Chapter 8
Market Failure: Public Goods and Common Resources
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Economics
Economics
by Boundless
Section 1
Public Goods
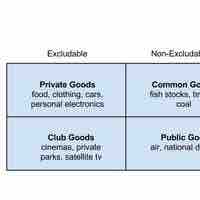
Defining a Good
There are four types of goods in economics, which are defined based on excludability and rivalrousness in consumption.

Private Goods
A private good is both excludable and rivalrous.

Public Goods
Individuals cannot be excluded from using a public good, and one individual's use of it does not limit its availability to others.
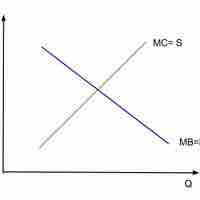
Optimal Quantity of a Public Good
The government is providing an efficient quantity of a public good when its marginal benefit equals its marginal cost.
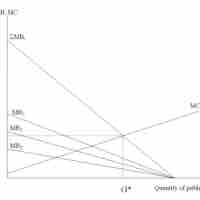
Demand for Public Goods
The aggregate demand curve for a public good is the vertical summation of individual demand curves.

Cost-Benefit Analysis
The government uses cost-benefit analysis to decide whether to provide a public good.
You are in this book
Boundless Economics
by Boundless

