Pregnancy
Background to the schools Wikipedia
SOS believes education gives a better chance in life to children in the developing world too. SOS Children is the world's largest charity giving orphaned and abandoned children the chance of family life.
Pregnancy (latin graviditas) is the carrying of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, inside the uterus of a female human. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets. Human pregnancy is the most studied of all mammalian pregnancies. Obstetrics is the medical field that studies and treats pregnant patients.
Childbirth usually occurs about 38 weeks from fertilization, i.e., approximately 40 weeks from the start of the last menstruation in humans. Thus, pregnancy lasts about nine months, although the exact definition of the English word “pregnancy” is a subject of controversy.
Terminology
One scientific term for the state of pregnancy is gravid, and a pregnant female is sometimes referred to as a gravida. Both words are rarely used in common speech. Similarly, the term " parity" (abbreviated as "para") is used for the number of previous successful live births. Medically, a woman who is not currently pregnant or who has never been pregnant is referred to as a "nulligravida", and in subsequent pregnancies as "multigravida" or "multiparous". Hence during a second pregnancy a woman would be described as "gravida 2, para 1" and upon delivery as "gravida 2, para 2". Incomplete pregnancies of abortions, miscarriages or stillbirths account for parity values being less than the gravida number, whereas a multiple birth will increase the parity value. Women who have never carried a pregnancy achieving more than 20 weeks of gestation age are referred to as "nulliparous".
The term embryo is used to describe the developing offspring during the first eight weeks following conception, and the term foetus is used from about two months of development until birth.
In many societies' medical and legal definitions, human pregnancy is somewhat arbitrarily divided into three trimester periods, as a means to simplify reference to the different stages of prenatal development. The first trimester carries the highest risk of miscarriage (natural death of embryo or foetus). During the second trimester, the development of the foetus can be more easily monitored and diagnosed. The beginning of the third trimester often approximates the point of viability, or the ability of the foetus to survive, with or without medical help, outside of the uterus.
Characteristics
Pregnancy occurs as the result of the female gamete or oocyte ( egg) being penetrated by the male gamete spermatozoon in a process referred to, in medicine, as " fertilization", or more commonly known as "conception". The fusion of male and female gametes usually occurs through the act of sexual intercourse. However, the advent of artificial insemination has also made achieving pregnancy possible in such cases where sexual intercourse is not potentially fertile (through choice or male/female infertility).
A number of medical signs are associated with pregnancy. These signs typically appear, if at all, within the first few weeks after conception. Although not all of these signs are universally present, nor are all of them diagnostic by themselves, taken together they make a presumptive diagnosis of pregnancy. These signs include the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the blood and urine, missed menstrual period, implantation bleeding that occurs at implantation of the embryo in the uterus during the third or fourth week after last menstrual period, increased basal body temperature sustained for over two weeks after ovulation, Chadwick's sign (darkening of the cervix, vagina, and vulva), Goodell's sign (softening of the vaginal portion of the cervix), Hegar's sign (softening of the uterus isthmus), and pigmentation of linea alba - Linea nigra, (darkening of the skin in a midline of the abdomen, caused by hyperpigmentation resulting from hormonal changes; it usually appears around the middle of pregnancy).
Duration
Though pregnancy begins at conception, it is more convenient to date from the first day of a woman's last menstrual period (acronym = LMP), or from the date of conception (if known). Starting from one of these dates, the expected date of delivery (acronym = EDD) can be calculated. Counting from the LMP, pregnancy usually lasts between 37 and 42 weeks, with the EDD at 40 weeks, 38 weeks after conception. 40 weeks is a little more than nine months and six days, which forms the basis of Naegele's rule for estimating date of delivery.
Pregnancy is considered 'at term' when gestation attains 37 complete weeks but is less than 42 (between 259 and 294 days since LMP). Events before completion of 37 weeks (259 days) are considered pre-term; from week 42 (294 days) events are considered post-term. When a pregnancy exceeds 42 weeks (294 days), the risk of complications for mother and fetus increases significantly. As such, obstetricians usually prefer to induce labour, in an uncomplicated pregnancy, at some stage between 41 and 42 weeks.
Recent medical literature prefers the terminology pre-term and post-term to premature and post-mature. Pre-term and post-term are unambiguously defined as above, whereas premature and postmature have historical meaning and relate more to the infant's size and state of development rather than to the stage of pregnancy.
Though these are the averages, the actual length of pregnancy depends on various factors. For example, the first pregnancy tends to last longer than subsequent pregnancies. Fewer than 10% of births occur on the due date; 50% of births are within a week of the due date, and almost 90% within two weeks.
Accurate dating of pregnancy is important, because it is used in calculating the results of various prenatal tests (for example, in the triple test). A decision may be made to induce labour if a fetus is perceived to be overdue. Due dates are only a rough estimate, and the process of accurately dating a pregnancy using the LMP method is complicated by the fact that not all women have 28 day menstrual cycles, nor ovulate on the 14th day following their last menstrual period.
Diagnosis
The beginning of pregnancy may be detected in a number of ways, including various pregnancy tests which detect hormones generated by the newly-formed placenta. Clinical blood and urine tests can detect pregnancy soon after implantation, which is as early as 6-8 days after fertilization. Home pregnancy tests are personal urine tests, which normally cannot detect a pregnancy until at least 12-15 days after fertilization. Both clinical and home tests can only detect the state of pregnancy, and cannot detect its age.
In the post-implantation phase, the blastocyst secretes a hormone named human chorionic gonadotropin which in turn, stimulates the corpus luteum in the woman's ovary to continue producing progesterone. This acts to maintain the lining of the uterus so that the embryo will continue to be nourished. The glands in the lining of the uterus will swell in response to the blastocyst, and capillaries will be stimulated to grow in that region. This allows the blastocyst to receive vital nutrients from the woman.
An early sonograph can determine the age of the pregnancy fairly accurately. In practice, doctors typically express the age of a pregnancy (i.e. an "age" for an embryo) in terms of "menstrual date" based on the first day of a woman's last menstrual period, as the woman reports it. Unless a woman's recent sexual activity has been limited, or she has been charting her cycles, or the conception is as the result of some types of fertility treatment (such as IUI or IVF) the exact date of fertilization is unknown. Absent symptoms such as morning sickness, often the only visible sign of a pregnancy is an interruption of her normal monthly menstruation cycle, (i.e. a "late period"). Hence, the "menstrual date" is simply a common educated estimate for the age of a fetus, which is an average of two weeks later than the first day of the woman's last menstrual period. The term "conception date" may sometimes be used when that date is more certain, though even medical professionals can be imprecise with their use of the two distinct terms. The due date can be calculated by using Naegele's rule. The expected date of delivery may also be calculated from sonogram measurement of the fetus. This method is slightly more accurate than methods based on LMP. The beginning of labour, which is variously called confinement or childbed, begins on the day predicted by LMP 3.6% of the time and on the day predicted by sonography 4.3% of the time.
Diagnostic criteria are: Women who have menstrual cycles and are sexually active, a period delayed by a few days or weeks is suggestive of pregnancy; elevated B-hcG to around 100,000 mIU/mL by 10 weeks of gestation.
Physiology
Pregnancy is typically broken into three periods, or trimesters, each of about three months. While there are no hard and fast rules, these distinctions are useful in describing the changes that take place over time.
First trimester
Traditionally, doctors have measured pregnancy from a number of convenient points, including the day of last menstruation, ovulation, fertilization, implantation and chemical detection. In medicine, pregnancy is often defined as beginning when the developing embryo becomes implanted into the endometrial lining of a woman's uterus. In some cases where complications may have arisen, the fertilized egg might implant itself in the fallopian tubes or the cervix, causing an ectopic pregnancy. Most pregnant women do not have any specific signs or symptoms of implantation, although it is not uncommon to experience light bleeding at implantation. Some women will also experience cramping during their first trimester. This is usually of no concern unless there is spotting or bleeding as well. The outer layers of the embryo grow and form a placenta, for the purpose of receiving essential nutrients through the uterine wall, or endometrium. The umbilical cord in a newborn child consists of the remnants of the connection to the placenta. The developing embryo undergoes tremendous growth and changes during the process of foetal development.
Morning sickness can occur in about seventy percent of all pregnant women and typically improves after the first trimester. Most miscarriages occur during this period.
Second trimester
Months 4 through 6 of the pregnancy are called the second trimester. Most women feel more energized in this period, and begin to seriously put on weight as the symptoms of morning sickness subside and eventually fade away. Although the fetus begins moving and takes a recognizable human shape during the first trimester, it is not until the second trimester that movement of the fetus, often referred to as " quickening", can be felt. This typically happens by the fourth month. The placenta is now fully functioning and the fetus is making insulin and urinating. The teeth are now formed inside the fetus's gums and the reproductive organs can be recognized, and can distinguish the fetus as male or female.
Third trimester
Final weight gain takes place, and the fetus begins to move regularly. The woman's navel will sometimes become convex, "popping" out, due to her expanding abdomen. This period of her pregnancy can be uncomfortable, causing symptoms like weak bladder control and back-ache. Movement of the fetus becomes stronger and more frequent and via improved brain, eye, and muscle function the fetus is prepared for ex utero viability. The woman can feel the fetus "rolling" and it may cause pain or discomfort when it is near the woman's ribs and spine.
It is during this time that a baby born prematurely may survive. The use of modern medical intensive care technology has greatly increased the probability of premature babies surviving, and has pushed back the boundary of viability to much earlier dates than would be possible without assistance. In spite of these developments, premature birth remains a major threat to the fetus, and may result in ill-health in later life, even if the baby survives.
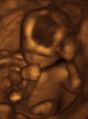
Prenatal development and sonograph images
Prenatal development is divided into two primary biological stages. The first is the embryonic stage, which lasts for about two months. At this point, the fetal stage begins. At the beginning of the foetal stage, the risk of miscarriage decreases sharply, all major structures including hands, feet, head, brain, and other organs are present, and they continue to grow and develop. When the fetal stage commences, a fetus is typically about 30 mm (1.2 inches) in length, and the heart can be seen beating via sonograph; the fetus bends the head, and also makes general movements and startles that involve the whole body. Brain stem activity has been detected as early as 54 days after conception, and the first measurable signs of EEG activity occur in the 12th week. Some fingerprint formation occurs from the beginning of the fetal stage.
One way to observe prenatal development is via ultrasound images. Modern 3D ultrasound images provide greater detail for prenatal diagnosis than the older 2D ultrasound technology. Whilst 3D is popular with parents desiring a prenatal photograph as a keepsake, both 2D and 3D are discouraged by the FDA for non-medical use, but there are no definitive studies linking ultrasound to any adverse medical effects. The following 3D ultrasound images were taken at different stages of pregnancy:
Physiological changes in pregnancy
The body must change its physiological and homeostatic mechanisms in pregnancy to ensure the fetus is provided for. Increases in blood sugar, breathing and cardiac output are all required.
Hormonal changes
Levels of progesterone and oestrogens rise continually throughout pregnancy, suppressing the hypothalamic axis and subsequently the menstrual cycle. The mother and the placenta also produces many hormones.
Prolactin levels increase due to maternal Pituitary gland enlargement by 50%. This mediates a change in the structure of the Mammary gland from ductal to lobular-alveolar. Parathyroid hormone is increased due to increases of calcium uptake in the gut and reabsorption by the kidney. Adrenal hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone also increase.
Placental lactogen is produced by the placenta and stimulates lipolysis and fatty acid metabolism by the mother, conserving blood glucose for use by the fetus. It also decreases maternal tissue sensitivity to insulin, resulting in gestational diabetes.
Physical changes
12-15kgs (26-33lbs) are gained during pregnancy due to fat deposition, growth of the reproductive organs and fetal tissues.
Cardiovascular changes
Blood volume increases by 40% in the first two trimesters. This is due to an increase in plasma volume through increased aldosterone. Progesterone may also interact with the aldosterone receptor, thus leading to increased levels. Red blood cell numbers increase due to increased erythropoietin levels.
Cardiac function is also modified, with increase heart rate and increased stroke volume. A decrease in vagal tone and increase in sympathetic tone is the cause. Blood volume increases act to increase stroke volume of the heart via Starling's law. After pregnancy the change in stroke volume is not reversed. Cardiac output rises from 4 to 7 litres in the 2nd trimester
Blood pressure also fluctuates. In the first trimester it falls. Initially this is due to decreased sensitivity to angiotensin and vasodilation provoked by increased blood volume. Later however, it is caused by decreased resistance to the growing uteroplacental bed.
Respiratory changes
Decreased functional residual capacity is seen, typically falling from 1.7 to 1.35 litres, due to the compression of the diaphragm by the uterus. Tidal volume increases, from 0.45 to 0.65 litres, giving an increase in pulmonary ventilation. This is necessary to meet the increased oxygen requirement of the body, which reaches 50ml/min - 20ml of which goes to reproductive tissues.
Progesterone may act centrally on chemoreceptors to reset the set point to a lower partial pressure of carbon dioxide. This maintains an increased respiration rate even at a decreased level of carbon dioxide.
Metabolic changes
An increased requirement for nutrients is given by fetal growth and fat deposition. Changes are caused by steroid hormones, lactogen and cortisol.
Maternal insulin resistance can lead to gestational diabetes. Increase liver metabolism is also seen, with increased gluconeogenesis to increase maternal glucose levels.
Renal changes
Renal plasma flow increases, as does aldosterone and erthropoietin production as discussed. The tubular maximum for glucose is reduced, which may precipitate gestational diabetes.
Management
Prenatal medical care is of recognized value throughout the developed world. Periconceptional Folic acid supplementation is the only type of supplementation of proven efficacy.
Nutrition
A balanced, nutritious diet is an important aspect of a healthy pregnancy. If the woman is healthy, balancing carbohydrates, fat, and proteins, and eating a variety of fruits and vegetables usually ensure good nutrition. Those whose diets are affected by health issues, religious requirements, or ethical beliefs may choose to consult a health professional for specific advice.
Adequate periconceptional folic acid (also called folate or Vitamin B9) intake has been proven to limit fetal neural tube defects, preventing spina bifida, a very serious birth defect. The neural tube develops during the first 28 days of pregnancy and this explains the necessity to guarantee adequate periconceptional folate intake. Folates (from folia, leaf) are abundant in spinach (fresh, frozen or canned), and are also found in green vegetables, salads, melon, hummus, and eggs. In the United States and Canada, most wheat products (flour, noodles) are fortified with folic acid.
Several micronutrients are important for the health of the developing fetus, especially in areas of the world where insufficient nutrition is prevalent. In developed areas, such as Western Europe and the United States, certain nutrients such as Vitamin D and calcium, required for bone development, may require supplementation.
There is some evidence that long-chain omega-3 (n-3) fatty acids have an effect on the developing fetus, but further research is required. At this time, supplementing the diet with foods rich in these fatty acids is not recommended, but is not harmful.
Dangerous bacteria or parasites may contaminate foods, particularly listeria and toxoplasma, toxoplasmosis agent. Careful washing of fruits and raw vegetables may remove these pathogens, as may thoroughly cooking leftovers, meat, or processed meat. Soft cheeses may contain listeria, if milk is raw the risk may increase. Cat feces pose a particular risk of toxoplasmosis. Pregnant women are also more prone to catching salmonella infection from eggs and poultry, which should be thoroughly cooked. Practicing good hygiene in the kitchen can reduce these risks.
Weight gain
Caloric intake must be increased, to ensure proper development of the fetus. The amount of weight gained during pregnancy varies between women. The National Health Service recommends that overall weight gain during the 9 month period for women who start pregnancy with normal weight be 10 to 12 kilograms (22–26 lb). During pregnancy, insufficient weight gain can compromise the health of the fetus. Women with fears of weight gain or with eating disorders may choose to work with a health professional, to ensure that pregnancy does not trigger disordered eating. Likewise, excessive weight gain can pose risks to the woman and the fetus. Women who are prone to being overweight may choose to plan a healthy diet and exercise plan to help moderate the amount of weight gained.
Sexuality during pregnancy
Most pregnant women can enjoy sexual intercourse throughout gravidity. Most research suggests that, during pregnancy, both sexual desire and frequency of sexual relations decrease. In context of this overall decrease in desire, some studies indicate a second-trimester increase, preceding a decrease. However, these decreases are not universal: a significant number of women report greater sexual satisfaction throughout their pregnancies.
Sex during pregnancy is a low-risk behaviour except when the physician advises that sexual intercourse be avoided, which may, in some pregnancies, lead to serious pregnancy complications or health issues such as a high-risk for premature labour or a ruptured uterus. Such a decision may be based upon a history of difficulties in a previous childbirth.
Some psychological research studies in the 1980s and '90s contend that it is useful for pregnant women to continue to have sexual activity, specifically noting that overall sexual satisfaction was correlated with feeling happy about being pregnant, feeling more attractive in late pregnancy than before pregnancy and experiencing orgasm. Sexual activity has also been suggested as a way to prepare for induced labour; some believe the natural prostaglandin content of seminal liquid can favour the maturation process of the cervix making it more flexible, allowing for easier and faster dilation and effacement of the cervix. However, the efficacy of using sexual intercourse as an induction agent "remains uncertain".
During pregnancy, the baby is protected from penetrative thrusting by the amniotic fluid in the womb and by the woman's abdomen.
Abortion
An abortion is the removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the uterus, resulting in or caused by its death. This can occur spontaneously or accidentally as with a miscarriage, or be artificially induced by medical, surgical or other means.
Progression
Complaints
The following are complaints that may occur during pregnancy:
- Back pain. A particularly common complaint in the third trimester when the patient's centre of gravity has shifted.
- Constipation. A complaint that is caused by decreased bowel motility secondary to elevated progesterone (normal in pregnancy), which can lead to greater absorption of water.
- Braxton Hicks contractions. Occasional, irregular, and often painless contractions that occur several times per day.
- Edema. Common complaint in advancing pregnancy. Caused by compression of the inferior vena cava (IVC) and pelvic veins by the uterus leads to increased hydrostatic pressure in lower extremities.
- Regurgitation, heartburn and nausea. Common complaints that may be caused by Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD); this is determined by relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and increased transit time in the stomach (normal in pregnancy)
- Haemorrhoids. Complaint that is often noted in advancing pregnancy. Caused by increased venous stasis and IVC compression leading to congestion in venous system along with increased abdominal pressure secondary to the pregnant space-occupying uterus and constipation.
- Pelvic girdle pain. A common complaint is pain, instability or dysfunction of the symphysis pubis and/or sacroiliac joints resulting from either excess strain or injury (such as Diastasis symphysis pubis) during the course of the pregnancy or birthing process.
- Increased urinary frequency. A common complaint referred by the gravida that is caused by increased intravascular volume, elevated GFR ( glomerular filtration rate), and compression of the bladder by the expanding uterus.
- Varicose veins. Common complaint caused by relaxation of the venous smooth muscle and increased intravascular pressure.
Childbirth
Childbirth is the process whereby an infant is born. It is considered by many to be the beginning of a person's life, and age is defined relative to this event in most cultures.
A woman is considered to be in labour when she begins experiencing regular uterine contractions, accompanied by changes of her cervix — primarily effacement and dilation. While childbirth is widely experienced as painful, some women do report painless labours, while others find that concentrating on the birth helps to quicken labour and lessen the sensations. Most births are successful vaginal births, but sometimes complications arise and a woman may undergo a caesarean section.
During the time immediately after birth, both the mother and the baby are hormonally cued to bond, the mother through the release of oxytocin, a hormone also released during breastfeeding.
Postnatal period
Context
There are fine distinctions between the concepts of fertilization and the actual state of pregnancy, which starts with implantation. In a normal pregnancy, the fertilization of the egg usually will have occurred in the Fallopian tubes or in the uterus. (Often, an egg may become fertilized yet fail to become implanted in the uterus.) If the pregnancy is the result of in-vitro fertilization, the fertilization will have occurred in a Petri dish, after which pregnancy begins when one or more zygotes implant after being transferred by a physician into the woman's uterus.
In the context of political debates regarding a proper definition of life, the terminology of pregnancy can be confusing. The medically and politically neutral term which remains is simply "pregnancy," though this can be problematic as it only refers indirectly to the embryo or fetus. De Crespigny observes that doctors' language has a powerful influence over the way patients think, and thus proposes that the best interests of patients are served by using language that both supports patient autonomy and is neutral.