British Airways
About this schools Wikipedia selection
SOS Children volunteers helped choose articles and made other curriculum material SOS Children works in 45 African countries; can you help a child in Africa?
| |
||||
|
||||
| Founded | 31 March 1974 (after BOAC & BEA merger) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOC # | 441 | |||
| Hubs |
|
|||
| Frequent-flyer program |
|
|||
| Airport lounge |
|
|||
| Alliance | Oneworld | |||
| Subsidiaries |
|
|||
| Fleet size | 256 | |||
| Destinations | 169 not incl. subsidiaries and code-shares | |||
| Company slogan |
|
|||
| Parent company | International Airlines Group | |||
| Headquarters | Waterside, Harmondsworth, England | |||
| Key people |
|
|||
| Revenue | ||||
| Website | www.britishairways.com | |||
British Airways (BA) is the flag carrier airline of the United Kingdom, based in Waterside, near its main hub at London Heathrow Airport. It is the largest airline in the UK based on fleet size, international flights and international destinations and second largest measured by passengers carried, behind easyJet.
The British Airways Board was established in 1971 to control the two nationalised airline corporations, BOAC and BEA, and two smaller, regional airlines, Cambrian Airways, from Cardiff, and Northeast Airlines, from Newcastle upon Tyne. On 31 March 1974, all four companies were merged to form British Airways. After almost 13 years as a state company, that was sold in February 1987 as part of a privatisation plan by the Conservative Government. The carrier soon expanded with the acquisition of British Caledonian in 1987 and Dan-Air, Gatwick-based carrier, in 1992.
A long-time Boeing customer, British Airways ordered 59 Airbus A320 family aircraft in August 1998. In 2007, it purchased 12 Airbus A380s and 24 Boeing 787 Dreamliners, marking the start of its long-haul fleet replacement. The centrepiece of the airline's long-haul fleet is the Boeing 747-400; with 52 examples in service, British Airways is the largest operator of this type in the world.
British Airways is a founding member of the Oneworld airline alliance, along with American Airlines, Cathay Pacific, Qantas, and the now defunct Canadian Airlines. The alliance has since grown to become the third largest, after SkyTeam and Star Alliance. British Airways' parent company, International Airlines Group, is listed on the London Stock Exchange and in the FTSE 100 Index.
On 12 November 2009, British Airways confirmed that it had reached a preliminary agreement to merge with Iberia. On 14 July 2010, the European Commission approved the merger under competition law, also allowing American Airlines to co-operate with the merged entity on transatlantic routes to the United States. The merger was completed on 21 January 2011, formally creating the International Airlines Group, IAG, the world's third-largest airline in terms of annual revenue and the second largest airline group in Europe. In 2012, IAG purchased British Midland International (BMI) and announced plans to open a new subsidiary based at London City Airport operating Airbus A318s.
British Airways was the airline partner of the London 2012 Olympic Games. On 18 May 2012 it flew the Olympic flame from Athens International Airport to RNAS Culdrose while carrying various dignitaries including Lord Sebastian Coe, Princess Anne, Olympics minister Hugh Robertson and London Mayor Boris Johnson, together with footballer David Beckham.
History

British Airways (BA) was created in 1974, when the British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) and British European Airways Corporation (BEA) were combined under the newly formed British Airways Board. Following two years of fierce competition with British Caledonian, the second-largest airline in Britain at the time, the Government changed its aviation policy in 1976 so the two carriers no longer would compete on long-haul routes.
British Airways and Air France operated the supersonic airliner Aerospatiale-BAC Concorde; the world's first supersonic passenger service first flew in January 1976 from London Heathrow to Bahrain. Services to the US were inaugurated to Washington Dulles airport on 24 May 1976; flights to New York JFK airport started on 22 September 1977. A service to Singapore was also operated in co-operation with Singapore Airlines, as a continuation of the flight to Bahrain. Following the Air France Concorde crash in Paris and a slump in air travel following the 11 September attacks in New York in 2001, it was decided to cease Concorde operations in 2003, after 27 years of service. The final commercial Concorde flight was BA002 from New York JFK to London Heathrow on 24 October 2003.
In 1981, the airline was instructed to prepare for privatisation by the Conservative government. Sir John King, later Lord King, was appointed Chairman, charged with bringing the airline back into profitability. King was credited with transforming the loss-making giant into one of the most profitable air carriers in the world, while many other large airlines struggled. The flag carrier was privatised and was floated on the London Stock Exchange in February 1987. In July 1987, British Airways effected the takeover of Britain's "second" airline, British Caledonian.
The formation of Richard Branson's Virgin Atlantic Airways in 1984 created a strong competitor for BA. In 1993, the intense rivalry between British Airways and Virgin Atlantic culminated in the former being sued for £610,000 for a "dirty tricks" campaign against Virgin and around £3 million in Virgin's legal costs. British Airways' campaign against Virgin included poaching Virgin Atlantic customers and tampering with private files belonging to Virgin. Following a court case, British Airways was forced to pay Virgin damages and legal costs causing BA management to apologise "unreservedly" for the alleged "dirty tricks" campaign. Six months after the "dirty tricks" campaign, Lord King stepped down as chairman in 1993 and was replaced by former deputy, Colin Marshall, while Robert Ayling took over as CEO.

In 1992, British Airways expanded through the acquisition of the financially troubled Dan-Air, giving BA a much larger presence at Gatwick airport. In March 1993, British Asia Airways, a subsidiary based in Taiwan, was formed to operate between London and Taipei. Additionally in 1993, BA purchased a 25% stake in Australian airline Qantas in March, and acquired Brymon Airways in May to form BA Connect. In September 1998, British Airways, along with American Airlines, Cathay Pacific, Qantas, and Canadian Airlines, formed the Oneworld airline alliance. Oneworld began operations on 1 February 1999, it is one of the largest airline alliances in the world, behind only SkyTeam and Star Alliance.
Benefits under CEO Robert Ayling's leadership included cost savings of £750m and the establishment of Go Fly in 1998. However, one year on, in 1999, British Airways reported an 84 percent drop in profits, its worst for seven years. In March 2000, Robert Ayling was removed from his position and British Airways announced Rod Eddington as his successor; Eddington would make further workforce cuts due to reduced demand following the 11 September attacks in 2001. In September 2004, BA announced the sale of its Qantas stake.
In September 2005, Willie Walsh, former Aer Lingus pilot and Managing Director, became the Chief Executive Officer of the company. In January 2008, BA unveiled its new subsidiary OpenSkies which takes advantage of the liberalisation of transatlantic traffic rights between Europe and the United States. As of 2008, OpenSkies flies non-stop from Paris to New York and Washington D.C.
On 30 July 2008, British Airways and Iberia, a Spanish fellow Oneworld partner, announced a merger plan; the two airlines would retain their original brands, similar to KLM and Air France in their merger agreement. An agreement to merge was confirmed in April 2010. In July 2010, the European Commission and US Department of Transport permitted the merger and to co-ordinate transatlantic routes with American Airlines. On 6 October 2010, the alliance between British Airways, American Airlines and Iberia formally began operations; the alliance generates an estimated £230 million annual cost-saving for BA, in addition to £330 million by the Iberia merge.
British Airways ceased trading on the London Stock Exchange on 21 January 2011, after 23 years as a constituent of the FTSE 100 index. On 21 January 2011, British Airways and Iberia merged, resulting in the world's third-largest airline in terms of annual revenue and the second largest airline group in Europe. Prior to merging, British Airways owned a 13.5% stake in Iberia, thus it received ownership of 55% of the combined “ International Airlines Group”, Iberia's other shareholders received the remaining 45%. In September 2010, Willie Walsh, the CEO of IAG, announced that IAG is looking at other airlines; and that a shortlist of twelve possible acquisitions existed. In early November 2011, IAG announced an agreement in principle to purchase British Midland International from Lufthansa.
Corporate affairs
Overview

British Airways trades on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index under the title of "International Airlines Group" following British Airways' merger with Iberia on 21 January 2011, with trading beginning on 24 January 2011.
British Airways has its head office, Waterside, in Harmondsworth, London Borough of Hillingdon, England. Waterside was completed in June 1998 to replace British Airways' previous head office, Speedbird House, on the grounds of London Heathrow Airport. The IAG has its operational headquarters in London and corporate headquarters in Madrid; it is incorporated under Spanish law as a " Sociedad Anónima", and pays taxes in Spain.
Operations
British Airways is the largest airline based in the United Kingdom in terms of fleet size, international flights, and international destinations and was, until 2008, the largest airline by passenger numbers as well. The airline carried 34.6 million passengers in 2008 but easyJet, a rival, low-cost carrier carried 44.5 million passengers that year, passing British Airways for the first time. British Airways holds a United Kingdom Civil Aviation Authority Type A Operating Licence, it is permitted to carry passengers, cargo, and mail on aircraft with 20 or more seats.
British Airways' main base is at London Heathrow Airport in west London, England, but it also has a major presence at Gatwick Airport. It also has a base at London City Airport, with a major presence from its subsidiary BA CityFlyer, who are the largest operator from LCY. BA had previously operated a significant hub at Manchester Airport. Manchester operations, and international services outside of London, ceased when the subsidiary, BA Connect, was sold due to a lack of profitability. Passengers wishing to travel internationally with BA either to or from regional UK destinations must now transfer in London. Heathrow airport is dominated by British Airways, due to their ownership of 40% of the slots available at the airport. The majority of BA services operate from Terminal 5, with the exception of some flights still at Terminal 3. T3 British Airways operations include long-haul codeshare flights and European flights.
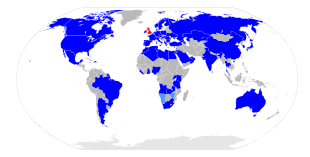
British Airways serves nearly 150 destinations, including six domestic. It is one of only ten carriers to fly to all six permanently inhabited continents.
BA CityFlyer is a wholly owned subsidiary based at London City Airport, and it flies 14 Embraer 170/190 aircraft. BA CityFlyer operates from London City Airport to 20 destinations throughout Europe. The airline mostly focuses on the financial market, however has recently grown in the leisure market. This included starting routes to Ibiza and Palma, and began flying to Venice in September 2012. The onboard product is identical to that of the BA Short Haul product from both LHR and LGW.
The former BEA Helicopters was renamed British Airways Helicopters in 1974 and operated passenger and offshore oil support services until it was sold in 1986. Other former subsidiaries include the German airline Deutsche BA from 1997 until 2003 and the French airline Air Liberté from 1997 to 2001. British Airways previously was the full owner of Airways Aero Associations Limited, operator of the British Airways flying club and an aerodrome under the BA brand at Wycombe Air Park, High Wycombe.
South Africa's Comair and Denmark's Sun Air of Scandinavia have been franchisees of British Airways since 1996. British Airways obtained a 15% stake in UK regional airline Flybe from the sale of BA Connect in March 2007; BA also owned a 10% stake in InterCapital and Regional Rail (ICRR), the company that managed the operations of Eurostar (UK) Ltd from 1998 to 2010, when the management of Eurostar was restructured.
With the creation of an Open Skies agreement between Europe and the United States in March 2008, British Airways started a new subsidiary airline called OpenSkies (previously known as "Project Lauren"). The airline started operations in June 2008, and now flies direct from Paris to New York JFK and Washington Dulles.
In addition to codesharing with the Oneworld alliance members, British Airways has codeshare agreements with Aer Lingus, Flybe, Kingfisher Airlines, Loganair, Meridiana fly and WestJet.
British Airways World Cargo
BA known as British Airways, Cargo is British Airways World Cargo, the world's twelfth-largest cargo airline based on total freight tonne-kilometres flown. BA World Cargo has global freight opportunities through the British Airways flight routes. In addition to the main fleet, BA World Cargo wet lease three Boeing 747-8F aircraft from Global Supply Systems on a multi-year basis, as well as utilising space on dedicated freighters operated by other carriers. Dedicated freighter services gives British Airways World Cargo the opportunity to service destinations that are not available on their passenger route network.
British Airways opened a World Cargo centre at Heathrow in the late 1990s; it is an automated freight handling centre capable of handling unusual and premium cargo, and fresh produce, of which it handles over 80,000 tons per year. BA World Cargo also handles freight at London's Gatwick and Stansted airports, and, through its partner British Airways Regional Cargo, at all of the main regional airports throughout the UK. In 2010, BAWC announced that it would wetlease three Boeing 747-8F aircraft from Global Supply Systems to replace the 747-400s. The first of these entered revenue service in November 2011 with the other two entering revenue service in December 2011.
In August 2007, British Airways agreed to plead guilty and pay a $300 million fine as a result of felony anti-trust charges in the United States for conspiring to fix air cargo prices. In 2009, BA announced that it had chosen to continue its longhaul freight operations at London Stansted Airport rather than relocate to Kent International Airport.
Industrial relations
Staff working for British Airways are represented by a number of trade unions, pilots are represented by British Air Line Pilots' Association, cabin crew by British Airlines Stewards and Stewardesses Association (a branch of Unite the Union), while other branches of Unite the Union represent other employees. During Bob Ayling's management, faced strike action by cabin crew over a £1 billion cost-cutting drive to return BA to profitability in 1997; this was the last time BA cabin crew would strike until 2009, although staff morale has reportedly been unstable since that incident. In an effort to increase interaction between management, employees, and the unions, various conferences and workshops have taken place, often with thousands in attendance.
In 2005, wildcat action was taken by union members over a decision by Gate Gourmet to not renew the contracts of 670 workers and replaced them with agency staff; it is estimated that the strike cost British Airways £30 million and caused disruption to 100,000 passengers. In October 2006, BA became involved in a civil rights dispute when a Christian employee was forbidden to wear a necklace baring the cross, a religious symbol. BA's practice of forbidding such symbols has been publically questioned by British politicians such as former Home Secretary John Reid and former Foreign Secretary Jack Straw.
Relations have been turbulent between BA and Unite. In 2007, cabin crew threatened strike action over salary changes to be imposed by BA management. The strike was called off at the last minute, British Airways losing £80 million. In December 2009, a ballot for strike action over Christmas received a high level of support, action was blocked by a court injunction that deemed the ballot illegal. Negotiations failed to stop strike action in March, BA withdrew perks for strike participants. Allegations were made by the Guardian newspaper that BA had consulted outside firms methods to undermine the unions, the story was later withdrawn. A strike was announced for May 2010, British Airways again sought an injunction. Members of the Socialist Workers Party disrupted negotiations between BA management and Unite to prevent industrial action. Further disruption struck when Derek Simpson, a Unite co-leader, was discovered to have leaked details of confidential negotiations online via Twitter.
Destinations
British Airways is one of the few airlines that fly to all six inhabited continents, along with Delta Air Lines, Emirates, Korean Air, Qantas, Qatar Airways, Singapore Airlines, South African Airways and United Airlines.
British Airways has codeshare agreements and/or partnerships with the following airlines:
|
|
British Airways also has interline agreements with the following airlines:
- Alaska Airlines
- Virgin America
Fleet
With the exception of the Boeing 707 and early Boeing 747 variants from BOAC, the airline as formed in 1972-4 inherited a mainly UK-built fleet of aircraft. The airline introduced the Boeing 737 and Boeing 757 into the fleet in the 1980s, followed by the Boeing 747–400 (British Airways is the largest operator with 55), Boeing 767 and Boeing 777 in the 1990s. Boeing-built aircraft for British Airways are allocated the customer code 36, which appears in their aircraft designation as a suffix, such as 737–436, 747–436 and 777–236.
Although British Airways utilises a large Boeing fleet, it has always operated aircraft from other manufacturers. British built aircraft were transferred from BEA (e.g. Trident) and BOAC (e.g. VC10), and in the 1980s the airline operated the Lockheed L-1011. It also operated the DC-10 and Airbus A320-100 through the acquisition of British Caledonian Airways in the 1980s. In August 1998, British Airways placed its first direct Airbus order, for 59 A320/A319s, to replace its own ageing fleet of Boeing 737s and A320-100s. British Airways replaced the L-1011 and DC-10 tri-jet fleet with more fuel-efficient, twinjet, Boeing 767 and 777 aircraft in the 1990s. In September 2007, BA placed its first order for long-haul Airbus jets, consisting of 12 firm orders for Airbus A380s and seven options. The Boeing 757 was withdrawn from British Airways service in late 2010.
British Airways will take delivery of its first Airbus A380 in July 2013 and have three in service by the end of the year. It will fly to Los Angeles on 15 October 2013, followed by Hong Kong from 15 November 2013.
The combined International Airlines Group entity, that BA is now a part of, operates over 400 aircraft, carries over 62 million passengers annually, and serves more than 200 destinations. As of February 2013 the British Airways fleet includes the following aircraft:
| Aircraft | In Service | Orders | Passengers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | J | W | M |
|
|||
| Airbus A318-100 | 2 | — | — | 32 | — | — | 32 |
| Airbus A319-100 | 44 | — | — | 36 | — | 77 | 113 |
| — | 12 | — | 113 | 125 | |||
| — | — | — | 132 | 132 | |||
| Airbus A320-200 | 46 | - | — | 52 | — | 83 | 135 |
| — | 12 | — | 143 | 155 | |||
| — | — | — | 162 | 162 | |||
| Airbus A321-200 | 17 | — | — | 67 | — | 86 | 153 |
| — | 12 | — | 168 | 180 | |||
| — | — | — | 188 | 188 | |||
| Airbus A380-800 | — | 12 | 14 | 97 | 55 | 303 | 469 |
| Boeing 737–400 | 19 | — | — | 38 | — | 101 | 139 |
| — | 10 | — | 137 | 147 | |||
| — | — | — | 153 | 153 | |||
| Boeing 747-400 | 55 | — | 14 | 70 | 30 | 177 | 291 |
| 14 | 70 | 30 | 185 | 299 | |||
| 14 | 52 | 36 | 243 | 345 | |||
| Boeing 767-300ER | 21 | — | — | 24 | 24 | 141 | 189 |
| — | — | — | 252 | 252 | |||
| — | — | — | 259 | 259 | |||
| Boeing 777–200 | 3 | — | 17 | 48 | 24 | 127 | 216 |
| Boeing 777–200ER | 43 | — | 12 | 48 | 32 | 127 | 219 |
| 14 | 48 | 40 | 122 | 224 | |||
| — | 48 | 24 | 203 | 275 | |||
| — | 40 | 24 | 219 | 283 | |||
| Boeing 777-300ER | 6 | 6 | 14 | 56 | 44 | 183 | 297 |
| Boeing 787–8 | — | 8 | — | 35 | 25 | 154 | 214 |
| Boeing 787–9 | — | 16 |
|
||||
| Total | 256 | 48 | |||||
A Cameron Balloons C-80 hot air balloon is also registered to the airline.
- British Airways World Cargo Fleet
- 3 Boeing 747-8F (operated by Global Supply Systems in BA livery)
Other aircraft types used between 1974 and 1983 were Vickers 953C, Boeing 707-300C and Boeing 747-200F while the Boeing 747-400F was operated from the 1990s to 2001 through Atlas Air and 2002 to early 2012 by Global Supply Systems, of these only one of Atlas Air's aircraft wore BA livery (World Tails, Chelsea Rose scheme), the others flew in Atlas and Global Supply's own colours.
Aircraft operated
|
|
Engine choice
The majority (77%) of the British Airways fleet is either powered by Rolls-Royce or IAE alliance engines, of which Rolls-Royce was a major contributor. The remaining 23% of the fleet is equally divided between General Electric and the CFM International consortium.
British Airways Engineering
The company has its own engineering branch to maintain its aircraft fleet, this includes line maintenance at over 70 airports around the world. As well as hangar facilities at Heathrow and Gatwick airport it has two major maintenance centres at Glasgow and Cardiff Airports and a new facility at Prestwick Airport treating wing skin corrosion on A319, A320 and A321 aircraft. From the beginning of 2012 most heavy maintenance on the Boeing 737-400 Gatwick-based fleet is now done at the Lufthansa Technik maintenance facility in Sofia, Bulgaria.
Recent aircraft orders
On 27 March 2007, British Airways placed an order for four 777-200ER aircraft with an option for four more; the order cost more than US$800 million at list price; BA has stated these are for fleet expansion. BA's first 777s were fitted with General Electric GE90 engines, but BA switched to Rolls-Royce Trent 800s for the nineteen most recent aircraft. This choice has been continued on the four most recent orders.
On 27 September 2007, BA announced their biggest order since 1998 by ordering thirty-six new long-haul aircraft. The company ordered twelve A380s with options on a further seven, and twenty-four Boeing 787s with eighteen options for delivery between 2013 and 2016. Rolls-Royce Trent engines were again selected for both orders with Trent 900s powering the A380s and Trent 1000s powering the 787s. The Boeing 787s will replace fourteen of British Airways' Boeing 767 fleet while the Airbus A380s will replace twenty of BA's oldest Boeing 747-400s and will most likely be used to increase capacity on key routes from London Heathrow. It is anticipated that the A380 will be launched on the Hong Kong route.
On 1 August 2008, BA announced orders for six Boeing 777-300ERs and options for four more as an interim measure to cover for delays over the deliveries of their 787-8/9s. Of the six that have been ordered, four will be leased and two will be fully acquired by British Airways. On 12 January 2009, Willie Walsh stated that the 777 purchase did not indicate a ruling out of the Airbus A350 for BA's fleet renewal programme and "the airline expects to reach a decision towards the end of the year."
In September 2009, British Airways began a premium service between London City Airport and New York-JFK using two Airbus A318s fitted with 32 lie-flat beds in an all business class cabin. The service operates under the flight numbers previously reserved for Concorde, BA001, BA002, BA003, and BA004. These services have since been transferred to British Airways Limited.
Marketing
Branding
The musical theme predominantly used on British Airways advertising is " The Flower Duet" by Léo Delibes. This, and the slogan "The World's Favourite Airline" were introduced in 1989 with the launch of the iconic "Face" advertisement. The slogan was dropped in 2001, after having been overtaken by Lufthansa in terms of passenger numbers. "Flower Duet" is still used by the airline, and has been through several different arrangements since 1989. The recent version of this melody was shown in 2007, with a new slogan, "Upgrade to British Airways". Other advertising slogans have included "The World's Favourite Airline", "The World's Best Airline", "We'll Take More Care Of You", and "Fly the Flag".
BA had an account for twenty-three years with Saatchi & Saatchi, who created many of their most famous advertisements, including the influential "Face" campaign; Saatchi & Saatchi imitated this advert for rival Silverjet in 2007 after BA discontinued their business activities. As of February 2007, BA's advertising agency is Bartle Bogle Hegarty.
Online, British Airways purchased the internet domain ba.com in 2002 from previous owner Bell Atlantic, 'BA' being the company's acronym and its IATA Airline code. In September 2011, BA launched its biggest advertising campaign in a decade, including a 90-second cinematic advert celebrating the airline's ninety-year heritage, and a new slogan "To Fly. To Serve".
British Airways is the official airline of the Wimbledon Championship tennis tournament, and the official airline and tier one partner of the 2012 Summer Olympics and Paralympics. British Airways was also the official airline of England's bid to host the 2018 Football World Cup.
Liveries and tail fins
Since its formation in 1974, though to a limited extent until all aircraft were repainted, British Airways' aeroplanes carried a Union Jack scheme painted on their tail fins. The original tail scheme was changed in 1984 as part of a new livery designed by Landor Associates. On 10 June 1997 there was a highly controversial change from the use of the British colours to ethnic logos and abstract world images, such as Delftware or Chinese calligraphy for example. All the designs related to countries on the company's network of routes. This caused problems with air traffic control: whereas previously controllers had been able to tell pilots to follow a BA plane, they were now harder to visually identify because each plane was painted in a range of different colours and colour schemes.
Several people spoke out against the change from the traditional Union Flag scheme, including the former Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher who covered the tail of a model BA plane with a white handkerchief captured by BBC News cameras. BA's traditional rival, Virgin Atlantic, quickly adopted the British flag along with the slogan "Britain's national flagcarrier". On 6 June 1999, BA CEO Bob Ayling announced that all BA planes would be repainted with the Union Flag, based on a design first used on Concorde.
Loyalty programmes
British Airways' loyalty program is called the Executive Club, featuring multiple tiers, has benefits such as access to special lounges and dedicated 'fast' queues. BA also invites its top corporate accounts to join a "Premier" incentive programme. British Airways operates airside lounges for passengers travelling in premium cabins and these are available to certain tiers of Executive Club members. First class passengers, as well as Gold Executive Club members, are entitled to use First Class Lounges. Business class passengers (called Club World or Club Europe in BA terms) as well as Silver Executive Club members may use Business lounges Often, at airports in which BA does not operate a departure lounge, a third party lounge is usually provided for premium/status passengers. In August 2011, British Airways announced changes to the Executive Club to maximise integration with the merge with Iberia.
Cabins
- Short haul
UK Domestic is British Airways' economy class on domestic UK flights. Flights into Heathrow are operated by Airbus A320 series aircraft, and flights into Gatwick are operated by Boeing 737 aircraft, which are in a one-class configuration.
Business UK operates the same cabin as UK Domestic, but has pre-flight lounge access. Euro Traveller is British Airways' economy class offering on flights from the UK to the rest of Europe. In-Flight Entertainment is offered on 767-300ER and some A320 aircraft.
Club Europe is the short-haul business class on all short-haul flights, except within the UK. This allows for access to business lounges at most airports. Since September 2009, Club Europe has seats in a 2–3 configuration on narrow-body aircraft.
- Mid haul
From October 2012, British Airways launched a brand new midhaul product on ex-British Midland routes with 7 ex- bmi A321s. These aircraft have been designated to serve 'midhaul' routes such as Almaty, Tbilisi, Baku, Amman, Beirut and Tel Aviv. The 'Club World' business class on these narrowbody aircraft is different to the product operated on the rest of BA's longhaul fleet - configured in a 1-2 configuration of 23 seats to allow for enough leg room and space for flat bed seats. In World Traveller, new seats were introduced. All seats are also fitted with the brand new Thales i5000 in-flight entertainment system.
- Long haul
First (rebranded from 'FIRST' in 2009) is the long-haul first class service on British Airways, offered only on Boeing 747 and some Boeing 777 aircraft. There are fourteen private "demi-cabins" per aircraft, each with a 6 ft 6 in (1.98 m) bed, a 15-inch (38 cm) wide entertainment screen, and in-seat power. In 2009, British Airways announced a major upgrade and refresh of upgrades.
Club World is the long-haul business class on Boeing 767, 777, 747, and Airbus A318 aircraft; the cabin features fully flat beds. On 13 November 2006, British Airways launched Next Generation New Club World, featuring larger seats.
World Traveller is the long-haul economy class offered on international flights to destinations outside Europe; offering seat-back entertainment and several complimentary drinks and meals. AVOD is offered on all 747, long-haul 767s and all but 16 of the 777s, with the remainder of those fitted with a 12 channel looped system. This system is currently being phased out and replaced with a new AVOD product as part of the aircraft's refurbishment programme. World Traveller Plus is the premium economy offering provided on all long-haul aircraft, which offers fewer seats per row, more seat comforts, and power sockets.
Seating policies
In March 2001, it was revealed that British Airways had a policy of not seating adult male passengers next to children who are sitting by themselves, even if a child's parents are elsewhere on the plane. This led to accusations of sex discrimination, with the company eventually admitting the offence in 2010 during a case brought by Mirko Fischer. The policy was dropped in August 2010 with the airline instead seating unaccompanied minors in a non discriminatory manner near the cabin crew.
In 2001, British Airways introduced a ten-abreast economy class configuration on the Boeing 777, an aircraft designed for nine-abreast seating. This utilised specially built narrow seats and aisles, and was applied to two GE-engined 777-200ERs used predominantly on Caribbean routes, and occasionally to Florida. These aircraft have since been converted back to 9-abreast.
Incidents and accidents
- In November 1974, British Airways Flight 870 from Dubai to London Heathrow, operated by a Vickers VC10, was hijacked in Dubai, landing at Tripoli for refuelling before flying on to Tunis. One hostage was murdered before the hijackers eventually surrendered after 84 hours. Captain Jim Futcher was awarded the Queen's Gallantry Medal, the Guild of Air Pilots and Air Navigators Founders Medal, the British Air Line Pilots Association Gold Medal and a Certificate of Commendation from British Airways for his actions during the hijacking, having returned to the aircraft to fly it knowing the hijackers were on board.
- On 10 September 1976, a Trident 3B on British Airways Flight 476, flying from London Heathrow to Istanbul collided in mid-air with an Inex Adria DC9-31 near Zagreb, Croatia, resulting in the 1976 Zagreb mid-air collision. All 54 passengers and 9 crew members on the BA aircraft died. This is the only fatal accident to a British Airways aircraft since the company's formation in 1974.
- On 24 June 1982, Flight 9, a Boeing 747–200, G-BDXH, City of Edinburgh flew through a cloud of volcanic ash and dust from the eruption of Mount Galunggung, causing extensive damage to the aircraft, including the failure of all four engines. The crew managed to glide the plane out of the dust cloud and restart all four of its engines, although one later had to be shut down again. The volcanic ash caused the cockpit window to be scrached to such an extent that it was not possible for the pilots to see out of the plane. However, the aircraft made a successful emergency landing at Halim Perdanakusuma International Airport just outside Jakarta, Indonesia. No people killed or injured.
- On 10 June 1990, Flight 5390, a BAC One-Eleven flight between Birmingham and Málaga, suffered a windscreen blowout due to the fitting of incorrect bolts the previous day. The Captain suffered major injuries after being partially blown out of the aircraft, however the co-pilot landed the plane safely at Southampton Airport. The captain, Tim Lancaster, despite the physical trauma he suffered, fully recovered and five months later he returned to duty.
- On 2 August 1990, Flight 149 landed at Kuwait International Airport four hours after the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, leading to the capture of the passengers and crew, and the destruction of the aircraft.
- On 17 January 2008, British Airways Flight 38, a Boeing 777-200ER G-YMMM, flying from Beijing to London, crash-landed approximately 1,000 feet (300 m) short of London Heathrow Airport's runway 27L, and slid onto the runway's threshold. This resulted in damage to the landing gear, the wing roots, and the engines, resulting in the first hull loss of a Boeing 777. There were 136 passengers and 16 crew on board. No people were killed, and there were no post-crash explosions or fires, but one serious and twelve minor injuries were sustained. The initial report from the Air Accidents Investigation Branch stated that the engines repeatedly failed to respond to commands for more thrust from both the autothrottle system and from manual intervention, beginning when the aircraft was at an altitude of 600 feet (180 m) and 2 miles (3.2 km) from touchdown. In September 2008, it was revealed that ice forming in the fuel might have caused the crash. In early 2009, Boeing sent an update to aircraft operators, identifying the problem as specific to the Rolls-Royce engine oil-fuel flow [heat exchanger] which has since been the subject of a fleet-wide modification programme to prevent recurrences of ice formation in the fuel flow.