Chapter 13
Heat and Heat Transfer
By Boundless
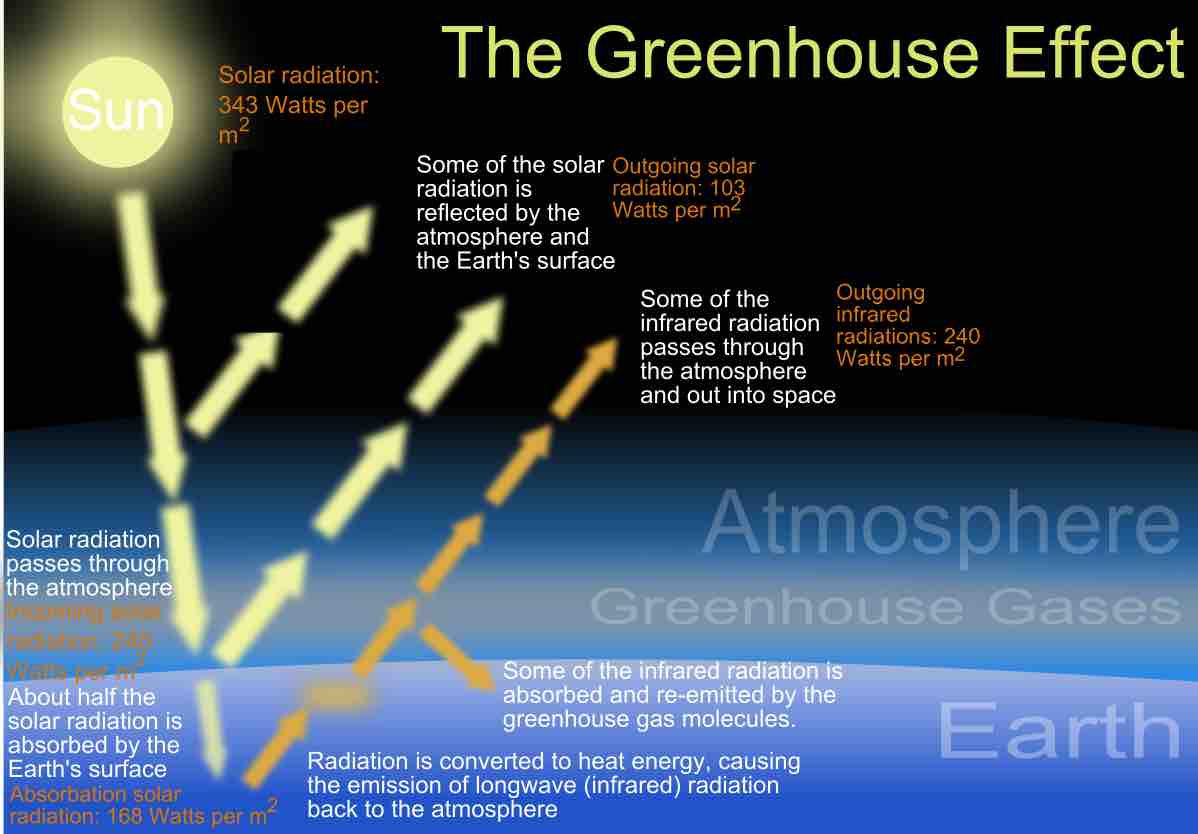
Heat is a measurable form of energy that can be transferred from one body to another; it is not a substance.
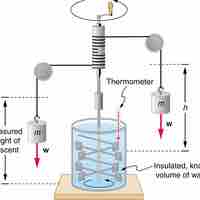
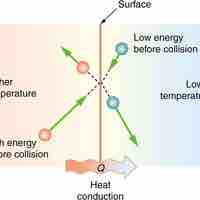
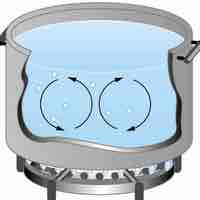
Heat is the spontaneous transfer of energy due to a temperature difference.

The internal energy of a system is the sum of all kinetic and potential energy in a system.
The heat capacity measures the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of an object or system by one degree Celsius.
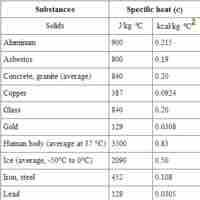
The specific heat is an intensive property that describes how much heat must be added to a particular substance to raise its temperature.
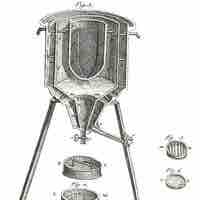
Calorimetry is the measurement of the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes.
An ideal gas has different specific heat capacities under constant volume or constant pressure conditions.

Calorimetry is used to measure the amount of heat produced or consumed in a chemical reaction.
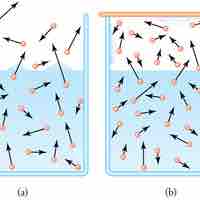
Evaporation is the process of molecules on a liquid's surface achieving sufficient energy to break free of the liquid and become gas.

At equilibrium, evaporation and condensation processes exactly balance and there is no net change in the volume of either phase.