Chapter 11
Motivation
By Boundless
According to evolutionary psychology, individuals are motivated to engage in behaviors that maximize their genetic fitness.
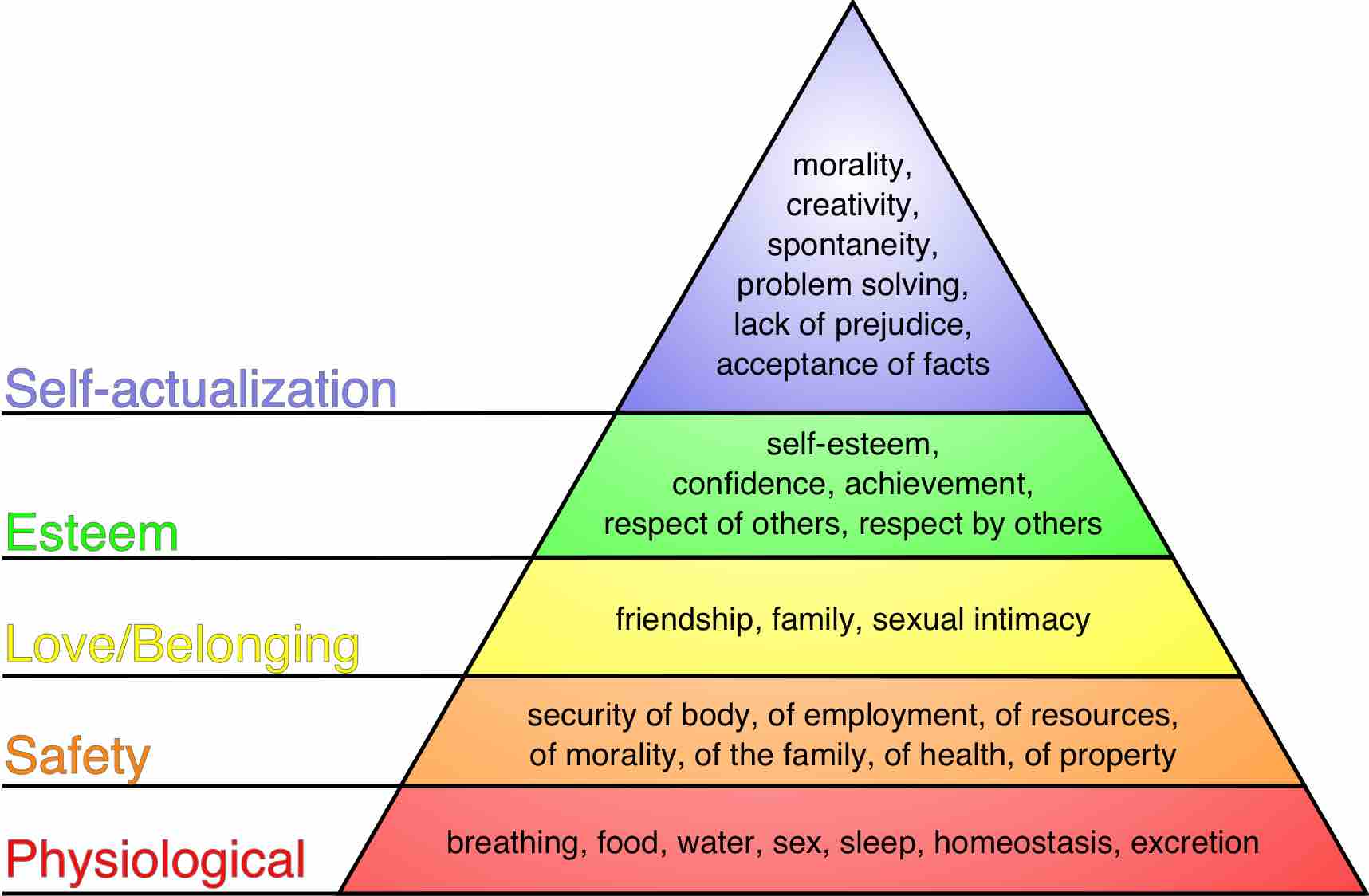
Maslow's theory is based on the premise that humans are motivated by needs that are hierarchically ranked.

According to drive-reduction theory, humans are motivated to satisfy physiological needs in order to maintain homeostasis.
Arousal theory expands upon drive-reduction theory by considering levels of arousal as potential motivators.

According to incentive theory, behavior is primarily motivated by the incentive of extrinsic factors.

Cognitive and achievement approaches to motivation examine how factors like achievement goals and cognitive dissonance influence motivation.
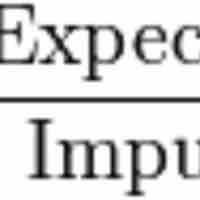
Temporal motivation theory emphasizes the impact of time and deadlines on our motivation to complete tasks.