Chapter 10
Competitive Markets
By Boundless
Perfect competition is a market structure that leads to the Pareto-efficient allocation of economic resources.
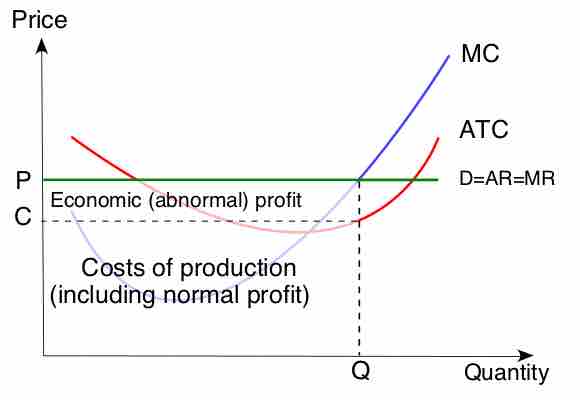
A firm in a perfectly competitive market may generate a profit in the short-run, but in the long-run it will have economic profits of zero.
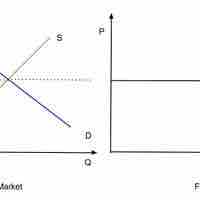
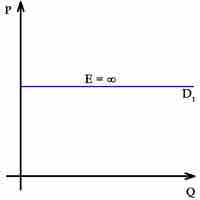
A perfectly competitive firm faces a demand curve is a horizontal line equal to the equilibrium price of the entire market.

Output is the amount of a good produced; revenue is the amount of income made from sales minus all business expenses.
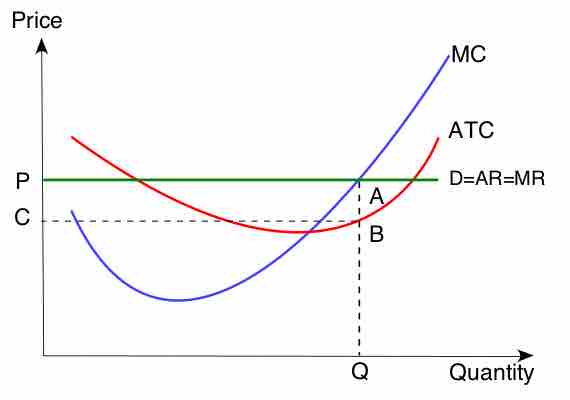
In order to maximize profit, the firm should set marginal revenue (MR) equal to the marginal cost (MC).
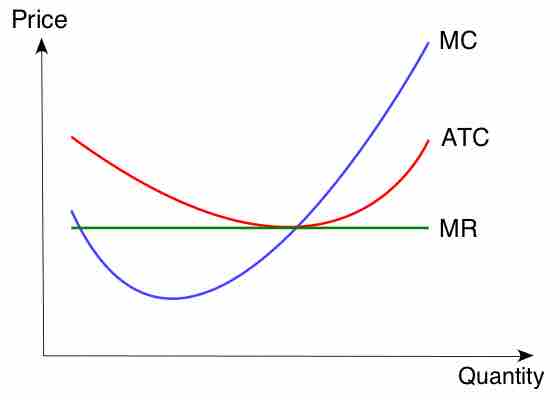
A firm will implement a production shutdown if the revenue from the sale of goods produced cannot cover the variable costs of production.
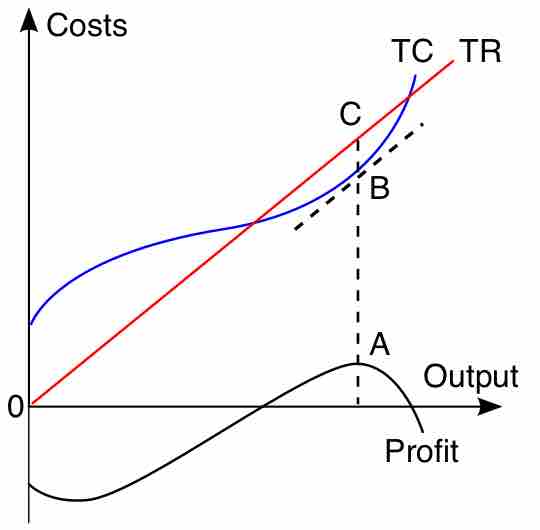
The total revenue-total cost perspective and the marginal revenue-marginal cost perspective are used to find profit maximizing quantities.
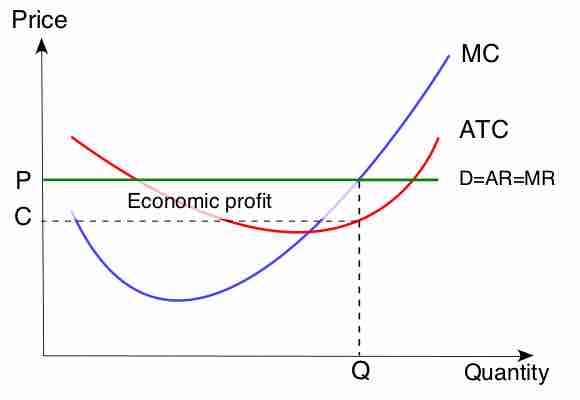
The short run is the conceptual time period where at least one factor of production is fixed in amount while other factors are variable.
The long-run supply curve in a perfectly competitive market has three parts; a downward sloping curve, a flat portion, and an upwards sloping curve.
The long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive market occurs when marginal revenue equals marginal costs, which is also equal to average total costs.
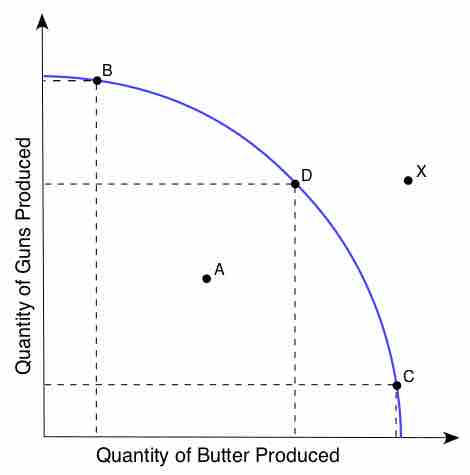
Productive efficiency occurs when production of a good is achieved at the lowest resource cost possible, given the level of production of other goods.

Free markets iterate towards higher levels of allocative efficiency, aligning the marginal cost of production with the marginal benefit for consumers.
The absence of barriers of entry and exit is a necessary condition for a market to be perfectly competitive.