Section 3
Infinite Sequences and Series
By Boundless
A sequence is an ordered list of objects and can be considered as a function whose domain is the natural numbers.
A series is the sum of the terms of a sequence.
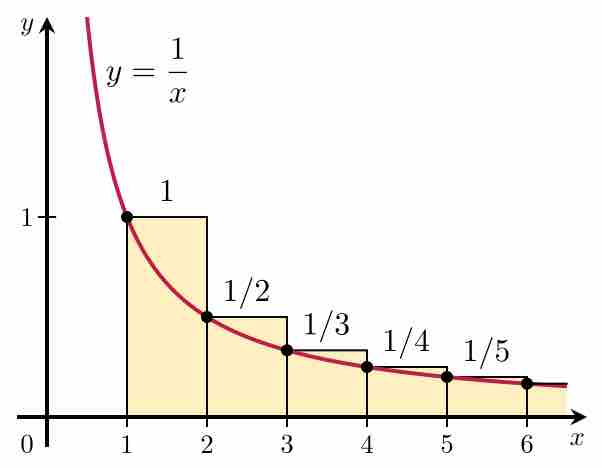
The integral test is a method of testing infinite series of nonnegative terms for convergence by comparing them to an improper integral.
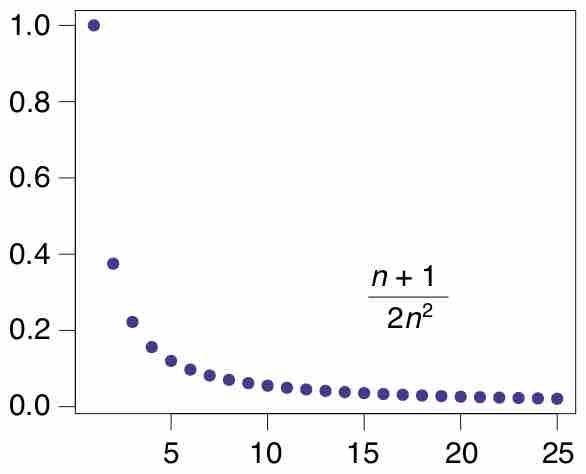
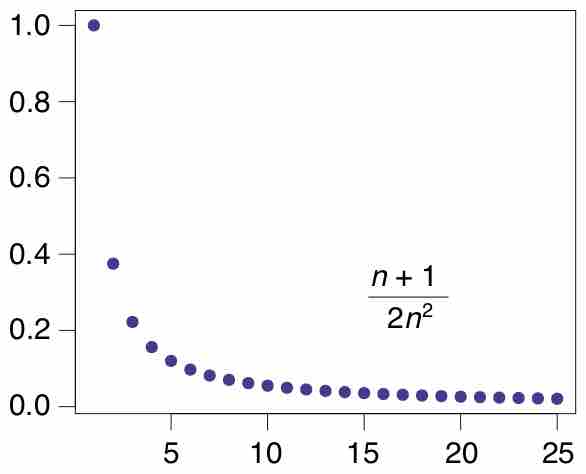
Comparison test may mean either limit comparison test or direct comparison test, both of which can be used to test convergence of a series.
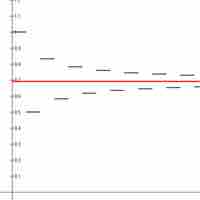
An alternating series is an infinite series of the form
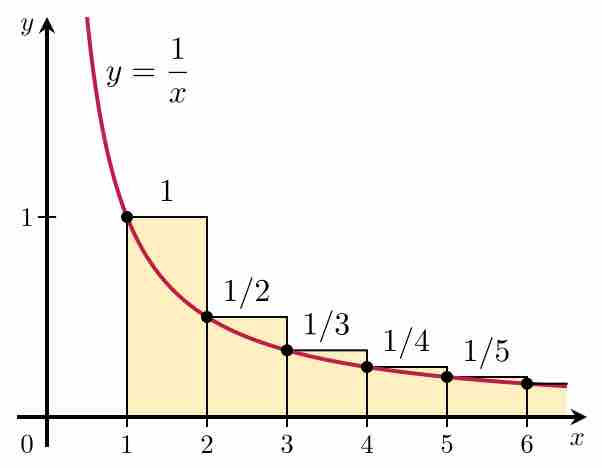
An infinite series of numbers is said to converge absolutely if the sum of the absolute value of the summand is finite.
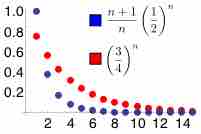
Convergence tests are methods of testing for the convergence or divergence of an infinite series.
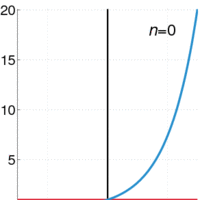
A power series (in one variable) is an infinite series of the form
A power function is a function of the form
Taylor series represents a function as an infinite sum of terms calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point.
Taylor series expansion can help approximating values of functions and evaluating definite integrals.
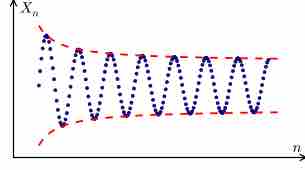
Infinite sequences and series can either converge or diverge.
For a sequence