grammatical case system, is relatively unaffected by the Germanic umlaut, and has levelled much of its morphology. Dutch historically has three grammatical genders, but this distinction has far fewer grammatical consequences than in German. Dutch shares with German the use of subject–verb–object word order in main clauses and subject–object–verb in subordinate clauses. Dutch vocabulary is mostly Germanic and contains the same Germanic core as German and English, while incorporating more Romance loans than German and fewer than English.
Names
While Dutch generally refers to the language as a whole, Belgian varieties are sometimes collectively referred to as Flemish. In both Belgium and Netherlands, the native official name for Dutch is Nederlands, and its dialects have their own name, e.g., Hollands "Hollander", West-Vlaams "West Flemish", Limburgs "Limburger", Brabants "Brabantine".
The language has been known under a variety of names. In Middle Dutch, dietsc (in the South) and diutsc, duutsc (in the North) were used to refer variably to Dutch, Low German, and German. This word is derived from diet "people" and was used to translate Latin (lingua) vulgaris "popular language" to set apart the Germanic vernacular from Latin (the language of writing and the Church) and Romance. An early form of this word appears Latinized in the Strasbourg Oaths (842 a.d.) as teudisca (lingua) to refer to the Rhenish Franconian portion of the oath and also underlies dialectal French thiois " Luxembourgish, Lorraine Franconian".
During the Renaissance in the 16th century, differentiation began to be made by opposing duytsch (modern Duits) "German" and nederduytsch "Low German" with dietsch or nederlandsch "Dutch", a distinction that is echoed in English later the same century with the terms High Dutch "German" and Low Dutch "Dutch". However, owing to Dutch commercial and colonial rivalry in the 16th and 17th centuries, the English term came to refer exclusively to the Dutch. In modern Dutch, Duits has narrowed in meaning to refer to "German", Diets went out of common use because of its Nazi associations and now somewhat romantically refers to older forms of Dutch, whereas Hollands and Vlaams are sometimes used to name the language as a whole for the varieties spoken in respectively The Netherlands and Belgium. Nederlands, the official Dutch word for "Dutch", did not become firmly established until the 19th century. The repeated use of neder- or "low" to refer to the language is a reference to the Netherlands' downriver location at the mouth of the Rhine (harking back to Latin nomenclature, e.g., Germania inferior vs. Germania superior) and the fact that it lies in the lowest dip of the Northern European plain.
Classification
- Indo-European languages
- Germanic
- West Germanic
- Low Franconian
- Dutch
- Afrikaans, Dutch-based creoles
- Dutch
- Low Franconian
- West Germanic
- Germanic
Dutch belongs to its own West Germanic sub-group, West Low Franconian, paired with its sister language Limburgian, or East Low Franconian, both of which stand out by mixing characteristics of Low German and German. Dutch is at one end of a dialect continuum known as the Rhenish fan where German gradually turns into Dutch. There was also at one time a dialect continuum that blurred the boundary between Dutch and Low German. In some small areas, there are still dialect continua, but they are gradually becoming extinct.
All three languages have shifted earlier /θ/ → /d/, show final-obstruent devoicing (Du brood "bread" [bro:t]), and experienced lengthening of short vowels in stressed open syllables which has led to contrastive vowel length that is used as a morphological marker. Dutch stands out from Low German and German in its retention of the clusters sp/st, shifting of sk to [sx] and initial g- to [ɣ], highly simplified morphology, and the fact it did not develop i-mutation as a morphological marker. In earlier periods, Low Franconian of either sort differed from Low German by maintaining a three-way plural verb conjugation ( Old Dutch -un, -it, -unt → Middle Dutch -en, -t, -en). In modern Dutch, however, the former 2nd-person plural (-t) took the place of the 2nd-person singular, and the plural endings were reduced into a single form -en (cf. Du jij maakt "you(sg) make" vs. wij/jullie/zij maken "we/you(pl)/they make"). However, it is still possible to distinguish it from German (which has retained the three-way split) and Low German (which has -t in the present tense: wi/ji/se niemmet "we/you(pl)/they take"). Dutch and Low German show the collapsing of older ol/ul/al + dental into ol + dental, but in Dutch wherever /l/ was pre-consonantal and after a short vowel, it vocalized, e.g., Du goud "gold", zout "salt", woud "woods" : LG Gold, Solt, Woold : Germ Gold, Salz, Wald.
With Low German, Dutch shares the development of /xs/ → /ss/ (Du vossen "foxes", ossen "oxen", LG Vösse, Ossen vs. Germ Füchse, Ochsen), /ft/ → [xt] /cht/ though it is far more common in Dutch (Du zacht "soft", LG sacht vs. Germ sanft, but Du lucht "air" vs. LG/Germ Luft), generalizing the dative over the accusative case for certain pronouns (Du mij "me" (MDu di "you (sg.)"), LG mi/di vs. Germ mich/dich), and neither has undergone German's distinctive second consonant shift. Dutch and Low German have also monophthongized Germanic *ai → ē and *au → ō in all positions, e.g., Du steen "stone", oog "eye", LG Steen, Oog vs. G Stein, Auge, though this is not true of Limburgian (cf. sjtein, oug).
Dutch shares with German the reflexive pronoun zich (Germ sich), though this was originally borrowed from Limburgian, which is why in most dialects ( Flemish, Brabantine) the usual reflexive is hem/haar, just like in the rest of West Germanic. Also, both languages have diphthongized Germanic ē² and long ō (Du hier "here", voet "foot", Germ hier, Fuß (from earlier fuoz) vs. LG hier [iː], Foot "foot" [oː]) and voiced pre-vocalic initial voiceless alveolar fricatives, e.g., Du zeven "seven", Germ sieben [z] vs. LG söven, seven [s]. The German pronoun wir "we" is absent from Dutch, but Limburgian has veer "we" instead of Dutch we (wij).
Geographic distribution
Dutch is an official language of the Netherlands, Belgium, Suriname, Aruba, Curaçao and Sint Maarten. Dutch is also an official language of several international organisations, such as the European Union and the Union of South American Nations. It is used unofficially in the Caribbean Community.
Europe
Netherlands
Dutch is the official and foremost language of the Netherlands, a nation of 16.7 million people of whom 96 percent speak Dutch as their mother tongue. In the province of Friesland and a small part of Groningen, Frisian is also recognised and is spoken by a few hundred thousand Frisians. In the Netherlands there are many different dialects, but these are often overruled and replaced by the language of the media, school, government (i.e., Standard Dutch). Immigrant languages are Indonesian, Turkish, English, Spanish, Berber, Moroccan Arabic, Papiamento, and Sranan. In the second generation these newcomers often speak Dutch as their mother tongue, sometimes alongside the language of their parents.
Belgium
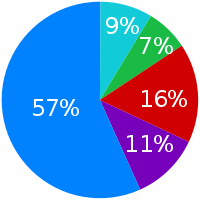
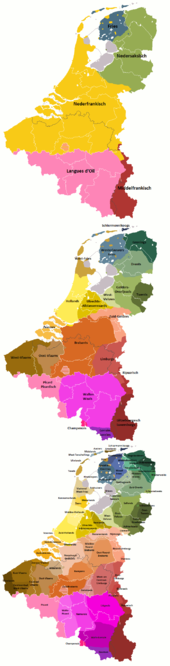
Belgium, a neighbouring nation of 11 million people, has three official languages, which are, in order from the greatest speaker population to the smallest, Dutch (sometimes colloquially referred to as Flemish), French, and German. An estimated 59% of all Belgians speak Dutch as their first language, while French is the mother tongue of 40%. Dutch is the official language of the Flemish Region (where it is the mother tongue of about 97% of the population) and one of the two official languages —along with French— of the Brussels Capital Region. Dutch is not official nor a recognised minority language in the Walloon Region, although on the border with the Flemish Region, there are four municipalities with language facilities for Dutch speakers. The most important Dutch dialects spoken in Belgium are West Flemish (spoken even in France in French Flanders, or Frans Vlaanderen), East Flemish, Brabantian, and Limburgish, the latter having a dialect continuum in northeastern Wallonia (as Low Dietsch).
Brussels
Since the founding of the Kingdom of Belgium in 1830, Brussels has transformed from being almost entirely Dutch-speaking, with a small French minority, to being a multilingual city with French as the majority language and lingua franca. This language shift, the Frenchification of Brussels, is rooted in the 18th century but accelerated after Belgium became independent and Brussels expanded past its original boundaries.
Not only is French-speaking immigration responsible for the frenchification of Brussels, but more importantly the language change over several generations from Dutch to French was performed in Brussels by the Flemish people themselves. The main reason for this was the low social prestige of the Dutch language in Belgium at the time. From 1880 on more and more Dutch-speaking people became bilingual resulting in a rise of monolingual French speakers after 1910. Halfway through the 20th century the number of monolingual French speakers carried the day over the (mostly) bilingual Flemish inhabitants. Only since the 1960s, after the fixation of the Belgian language border and the socio-economic development of Flanders was in full effect, could Dutch stem the tide of increasing French use. This phenomenon is, together with the future of Brussels, one of the most controversial topics in all of Belgian politics.
Today an estimated 16 percent of city residents are native speakers of Dutch, while an additional 13 percent claim to have a "good to excellent" knowledge of Dutch.
France
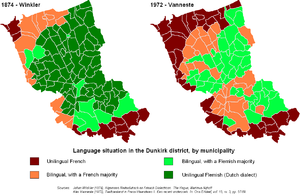
French Flemish, a variant of West Flemish, is spoken in the north-east of France by an estimated population of 20,000 daily speakers and 40,000 occasional speakers. It is spoken alongside French, which is gradually replacing it for all purposes and in all areas of communication. Neither Dutch nor its regional French Flemish variant is afforded legal status in France, either by the central or regional public authorities, by the education system or before the courts. In brief, the state takes no measures to ensure the use of Dutch in France.
In the 9th century the Germanic–Romance language border went from the mouth of the Canche to just north of the city of Lille, where it coincided with the present language border in Belgium. From the late 9th century on, the border gradually started to shift northward and eastward to the detriment of the Germanic language. Boulogne-sur-Mer was bilingual up to the 12th century, Calais up to the 16th century, and Saint-Omer until the 18th century. The western part of the County of Flanders, consisting of the castellanies of Bourbourg, Bergues, Cassel and Bailleul, became part of France between 1659 and 1678. However, the linguistic situation in this formerly monolingually Dutch-speaking region did not dramatically change until the French Revolution in 1789, and Dutch continued to fulfil the main functions of a cultural language throughout the 18th century. During the 19th century, especially in the second half of it, Dutch was banned from all levels of education and lost most of its functions as a cultural language. The cities of Dunkirk, Gravelines and Bourbourg had become predominantly French-speaking by the end of the 19th century. In the countryside, until World War I, many elementary schools continued to teach in Dutch, and the Roman Catholic Church continued to preach and teach the cathechism in Flemish in many parishes. Nonetheless, since French enjoyed a much higher status than Dutch, from about the interbellum onward everybody became bilingual, the generation born after World War II being raised exclusively in French. In the countryside, the passing on of Flemish stopped during the 1930s or 1940s. As a consequence, the vast majority of those still having an active command of Flemish belong to the generation of over the age of 60. Therefore, complete extinction of French Flemish can be expected in the coming decades.
Asia
Despite the Dutch presence in Indonesia for almost three hundred and fifty years, the Dutch language has no official status there and the small minority that can speak the language fluently are either educated members of the oldest generation, or employed in the legal profession, as some legal codes are still only available in Dutch. Many universities include Dutch as a source language, mainly for law and history students (roughly 35,000 of them nationally).
Contrary to other European nations, the Dutch chose to not follow a policy of language expansion amongst the indigenous peoples of their colonies. In the last quarter of the 19th century, however, a local elite gained proficiency in Dutch so as to meet the needs of expanding bureaucracy and business. Nevertheless, the Dutch government remained reluctant to teach Dutch on a large scale out of fear of destabilising the colony. Dutch, the language of power, was supposed to remain in the hands of the leading elite. Instead, use of local languages —or, where this proved to be impractical, of Malay— was encouraged. As a result, less than two percent of Indonesians could speak Dutch in 1940. Only when in 1928 the Indonesian nationalist movement had chosen Malay as a weapon against Dutch influence, the colonial authorities gradually began to introduce Dutch in the educational curriculum. But because of the chaos of the 1942 Japanese invasion and the subsequent Indonesian independence in 1945, this shift in policy did not come into full effect.
After independence, Dutch was dropped as an official language and replaced by Malay. Yet the Indonesian language inherited many words from Dutch, both in words for everyday life, and as well in scientific or technological terminology. One scholar argues that 20% of Indonesian words can be traced back to Dutch words, many of which transliterated to reflect phonetic pronunciation e.g. kantoor (Dutch for "office") in Indonesian is kantor, while bus ("bus") becomes bis.
In addition, many Indonesian words are calques on Dutch, for example, rumah sakit (Indonesian for "hospital") is calqued on the Dutch ziekenhuis (literally "sick house"), kebun binatang ("zoo") on dierentuin (literally "animal garden"), undang-undang dasar ("constitution") from grondwet (literally "basic law"). These account for some of the differences in vocabulary between Indonesian and Malay.
The first spelling system for Indonesian, devised by Charles van Ophuijsen was influenced by Dutch, with the use of Dutch letter combinations such as oe. For example, tempo doeloe (meaning "the past") was pronounced as one vowel like in moeder (Dutch for "mother"). In 1947, this was changed to u, hence tempo dulu. However, the letter combination oe continued to be used in people's names, for example, the spelling of the names of the first and second Presidents, Sukarno and Suharto are often written as Soekarno and Soeharto. In 1972, following an agreement with Malaysia to harmonise the spelling of Indonesian and Malay, other Dutch-influenced letter combinations such as tj and dj were replaced with c and j, hence tjap ("brand" in Indonesian) became cap and Djakarta, the country's capital, became Jakarta.
Dutch-based creole languages spoken (now or formerly) in the Dutch East Indies include Javindo and Petjo, most of whose speakers were Indo or Eurasians. As a result of Indo emigration to the Netherlands following independence, the use of these languages declined.
The century and half of Dutch rule in Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) and southern India left few traces of the Dutch language. A few words such as tapal, kokin and kakhuis are still used in some of the Indian languages.
Oceania
After the declaration of independence of Indonesia, Western New Guinea remained a Dutch colony until 1962, known as Netherlands New Guinea. Despite prolonged Dutch presence, the Dutch language is not spoken by many Papuans, the colony having been ceded to Indonesia in 1963.
Immigrant communities can be found in Australia and New Zealand. The 2006 Australian census showed 36,179 people speaking Dutch at home. At the 2006 New Zealand Census, 26,982 people, or 0.70 percent of the total population, reported to speak Dutch to sufficient fluency that they could hold an everyday conversation.
Americas
In contrast to the colonies in the East Indies, from the second half of the 19th century onwards, the Netherlands envisaged expansion of Dutch in its colonies in the West Indies. Until 1863, when slavery was abolished in the West Indies, slaves were forbidden to speak Dutch. Most important were the efforts of Christianisation through Dutchification, which did not occur in Indonesia owing to a policy of non-involvement in the Islamised regions. Secondly, most of the people in the Colony of Surinam (now Suriname) worked on Dutch plantations, which reinforced the importance of Dutch as a means for direct communication. In Indonesia, the colonial authorities had less interference in economic life. The size of the population was decisive: whereas the Antilles and Surinam combined only had a few hundred thousand inhabitants, Indonesia had many millions, by far outnumbering the population of the Netherlands.
Suriname
In Suriname, where in the second half of the 19th century the Dutch authorities introduced a policy of assimilation, Dutch is the sole official language and over 60 percent of the population speaks it as a mother tongue. A further twenty-four percent of the population speaks Dutch as a second language. Suriname gained its independence from the Netherlands in 1975 and has been an associate member of the Dutch Language Union since 2004. The lingua franca of Suriname, however, is Sranan Tongo, spoken natively by about a fifth of the population.
Caribbean
In Aruba, Curaçao and Sint Maarten, all part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Dutch is the official language but spoken as a first language by only seven to eight percent of the population, although most native-born people on the islands can speak the language since the education system is in Dutch at some or all levels. The lingua franca of Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao is Papiamento, a creole language that originally developed among the slave population. The population of the three northern Antilles, Sint Maarten, Saba, and Sint Eustatius, is predominantly English-speaking.
North America
In New Jersey in the United States, an almost extinct dialect of Dutch, Jersey Dutch, spoken by descendants of 17th century Dutch settlers in Bergen and Passaic counties, was still spoken as late as 1921. Other Dutch-based creole languages once spoken in the Americas include Mohawk Dutch (in Albany, New York), Berbice (in Guyana), Skepi (in Essequibo, Guyana) and Negerhollands (in the United States Virgin Islands). Pennsylvania Dutch is not a member of the set of Dutch dialects and is less misleadingly called Pennsylvania German.
Martin Van Buren, former President of the United States, spoke Dutch as his first language and is the only U.S. President to have spoken a language other than English as his first language. Dutch prevailed for many generations as the dominant language in parts of New York along the Hudson River. Another famous American born in this region who spoke Dutch as a first language was Sojourner Truth.
According to the 2000 United States census, 150,396 people spoke Dutch at home, while according to the 2006 Canadian census, this number reaches 160,000 Dutch speakers. In Canada, Dutch is the fourth most spoken language by farmers, after English, French and German, and the fifth most spoken non-official language overall (by 0.6% of Canadians).
Africa
Belgian Africa
Belgium, which had gained its independence from the Netherlands in 1830, also held a colonial empire from 1901 to 1962, consisting of the Belgian Congo and Ruanda-Urundi. Unlike Belgium itself, the colonies had no de jure official language. Although a majority of Belgians residing in the colonies were Dutch-speaking, French was de facto the sole language used in administration, jurisdiction and secondary education. After World War II, proposals of dividing the colony into a French-speaking and a Dutch-speaking part—after the example of Belgium—were discussed within the Flemish Movement. In general, however, the Flemish Movement was not as strong in the colonies as in the mother country. Although in 1956, on the eve of Congolese independence, an estimated 50,000 out of a total of 80,000 Belgian nationals would have been Flemish, only 1,305 out of 21,370 children were enrolled in Dutch-language education. When the call for a better recognition of Dutch in the colony got louder, the évolués ("developed Congolese")—among them Mobutu Sese Seko—argued that Dutch had no right over the indigenous languages, defending the privileged position of French. Moreover, the image of Afrikaans as the language of the apartheid was injurious to the popularity of Dutch.
The colonial authorities used Lingala, Kongo, Swahili and Tshiluba in communication with the local population and in education. In Ruanda-Urundi this was Kirundi. Knowledge of French—or, to an even lesser extent, Dutch—was hardly passed on to the natives, of whom only a small number were taught French to work in local public services. After their independence, French would become an official language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda and Burundi. Of these, Congo is the most francophone country. Knowledge of Dutch in former Belgian Africa is virtually nonexistent.
Afrikaans
The largest legacy of the Dutch language lies in South Africa, which attracted large numbers of Dutch, Flemish and other northwest European farmer (in Dutch, boer) settlers, all of whom were quickly assimilated. After the colony passed into British hands in the early 19th century, the settlers spread into the hinterland, taking their language with them. The subsequent isolation from the rest of the Dutch-speaking world made the Dutch as spoken in Southern Africa evolve into what is now Afrikaans. European Dutch remained the literary language until the early 20th century, when under pressure of Afrikaner nationalism the local "African" Dutch was preferred over the written, European-based standard. In 1925, section 137 of the 1909 constitution of the Union of South Africa was amended by Act 8 of 1925, stating "the word Dutch in article 137 [...] is hereby declared to include Afrikaans". The new constitution of 1961 only listed English and Afrikaans as official languages. It is estimated that between 90% to 95% of Afrikaans vocabulary is ultimately of Dutch origin. Both languages are still largely mutually intelligible, although this relation can in some fields (such as lexicon, spelling and grammar) be asymmetric, as it is easier for Dutch speakers to understand written Afrikaans than it is for Afrikaans speakers to understand written Dutch. Afrikaans is grammatically far less complex than Dutch, and vocabulary items are generally altered in a clearly patterned manner, e.g. vogel becomes voël "bird" and regen becomes reën "rain").
It is the third language of South Africa in terms of native speakers (~13.5%), of whom 53 percent are Coloureds and 42.4 percent Whites. In 1996, 40 percent of South Africans reported to know Afrikaans at least at a very basic level of communication. It is the lingua franca in Namibia, where it is spoken natively in 11 percent of households. In total, Afrikaans is the first language in South Africa alone of about 6.8 million people and is estimated to be a second language for at least 10 million people worldwide, compared to over 23 million and 5 million respectively, for Dutch.
History
The history of the Dutch language begins around AD 450–500 after Old Frankish, one of the many West Germanic tribal languages, was split by the Second Germanic consonant shift. At more or less the same time the Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law led to the development of the direct ancestors of modern Dutch Low Saxon, Frisian and English. The northern dialects of Old Frankish generally did not participate in either of these two shifts, except for a small amount of phonetic changes, and are hence known as Old Low Franconian; the "Low" refers to dialects not influenced by the consonant shift. The most south-eastern dialects of the Franconian languages became part of High—though not Upper— German even though a dialect continuum remained. The fact that Dutch did not undergo the sound changes may be the reason why some people say that Dutch is like a bridge between English and German. Within Old Low Franconian there were two subgroups: Old East Low Franconian and Old West Low Franconian, which is better known as Old Dutch. East Low Franconian was eventually absorbed by Dutch as it became the dominant form of Low Franconian, although it remains a noticeable substrate within the southern Limburgish dialects of Dutch. As the two groups were so similar, it is often difficult to determine whether a text is Old Dutch or Old East Low Franconian; hence most linguists will generally use Old Dutch synonymously with Old Low Franconian and mostly do not differentiate.
Dutch, like other Germanic languages, is conventionally divided into three development phases which were:
- 450(500)–1150 Old Dutch (First attested in the Salic Law)
- 1150–1500 Middle Dutch (Also called " Diets" in popular use, though not by linguists)
- 1500–present Modern Dutch (Saw the creation of the Dutch standard language and includes contemporary Dutch)
The transition between these languages was very gradual and one of the few moments linguists can detect somewhat of a revolution is when the Dutch standard language emerged and quickly established itself. Standard Dutch is very similar to most Dutch dialects.
The development of the Dutch language is illustrated by the following sentence in Old, Middle and Modern Dutch:
- "Irlôsin sol an frithe sêla mîna fan thên thia ginâcont mi, wanda under managon he was mit mi" (Old Dutch)
- "Erlossen sal [hi] in vrede siele mine van dien die genaken mi, want onder menegen hi was met mi" (Middle Dutch)
(Using same word order)
- "Verlossen zal hij in vrede ziel mijn van degenen die [te] na komen mij, want onder menigeen hij was met mij" (Modern Dutch)
- "Hi sal mijn ziele in vrede verlossen van die gene die mi ghenaken, want si waren onder veel teghen mi." (Vorstermansbijbel, 1528/1531)
(Using correct contemporary Dutch word order)
- "Hij zal mijn ziel in vrede verlossen van degenen die mij te na komen, want onder menigeen was hij met mij" (Modern Dutch) (see Psalm 55:19)
- "He shall my soul in peace free from those who me too near come, because amongst many was he with me" (English literal translation in the same word order)
- "He will deliver my soul in peace from those who attack me, because, amongst many, he was with me" (English translation in unmarked word order) (see Psalm 55:18)
A process of standardisation started in the Middle Ages, especially under the influence of the Burgundian Ducal Court in Dijon (Brussels after 1477). The dialects of Flanders and Brabant were the most influential around this time. The process of standardisation became much stronger at the start of the 16th century, mainly based on the urban dialect of Antwerp. In 1585 Antwerp fell to the Spanish army: many fled to the Northern Netherlands, especially the province of Holland, where they influenced the urban dialects of that province. In 1637, a further important step was made towards a unified language, when the Statenvertaling, the first major Bible translation into Dutch, was created that people from all over the United Provinces could understand. It used elements from various, even Dutch Low Saxon, dialects but was predominantly based on the urban dialects of Holland.
Dialects
Dutch dialects are remarkably diverse.
Sounds
Dutch devoices all obstruents at the ends of words (e.g. a final /d/ becomes [t]), which presents a problem for Dutch speakers when learning English. This is partly reflected in the spelling: the singular of huizen (houses) becomes huis, and that of duiven (doves) becomes duif. The other cases, viz. "p"/"b" and "d"/"t" are always written with the letter for the voiced consonant, although a devoiced one is actually pronounced, e.g. sg. baard (beard), pronounced as baart, has plural baarden and sg. rib (rib), pronounced as rip has plural ribben.
Because of assimilation, often the initial consonant of the next word is also devoiced, e.g. het vee (the cattle) is /(h)ətfe/. This process of devoicing is taken to an extreme in some regions (Amsterdam, Friesland) with almost complete loss of /v/, /z/ and /ɣ/. These phonemes are certainly present in the middle of a word. Compare standard Dutch pronunciation logen and loochen /loɣən/ vs. /loxən/. In the dialects the contrast is even greater: /loʝən/ vs. /loçən/.
The final n of the plural ending -en is often not pronounced (as in Afrikaans where it is also dropped in the written language), except in the northeast Netherlands where dialects of Low German are traditionally spoken.
Vowels
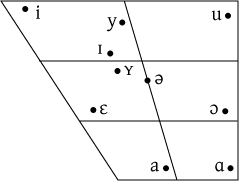
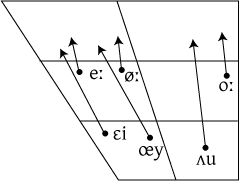
The vowel inventory of Dutch is large, with 13 simple vowels and four diphthongs. The vowels /eː/, /øː/, /oː/ are included on the diphthong chart because they are actually produced as narrow closing diphthongs in many dialects, but behave phonologically like the other simple vowels. [ɐ] (a near-open central vowel) is an allophone of unstressed /a/ and /ɑ/.
| IPA chart of Netherlandic Dutch monophthongs |
|---|
 |
| IPA chart of Netherlandic Dutch diphthongs |
 |
| Symbol | Example | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | IPA | orthography | English translation |
| ɪ | kɪp | kip | 'chicken' |
| i | bit | biet | 'beetroot' |
| ʏ | ɦʏt | hut | 'cabin' |
| y | fyt | fuut | 'grebe' |
| ɛ | bɛt | bed | 'bed' |
| eː | beːt | beet | 'bite' |
| ə | də | de | 'the' |
| øː | nøːs | neus | 'nose' |
| ɑ | bɑt | bad | 'bath' |
| aː | zaːt | zaad | 'seed' |
| ɔ | bɔt | bot | 'bone' |
| oː | boːt | boot | 'boat' |
| u | ɦut | hoed | 'hat' |
| ɛi | ɛi, ʋɛin | ei, wijn | 'egg', 'wine' |
| œy | œy | ui | 'onion' |
| ʌu | zʌut, fʌun | zout, faun | 'salt', 'faun' |
Some vowels are pronounced differently when followed by 'r', but this is not normally reflected in the IPA rendering, since they are allophones. The vowel in beer, being different from both bet and beet, is usually represented by /eː/. Similarly the one in boor, is neither like bot nor boot, and represented by /oː/.
Consonants
The syllable structure of Dutch is (C)(C)(C)V(C)(C)(C)(C). Many words, as in English, begin with three consonants; for example, straat (street). There are words that end in four consonants, e.g., herfst 'autumn', ergst 'worst', interessantst 'most interesting', sterkst 'strongest', the last three of which are superlative adjectives.
The highest number of consonants in a single cluster is found in the word slechtstschrijvend 'writing worst' with 7 consonant phonemes (though in normal speech the number of phonemes is usually reduced to 6 because of assimilation of 'tstsch' to 'stsch', or even to 5 by many speakers who pronounce the cluster 'schr' as 'sr').
Like most Germanic languages, the Dutch consonant system did not undergo the High German consonant shift and has a syllable structure that allows fairly complex consonant clusters. Dutch is often noted for its prominent use of velar fricatives.
| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | ||||||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | k | (ʔ)1 | ||||
| voiced | b | d | ɡ 2 | ||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | s | ʃ 3 | ç 4 | x ~ χ 4 | |||
| voiced | v 5 | z 5 | ʒ 3 | ʝ 5 | ɣ 5 | ʁ 6 | ɦ 5 | ||
| Trill | r 6 | ||||||||
| Approximant | β ~ ʋ 7 | l 8 | j | ||||||
Notes:
- ^1 [ʔ] is not a separate phoneme in Dutch, but is inserted before vowel-initial syllables within words after /a/ and /ə/ and often also at the beginning of a word.
- ^2 /ɡ/ is not a native phoneme of Dutch and only occurs in borrowed words, like goal or when /k/ is voiced, like in zakdoek [zɑɡduk].
- ^3 /ʃ/ and /ʒ/ are not native phonemes of Dutch, and usually occur in borrowed words, like show and bagage ('baggage'). However, /s/ + /j/ phoneme sequences in Dutch are often realized as [ʃ], like in the word huisje ('little house').
- ^4 The sound spelled
is a uvular fricative in Standard Dutch and velar in Belgian dialects. - ^5 In some dialects, the voiced fricatives have almost completely merged with the voiceless ones; /ɦ/ is usually realized as [h], in the North /v/ is usually realized as [f], /z/ is usually realized as [s], yet only in the North. In the South /v/ is pronounced [v] and /z/ is [z]. In the North /ɣ/ is usually realized as [x], whereas in the South the distinction between /ʝ/ and /ç/ has been preserved.
- ^6 The realization of the /r/ phoneme varies considerably from dialect to dialect. In "standard" Dutch, /r/ is realized as the alveolar trill [r], but the uvular trill [ʀ] is a common alternative. In some dialects it is realized as the alveolar tap [ɾ], the voiced uvular fricative [ʁ], or as the alveolar approximant [ɹ]. The alveolar approximant is used especially at the end of a word.
- ^7 The realization of the /ʋ/ varies considerably from the Northern to the Southern and Belgium dialects of the Dutch language. A number of Belgian dialects pronounce it like a bilabial approximant ([β]). Other, mainly Northern Dutch, dialects pronounce it as a labiodental approximant: [ʋ]. Furthermore, in Suriname it is pronounced [w].
- ^8 The lateral /l/ is slightly velarized postvocalically.
| Symbol | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | IPA | orthography | English translation | |
| p | pɛn | pen | 'pen' | |
| b | bit | biet | 'beetroot' | |
| t | tɑk | tak | 'branch' | |
| d | dɑk | dak | 'roof' | |
| k | kɑt | kat | 'cat' | |
| ɡ | ɡoːl | goal | 'goal' (sports) | |
| m | mɛns | mens | 'human being' or 'mankind' | |
| n | nɛk | nek | 'neck' | |
| ŋ | ɛŋ | eng | 'scary' | |
| f | fits | fiets | 'bicycle' | |
| v | oːvən | oven | 'oven' | |
| s | sɔk | sok | 'sock' | |
| z | zeːp | zeep | 'soap' | |
| ʃ | ʃaːɫ | sjaal | 'shawl' | |
| ʒ | ʒyːri | jury | 'jury' | |
| x (North) | ɑxt | acht | 'eight' | |
| ç (South) | ɑçt | acht | 'eight' | |
| ɣ (North) | ɣaːn | gaan | 'to go' | |
| ʝ (South) | ʝaːn | gaan | 'to go' | |
| r | rɑt | rat | 'rat' | |
| ɦ | ɦut | hoed | 'hat' | |
| ʋ | ʋɑŋ | wang | 'cheek' | |
| j | jɑs | jas | 'coat' | |
| l | lɑnt | land | 'land / country' | |
| ɫ | ɦeːɫ | heel | 'whole' | |
| ʔ | bəʔaːmən | beamen | 'to confirm' | |
Common difficulties
Some Dutch vowel sounds are not straightforward. Diphthongs such as the
The morphological flexibility and cohesiveness of Dutch sometimes produces words that might baffle speakers of other languages owing to the large number of consonant clusters, such as the word angstschreeuw [ɑŋstsxreːw] "scream in fear", which has a total of six in a row -ngstschr- (the ng and ch being digraphs). It has to be noted though that the pronunciation of a word can differ greatly from its written form. In this case, angstschreeuw actually contains 6 consonant sounds (ng-s-t-s-ch-r) originating from two distinct compounded words (angst and schreeuw), which is reduced further by some speakers in connected speech by blending consecutive consonants (ch and r) into one sound. This can be even further shortened to [ɑŋsreːw] by those who normally reduce the schr-sequence to sr.
Historical sound changes
Dutch (with the exception of the Limburg dialects) did not undergo the second or High German consonant shift—compare German machen /-x-/ vs. Dutch maken, English make; German Pfanne /pf-/ vs. Dutch pan, English pan; German zwei /ts-/ vs. Dutch twee, English two.
Dutch underwent a few changes of its own. For example, words in -old/olt lost the /l/ to a diphthong after l-vocalization (compare English old, German alt vs. Dutch oud), and -ks- sounds were reduced to -s- (compare English fox, German Fuchs vs. Dutch vos).
Germanic */uː/ fronted to /yː/, which in turn became a diphthong /œy/, spelt 〈ui〉. Long */iː/ also diphthongized to /ɛi/, spelt 〈ij〉.
The phoneme /ɡ/, originally in allophonic variation with /ɣ/, became /ɣ/ in every position except after /n/ (where it instead merged with /n/ into /ŋ/). It later palatalised to /ʝ/ in the South (Flanders, Limburg, Brabant). A similar development took place in the neighbouring Western dialects of German, where the palatisation has gone so far as to merge /ɡ/ with /j/ (also heard in Kerkrade).
Polder Dutch
A notable deviation from the official pronunciation of Standard Dutch in younger generations in the Netherlands has been dubbed "Polder Dutch" by Jan Stroop. The diphthongs spelt
This change is interesting from a sociolinguistic point of view because it has apparently happened relatively recently, in the 1970s, and was pioneered by older well-educated women from the upper middle classes. The lowering of the diphthongs has long been current in many Dutch dialects, and is comparable to the English Great Vowel Shift, and the diphthongisation of long high vowels in Modern High German, which centuries earlier reached the state now found in Polder Dutch. Stroop theorizes that the lowering of open-mid to open diphthongs is a phonetically "natural" and inevitable development and that Dutch, after having diphthongised the long high vowels like German and English, "should" have lowered the diphthongs like German and English as well. Instead, he argues, this development has been artificially frozen in an "intermediate" state by the standardisation of Dutch pronunciation in the 16th century, where lowered diphthongs found in rural dialects were perceived as ugly by the educated classes and accordingly declared substandard. Now, however, in his opinion, the newly affluent and independent women can afford to let that natural development take place in their speech. Stroop compares the role of Polder Dutch with the urban variety of British English pronunciation called Estuary English.
Among Belgian Dutch speakers, this vowel shift is not taking place, as the diphthongs /ɛi/, /ɔu/ and /œy/ are often pronounced as the monophthongs /ɛː/, /ɔː/ and /œː/.
Grammar
Dutch is grammatically similar to German, such as in syntax and verb morphology (for a comparison of verb morphology in English, Dutch and German, see Germanic weak verb and Germanic strong verb). Dutch has grammatical cases, but these are now mostly limited to pronouns and a large number of set phrases. Inflected forms of the articles are also often found in surnames and toponyms. Originally, Dutch had three genders: masculine, feminine and neuter, although for many speakers, masculine and feminine have merged to form the common gender (de), while the neuter (het) remains distinct as before. This gender system is similar to those of most Continental Scandinavian languages. Many Belgian speakers still make a clear distinction between masculine and feminine words (see Gender in Dutch). As in English, but to a lesser degree, the inflectional grammar of the language (e.g., adjective and noun endings) has simplified over time.
Genders and cases
The table of definite articles below demonstrates that contemporary Dutch is less complex than German. The article has just two forms, de and het, more complex than English, which has only "the". The use of the older inflected form den in the dative or accusative as well as use of 'der' in the dative are restricted to numerous set phrases, surnames and toponyms.
| Dutch | German | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masculine singular | Feminine singular | Neuter singular | Plural (any gender) | Masculine singular | Feminine singular | Neuter singular | Plural (any gender) | |
| Nominative | de [də] | de | het [ɦət] | de | der | die | das | die |
| Genitive | (des) / van de | (der) / van de | (des) / van het | (der) / van de | des | der | des | der |
| Dative | de | de | het | de | dem | der | dem | den |
| Accusative | de | de | het | de | den | die | das | die |
In modern Dutch, the genitive articles 'des' and 'der' are only commonly used in idioms. Other usage is typically considered archaic or poetic. In most circumstances, the preposition 'van' is instead used, followed by the normal definitive article 'de' or 'het'. For the idiomatic use of the articles in the genitive, see for example:
- Masculine singular: "des duivels" (litt: of the devil) (common proverbial meaning: Seething with rage)
- Feminine singular: het woordenboek der Friese taal (the dictionary of the Frisian language)
- Neuter singular: de vrouw des huizes (the lady of the house)
- Plural: de voortgang der werken (the progress of (public) works)
In contemporary usage, the genitive case still occurs a little more often with plurals than with singulars, as the plural article is 'der' for all genders and no special noun inflection must be taken account of. 'Der' is commonly used in order to avoid reduplication of 'van', e.g. het merendeel der gedichten van de auteur instead of het merendeel van de gedichten van de auteur ("the bulk of the author's poems").
There are also genitive forms for the pronoun die/dat ("that [one], those [ones]"), namely diens for masculine and neuter singulars and dier for feminine singular and all plurals. Although usually avoided in common speech, these forms can be used instead of possessive pronouns to avoid confusion. Compare:
- Hij vertelde van zijn zoon en zijn vrouw. – He told about his son and his (own) wife.
- Hij vertelde van zijn zoon en diens vrouw. – He told about his son and the latter's wife.
Analogically, the relative and interrogative pronoun wie ("who") has the genitive forms wiens and wier (corresponding to English "whose", but less frequent in use).
Dutch also has a range of fixed expressions that make use of the genitive articles, which can be abbreviated using apostrophes. Common examples include "'s ochtends" (with 's as abbreviation of des; in the morning) and "desnoods" (lit: of the need, translated: if necessary).
The Dutch written grammar has simplified over the past 100 years: cases are now mainly used for the pronouns, such as ik (I), mij, me (me), mijn (my), wie (who), wiens (whose: masculine or neuter singular), wier (whose: feminine singular, masculine or feminine plural). Nouns and adjectives are not case inflected (except for the genitive of proper nouns (names): -s, -'s or -'). In the spoken language cases and case inflections had already gradually disappeared from a much earlier date on (probably the 15th century) as in many continental West Germanic dialects.
Inflection of adjectives is more complicated. The adjective receives no ending with indefinite neuter nouns in singular (as with een /ən/ 'a/an'), and -e in all other cases. (This was also the case in Middle English, as in "a goode man".) Note that fiets belongs to the masculine/feminine category, and that water and huis are neuter. Water has no plural form.
| Masculine singular or feminine singular | Neuter singular | Plural (any gender) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definite (with definite article or pronoun) |
de mooie fiets (the beautiful bicycle) | het mooie huis (the beautiful house) |
de mooie fietsen (the beautiful bicycles) de mooie huizen (the beautiful houses) |
| Indefinite (with indefinite article or no article and no pronoun) |
een mooie fiets (a beautiful bicycle) koude soep (cold soup) |
een mooi huis (a beautiful house) koud water (cold water) |
mooie fietsen (beautiful bicycles) mooie huizen (beautiful houses) |
An adjective has no e if it is in the predicative: De soep is koud.
More complex inflection is still found in certain lexicalized expressions like de heer des huizes (literally, the man of the house), etc. These are usually remnants of cases (in this instance, the genitive case which is still used in German, cf. Der Herr des Hauses) and other inflections no longer in general use today. In such lexicalized expressions remnants of strong and weak nouns can be found too, e.g. in het jaar des Heren (Anno Domini), where “-en” is actually the genitive ending of the weak noun. Also in this case, German retains this feature.
Word order
Dutch exhibits subject–object–verb word order, but in main clauses the conjugated verb is moved into the second position in what is known as verb second or V2 word order. This makes Dutch word order almost identical to that of German, but often different from English, which has subject–verb–object word order and has since lost the V2 word order that existed in Old English.
An example sentence used in some Dutch language courses and textbooks is "Ik kan mijn pen niet vinden omdat het veel te donker is", which translates into English word for word as "I can my pen not find because it far too dark is", but in standard English word order would be written "I cannot find my pen because it is far too dark". If the sentence is split into a main and subclause and the verbs highlighted, the logic behind the word order can be seen.
Main clause: "Ik kan mijn pen niet vinden "
Verbs are placed in the final position, but the conjugated verb, in this case "kan" (can), is made the second element of the clause.
Subclause: "omdat het veel te donker is "
The verb or verbs always go in the final position.
Diminutives
Dutch nouns can take endings for size: -je for singular diminutive and -jes for plural diminutive. Between these suffixes and the radical can come extra letters depending on the ending of the word:
- boom (tree) – boompje
- ring (ring) – ringetje
- koning (king) – koninkje
- tien (ten) – tientje (a ten euro note)
These diminutives are very common. As in German, all diminutives are neuter. In the case of words like "het meisje" (the girl), this is different from the natural gender. A diminutive ending can also be appended to an adverb or adjective (but not when followed by a noun).
- klein (little, small) – een kleintje (a small one)
Compounds
Like most Germanic languages, Dutch forms noun compounds, where the first noun modifies the category given by the second (hondenhok = doghouse). Unlike English, where newer compounds or combinations of longer nouns are often written in open form with separating spaces, Dutch (like the other Germanic languages) either uses the closed form without spaces (boomhuis = tree house) or inserts a hyphen (VVD-coryfee = outstanding member of the VVD, a political party). Like German, Dutch allows arbitrarily long compounds, but the longer they get, the less frequent they tend to be. The longest serious entry in the Van Dale dictionary is wapenstilstandsonderhandeling (ceasefire negotiation). Leafing through the articles of association (Statuten) one may come across a 30-letter vertegenwoordigingsbevoegdheid (authorisation of representation). An even longer word cropping up in official documents is ziektekostenverzekeringsmaatschappij (health insurance company) though the shorter ziektekostenverzekeraar (health insurer) is more common.
Notwithstanding official spelling rules, some Dutch people nowadays tend to write the parts of a compound separately, a practice sometimes dubbed de Engelse ziekte (the English disease).
Vocabulary
Dutch vocabulary is predominantly Germanic in origin, considerably more so than English. This difference is mainly due to the heavy influence of Norman on English, and to Dutch patterns of word formation, such as the tendency to form long and sometimes very complicated compound nouns, being more similar to those of German and the Scandinavian languages. The Dutch vocabulary is one of the richest in the world and comprises at least 268,826 headwords. In addition, the Woordenboek der Nederlandsche Taal (English: "The Dictionary of the Dutch language") is the largest dictionary in the world in print and has over 430,000 entries of Dutch words.
Like English, Dutch includes words of Greek and Latin origin. French has also contributed a large number of words, most of which have entered into Dutch vocabulary via the Netherlands and not via Belgium, in spite of the cultural and economic dominance exerted by French speakers in Belgium until the first half of the 20th century. This happened because the status French enjoyed as the language of refinement and high culture inspired the affluent upper and upper-middle classes in the Netherlands to adopt many French terms into the language. In Belgium no such phenomenon occurred, since members of the upper and upper-middle classes would have spoken French rather than Frenchify their Dutch. French terms heavily influenced Dutch dialects in Flanders, but Belgian speakers did (and do) tend to resist French loanwords when using standard Dutch. Nonetheless some French loanwords of relatively recent date have become accepted in standard Dutch, also in Belgium, albeit with a shift in meaning and not as straight synonyms for existing Dutch words. For example, "blesseren" (from French blesser, to injure) is almost exclusively used to refer to sports injuries, while in other contexts the standard Dutch verbs "kwetsen" and "verwonden" continue to be used.
Especially on the streets and in many professions, there is a steady increase of English loanwords, rather often pronounced or applied in a different way (see Dutch pseudo-anglicisms). The influx of English words is maintained by the dominance of English in the mass media and on the Internet.
The most important dictionary of the modern Dutch language is the Van Dale groot woordenboek der Nederlandse taal, more commonly referred to as the Dikke van Dale ("dik" means "thick"). However, it is dwarfed by the 45,000-page Woordenboek der Nederlandsche Taal, a scholarly endeavour that took 147 years from initial idea to first edition.
Writing system
Dutch is written using the Latin script. Dutch uses one additional character beyond the standard alphabet, the digraph IJ. It has a relatively high proportion of doubled letters, both vowels and consonants, due to the formation of compound words and also to the spelling devices for distinguishing the many vowel sounds in the Dutch language. An example of five consecutive doubled letters is the word voorraaddoos (supply box).
The diaeresis (Dutch: trema) is used to mark vowels that are pronounced separately. In the most recent spelling reform, a hyphen has replaced the diaeresis in compound words (i.e., if the vowels originate from separate words, not from prefixes or suffixes), e.g. zeeëend (seaduck) is now spelled zee-eend.
The acute accent occurs mainly on loanwords like café, but can also be used for emphasis or to differentiate between two forms. Its most common use is to differentiate between the indefinite article 'een' (a, an) and the numeral 'één' (one); also 'hé' (hey, also written 'hee').
The grave accent is used to clarify pronunciation ('hè' [what?, what the ...?, tag question 'eh?'], 'bèta') and in loanwords ('caissière' [female cashier], 'après-ski'). In the recent spelling reform, the accent grave was dropped as stress sign on short vowels in favour of the acute accent (e.g. 'wèl' was changed to 'wél').
Other diacritical marks such as the circumflex only occur on a few words, most of them loanwords from French. The characters 'Ç', 'ç', 'Ñ' or 'ñ' can also be found in the dutch language but the words which contain one of these characters are loanwords too and these words are inherited from Spain and Portugal. They don't occur very often.
The official spelling is set by the Wet schrijfwijze Nederlandsche taal (Law on the writing of the Dutch language; Belgium 1946, Netherlands 1947; based on a 1944 spelling revision; both amended in the 1990s after a 1995 spelling revision). The Woordenlijst Nederlandse taal, more commonly known as "het groene boekje" (i.e. "the green booklet", because of its colour), is usually accepted as an informal explanation of the law. However, the official 2005 spelling revision, which reversed some of the 1995 changes and made new ones, has been welcomed with a distinct lack of enthusiasm in both the Netherlands and Belgium. As a result, the Genootschap Onze Taal (Our Language Society) decided to publish an alternative list, "het witte boekje" ("the white booklet"), which tries to simplify some complicated rules and offers several possible spellings for many contested words. This alternative orthography is followed by a number of major Dutch media organisations but mostly ignored in Belgium.
Dutch as a foreign language
As a foreign language, Dutch is mainly taught in primary and secondary schools in areas adjacent to the Netherlands and Flanders. In French-speaking Belgium, over 300,000 pupils are enrolled in Dutch courses, followed by over 20,000 in the German states of Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia, and over 7,000 in the French region of Nord-Pas de Calais (of which 4,550 are in primary school). Dutch is the obligatory medium of instruction in schools in Suriname, even for non-native speakers. Dutch is taught in various educational centres in Indonesia, the most important of which is the Erasmus Language Centre (ETC) in Jakarta. Each year, some 1,500 to 2,000 students take Dutch courses there. In total, several thousand Indonesians study Dutch as a foreign language.
At an academic level, Dutch is taught in over 225 universities in more than 40 countries. About 10,000 students worldwide study Dutch at university. The largest number of faculties of neerlandistiek can be found in Germany (30 universities), followed by France and the United States (20 each). Five universities in the United Kingdom offer the study of Dutch. Owing to centuries of Dutch rule in Indonesia, many old documents are written in Dutch. Many universities therefore include Dutch as a source language, mainly for law and history students. In Indonesia this involves about 35,000 students. In South Africa, the number is difficult to estimate, since the academic study of Afrikaans inevitably includes the study of Dutch. Elsewhere in the world, the number of people learning Dutch is relatively small.