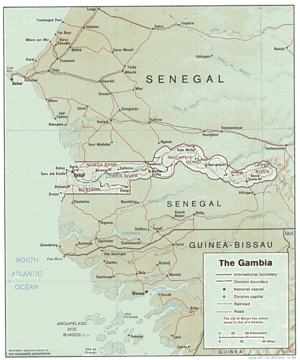
Geography of the Gambia
Did you know...
The articles in this Schools selection have been arranged by curriculum topic thanks to SOS Children volunteers. All children available for child sponsorship from SOS Children are looked after in a family home by the charity. Read more...
The Gambia is a very small and narrow country with the border based on the Gambia River. The country is less than 48 km wide at its greatest width. The country's present boundaries were defined in 1889 after an agreement between the United Kingdom and France. It is often claimed by Gambians that the distance of the borders from the Gambia River correspond to the area that British naval cannon of the time could reach from the river's channel. However, there is no historical evidence to support the story, and the border was actually delineated using careful surveying methods by the Franco-British boundary commission. Apart from its coastline, where The Gambia borders the Atlantic Ocean, it is an enclave of Senegal and is by far the smallest country on the continent of Africa.
Climate
The Gambia has a subtropical climate with distinct cool and hot seasons. From November to mid-May there is uninterrupted dry weather, with temperatures as low as 16 °C (60.8 °F) in Banjul and surrounding areas. Hot, humid weather predominates the rest of the year, with a rainy season from June to October; during this period, temperatures may rise as high as 43 °C (109.4 °F) but are usually lower near the sea. Mean temperatures range from 23 °C (73.4 °F) in January to 27 °C (80.6 °F) in June along the coast, and from 24 °C (75.2 °F) in January to 32 °C (89.6 °F) in May inland. The average annual rainfall ranges from 920 mm (36.2 in) in the interior to 1,450 mm (57.1 in) along the coast.
Terrain
The grassy flood plain of the Gambia river, which contains Guinean mangroves near the coast, with West Sudanian savanna upriver inland.
Statistics
Location: Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and Senegal.
Geographic coordinates: 13°28′N 16°34′W
Map references: Africa
Area:
total: 11,300 km²
land: 10,000 km²
water: 1,300 km²
Area - comparative: slightly less than Jamaica; slightly less than the size of Delaware.
Land boundaries:
total: 740 km
border countries: Senegal 740 km
Coastline: 80 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone: 18 nmi (33.3 km; 20.7 mi)
continental shelf: not specified
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Climate: tropical; hot, rainy season (June to November); cooler, dry season (November to May)
Terrain: flood plain of the Gambia river flanked by some low hills
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Red Rock 53 m
Natural resources: fish, groundnuts (peanuts), titanium, tin, zircon, silica sand, clay, petroleum
Land use:
arable land: 27.88%
permanent crops: 0.44%
other: 71.68% (2005 est.)
Irrigated land: 20 km² (2003)
Natural hazards: drought (rainfall has dropped by 30% in the last 30 years)
Environment - current issues: deforestation; desertification; water-borne diseases prevalent
Environment - international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements