Geography of Guinea-Bissau
Did you know...
SOS Children has tried to make Wikipedia content more accessible by this schools selection. Child sponsorship helps children one by one http://www.sponsor-a-child.org.uk/.
This article describes the geography of Guinea-Bissau.
Climate
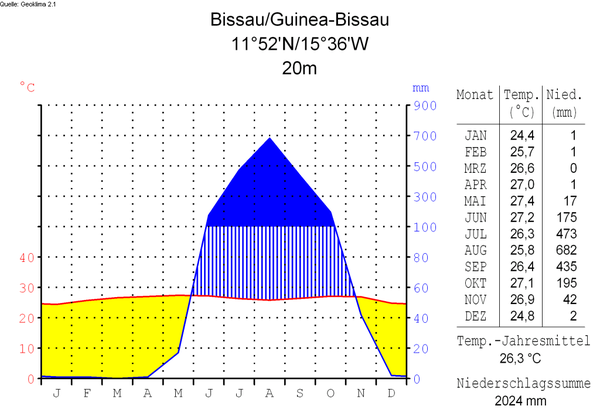
The climate in Guinea-Bissau is tropical. This means it is generally hot and humid. It has a monsoonal-type rainy season (June to November) with southwesterly winds and a dry season (December to May) with northeasterly harmattan winds.
Guinea-Bissau is warm all year around and there is little temperature fluctuation; it averages 26.3 °C (79.3 °F). The average rainfall for Bissau is 2,024 millimetres (79.7 in) although this is almost entirely accounted for during the rainy season which falls between June and September/October. From December through April, the country experiences drought.
Terrain and ecology
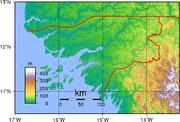
The terrain of Guinea-Bissau is mostly low coastal plain with swamps of Guinean mangroves rising to Guinean forest-savanna mosaic in the east.
The lowest point on Guinea-Bissau is at sea level at the Atlantic Ocean . The highest point on Guinea-Bissau is 300 metres above sea level at an unnamed location in the northeast corner of the country .
Natural resources found in Guinea-Bissau include fish, timber, phosphates, bauxite, clay, granite, limestone and unexploited deposits of petroleum . 8.31% of the land is arable and 250 square kilometres is irrigated. Natural hazards include a hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze that may reduce visibility during the dry season and brush fires . Severe environmental issues include deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing and overfishing .
Near the Senegal border there have been historic sightings of the Painted Hunting Dog, Lycaon pictus, but that endangered canid may now be extirpated in that locale.
Bissagos Islands
Information from the CIA World Factbook
- Location
- Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea and Senegal
- Geographic coordinates
- 12°00′N 15°00′W
- Map references
- Africa
- Area
-
- Total: 36,120 km²
- Land: 28,000 km²
- Water: 8,120 km²
- Area—comparative
- Slightly less than three times the size of Connecticut
- Land boundaries
-
- Total: 724 km
- Border countries: Guinea 386 km, Senegal 338 km
- Coastline
- 350 km
- Maritime claims
-
- Exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
- Terrain
- Mostly low coastal plain rising to savanna in east
- Elevation extremes
-
- Lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
- Highest point: Unnamed location in the northeast corner of the country 300 m
- Natural resources
- Fish, timber, phosphates, bauxite, unexploited deposits of petroleum
- Land use
-
- Arable land: 11%
- Permanent crops: 1%
- Permanent pastures: 38%
- Forests and woodland: 38%
- Other: 12% (1993 est.)
- Irrigated land
- 17 km² (1993 est.)
- Natural hazards
- Hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze may reduce visibility during dry season; brush fires
- Environment—current issues
- Deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing; overfishing
- Environment—international agreements
-
- Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Wetlands
- Signed, but not ratified: None of the selected agreements