Section 3
Partial Derivatives
By Boundless
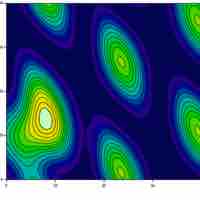
Multivariable calculus is the extension of calculus in one variable to calculus in more than one variable.
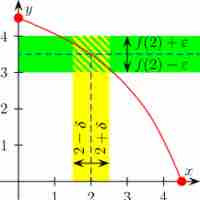
A study of limits and continuity in multivariable calculus yields counter-intuitive results not demonstrated by single-variable functions.
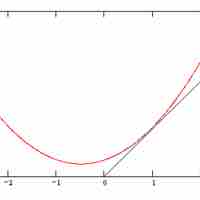
A partial derivative of a function of several variables is its derivative with respect to a single variable, with the others held constant.
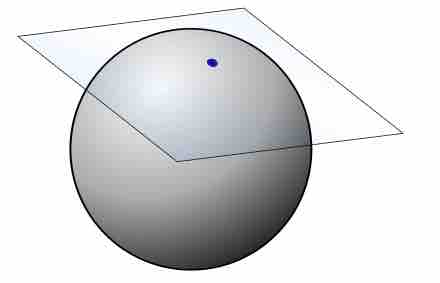
The tangent plane to a surface at a given point is the plane that "just touches" the surface at that point.
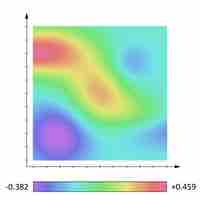
For a function
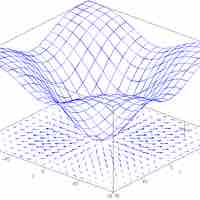
The directional derivative represents the instantaneous rate of change of the function, moving through
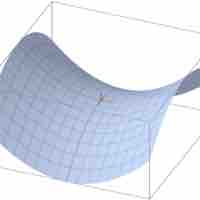
The second partial derivative test is a method used to determine whether a critical point is a local minimum, maximum, or saddle point.
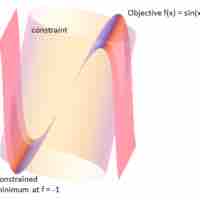
The method of Lagrange multipliers is a strategy for finding the local maxima and minima of a function subject to equality constraints.

To solve an optimization problem, formulate the function
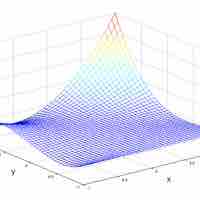
Finding extrema can be a challenge with regard to multivariable functions, requiring careful calculation.