The Daily Programmer: "Bellman's Algorithm"
An alternative approach to path finding is Bellman's algorithm. This page explains that approach and its implementation.
In this post, we will study an algorithm for single source shortest path on a graph with negative weights but no negative cycles.
Here are some points to keep in mind regarding the different algorithms studied so far:
- Breadth First Search: For graphs where the edge-weights are either zero or all same.
- Dijkstra's Algorithm: For graphs where the edge-weights are non-negative. Uses greedy strategy.
- Bellman-Ford Algorithm: For graphs where the edge-weights may be negative, but no negative weight cycle exists. Uses dynamic programming.
This post contains array - based implementation for simplicity. Another way is to use linked lists using dynamic allocation.
An example graph taken from Introduction to Algorithms:
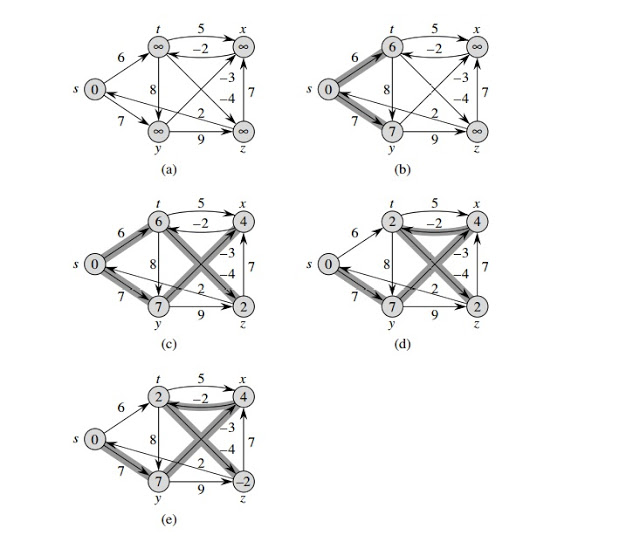
The code in C is as follows. Its time complexity is O (VE).
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Bellman_Ford(int G[20][20] , int V, int E, int edge[20][2])
{
int i,u,v,k,distance[20],parent[20],S,flag=1;
for(i=0;i<V;i++)
distance[i] = 1000 , parent[i] = -1 ;
printf("Enter source: ");
scanf("%d",&S);
distance[S-1]=0 ;
for(i=0;i<V-1;i++)
{
for(k=0;k<E;k++)
{
u = edge[k][0] , v = edge[k][1] ;
if(distance[u]+G[u][v] < distance[v])
distance[v] = distance[u] + G[u][v] , parent[v]=u ;
}
}
for(k=0;k<E;k++)
{
u = edge[k][0] , v = edge[k][1] ;
if(distance[u]+G[u][v] < distance[v])
flag = 0 ;
}
if(flag)
for(i=0;i<V;i++)
printf("Vertex %d -> cost = %d parent = %d\n",i+1,distance[i],parent[i]+1);
return flag;
}
int main()
{
int V,edge[20][2],G[20][20],i,j,k=0;
printf("BELLMAN FORD\n");
printf("Enter no. of vertices: ");
scanf("%d",&V);
printf("Enter graph in matrix form:\n");
for(i=0;i<V;i++)
for(j=0;j<V;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&G[i][j]);
if(G[i][j]!=0)
edge[k][0]=i,edge[k++][1]=j;
}
if(Bellman_Ford(G,V,k,edge))
printf("\nNo negative weight cycle\n");
else printf("\nNegative weight cycle exists\n");
return 0;
}
It's output on the above graph is:

Source: http://www.thedailyprogrammer.com/2015/07/bellman-ford-algorithm.html This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.