Chapter 8
Joints
By Boundless
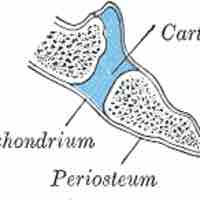
Fibrous joints are also called fixed or immovable joints because they do not move.
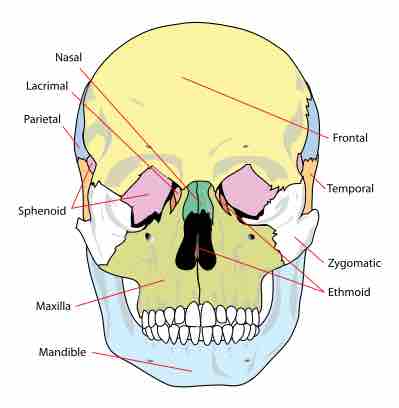
A suture is a type of fibrous joint (synarthrosis) bound by Sharpey's fibers that only occurs in the skull (cranium).
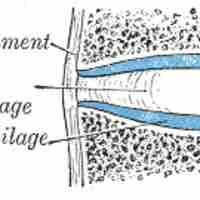
Syndesmoses are slightly movable joints formed where an interosseous ligament joins two bones.
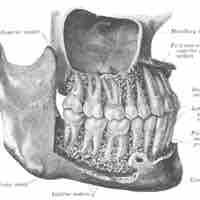
A gomphosis is a fibrous joint that binds the teeth to bony sockets in the bones of the maxilla mandible.
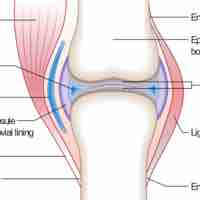
A synovial joint or diarthrosis occurs at articulating bones to allow movement. It is distinguished by a surrounding synovial capsule.
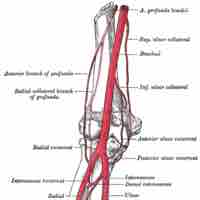
Synovial joints are highly innervated but vascularized indirectly by nearby tissues.
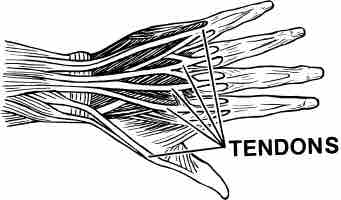
Joints are cushioned by small fluid-filled sacs called bursae and stabilized by tough bands of fibrous connective tissue called tendons.
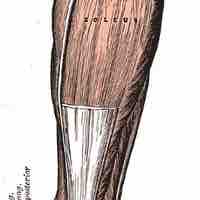
Tendons provide stability at joints.
Synovial joints allow an individual to achieve a wide range of movements.
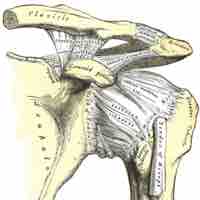
There are six different types of synovial joint based on their shapes, each allowing a different kind of movement.