Crocodile
Background Information
Arranging a Wikipedia selection for schools in the developing world without internet was an initiative by SOS Children. SOS Children is the world's largest charity giving orphaned and abandoned children the chance of family life.
| Crocodiles Temporal range: Eocene – Recent, 55–0Ma |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus) | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Crocodylomorpha |
| Order: | Crocodylia |
| Superfamily: | Crocodyloidea |
| Family: | Crocodylidae Cuvier, 1807 |
| Type species | |
| Crocodylus niloticus Laurenti, 1768 |
|
Crocodiles (Crocodylidae) are large aquatic tetrapods that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. Lizards, snakes and crocodiles are all scaled diapsids, but crocodiles are archosaurs, which means they are genetically closer to birds and the extinct dinosaurs. Crocodylidae is classified as a biological family or subfamily.
The term can also be used more loosely to include all extant members of the order Crocodilia: which includes the crocodiles of Crocodylidae, the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae) and the gharials (family Gavialidae), and the rest of Crocodylomorpha, which includes prehistoric crocodile relatives and ancestors.
Crocodiles tend to congregate in freshwater habitats such as rivers, lakes, wetlands and sometimes in brackish water. They feed mostly on vertebrates (fish, reptiles, and mammals), and sometimes on invertebrates ( molluscs and crustaceans), depending on species. They first appeared during the Eocene epoch, about 55 million years ago.
Etymology
The word "crocodile" comes from the Ancient Greek κροκόδιλος (crocodilos), "lizard," used in the phrase ho krokódilos tou potamoú, "the lizard of the (Nile) river".
There are several variant Greek forms of the word attested, including the later form κροκόδειλος (crocodeilos) found cited in many English reference works. In the Koine Greek of Roman times, crocodilos and crocodeilos would have been pronounced identically, and either or both may be the source of the Latinized form crocodīlus used by the ancient Romans.
Crocodilos or crocodeilos is a compound of krokè ("pebbles"), and drilos/dreilos ("worm"), although drilos is only attested as a colloquial term for "penis". It is ascribed to Herodotus, and supposedly describes the basking habits of the Egyptian crocodile.
The form crocodrillus is attested in Medieval Latin. It is not clear whether this is a medieval corruption or derives from alternate Greco-Latin forms (late Greek corcodrillos and corcodrillion are attested).
A (further) corrupted form cocodrille is found in Old French and was borrowed into Middle English as cocodril(le). The Modern English form crocodile was adapted directly from the Classical Latin crocodīlus in the 16th century, replacing the earlier form.
The use of -y- in the scientific name Crocodylus (and forms derived from it) is a corruption introduced by Laurenti (1768).
Description
- Crocodiles are similar to alligators and caimans; for their common biology and differences between them, see Crocodilia.
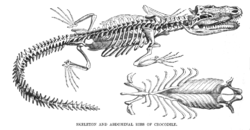
Despite their prehistoric look, crocodiles are among the more biologically complex reptiles. Unlike other reptiles, a crocodile has a cerebral cortex, a four-chambered heart, and the functional equivalent of a diaphragm, by incorporating muscles used for aquatic locomotion into respiration (e.g. m. diaphragmaticus); Its external morphology, on the other hand, is a sign of its aquatic and predatory lifestyle.
A crocodile’s physical traits allow it to be a successful predator. Its streamlined body enables it to swim swiftly, it also tucks its feet to the side while swimming, which makes it faster by decreasing water resistance. Its webbed feet, though not used to propel the animal through the water, allow it to make fast turns and sudden moves in the water or initiate swimming. Webbed feet are an advantage in shallower water, where the animal sometimes moves around by walking.
Crocodiles have a palatal flap, a rigid tissue at the back of the mouth that blocks the entry of water. The palate has a special path from the nostril to the glottis that bypasses the mouth. The nostrils are closed during submergence. Like other archosaurs, crocodilians are diapsid, although their post-temporal fenestrae are reduced. The walls of the braincase are bony, but lack supratemporal and postfrontal bones. Their tongues are not free, but held in place by a membrane that limits movement; as a result, crocodiles are unable to stick out their tongues.
Crocodilian scales have pores believed to be sensory in function, analogous to the lateral line in fishes. They are particularly seen on their upper and lower jaws. Another possibility is that they are secretory, as they produce an oily substance, which appears to flush mud off.
Crocodiles are very fast over short distances, even out of water. Since they feed by grabbing and holding onto their prey, they have evolved sharp teeth for tearing and holding onto flesh, and powerful muscles to close the jaws and hold them shut. These jaws can bite down with immense force, by far the strongest bite of any animal. The pressure of the crocodile's bite is more than 5,000 pounds per square inch (30,000 kPa), compared to just 335 pounds per square inch (2,300 kPa) for a Rottweiler, 400 pounds per square inch (2,800 kPa) for a large great white shark, 800 pounds per square inch (6,000 kPa) to 1,000 pounds per square inch (7,000 kPa) for a hyena, or 2,000 pounds per square inch (10,000 kPa) for a large alligator. The jaws are opened, however, by a very weak set of muscles. Crocodiles can thus be subdued for study or transport by taping their jaws or holding their jaws shut with large rubber bands cut from automobile inner tubes. They have limited lateral (side-to-side) neck movement.
Biology and behaviour
Crocodiles are ambush hunters, waiting for fish or land animals to come close, then rushing out to attack. As cold-blooded predators, they have a very slow metabolism, so they can survive long periods without food. Despite their appearance of being slow, crocodiles are top predators in their environment, and various species have been observed attacking and killing sharks.
Herodotus claimed that Nile crocodiles had a symbiotic relationship with certain birds, such as the Egyptian plover, which enter the crocodile's mouth and pick leeches feeding on the crocodile's blood; with no evidence of this interaction actually occurring in any crocodile species, it is most likely mythical or allegorical fiction.
Many large crocodilians swallow stones (called gastroliths or stomach stones), which may act as ballast to balance their bodies or assist in crushing food, similar to grit in birds.
Salt glands are present in the tongues of most crocodylids and they have a pore opening on the surface of the tongue. They appear to be similar to those in marine turtles; they seem to be absent in Alligatoridae.
Crocodilians can produce sounds during distress and in aggressive displays. They can also hear well, but their tympanic membranes are concealed by flat flaps that may be raised or lowered by muscles.
Crocodiles eat fish, birds, mammals and occasionally smaller crocodiles.
Crocodiles are protected in many parts of the world, but they also are farmed commercially. Their hides are tanned and used to make leather goods such as shoes and handbags; crocodile meat is also considered a delicacy. The most commonly farmed species are the saltwater and Nile crocodiles, while a hybrid of the saltwater and the rare Siamese crocodile is also bred in Asian farms. Farming has resulted in an increase in the saltwater crocodile population in Australia, as eggs are usually harvested from the wild, so landowners have an incentive to conserve their habitat.
Crocodiles are more closely related to birds and dinosaurs than to most animals classified as reptiles, the three being included in the group Archosauria ('ruling reptiles'). See Crocodilia for more information.
Crocodile embryos do not have sex chromosomes, and unlike humans, sex is not determined genetically. Sex is determined by temperature, with males produced at around 31.6 °C (89 °F), and females produced at slightly lower and higher temperatures. The average incubation period is around 80 days, and also is dependent on temperature.
Crocodiles may possess a form of homing instinct. In northern Australia, three rogue saltwater crocodiles were relocated 400 kilometres by helicopter, but had returned to their original locations within three weeks, based on data obtained from tracking devices attached to the reptiles.
The land speed record for a crocodile is 17 km/h (11 mph) measured in a galloping Australian freshwater crocodile. Maximum speed varies from species to species. Certain species can indeed gallop, including Cuban crocodiles, New Guinea crocodiles, African dwarf crocodiles, and even small Nile crocodiles. The fastest means by which most species can move is a kind of "belly run", where the body moves in a snake-like fashion, limbs splayed out to either side paddling away frantically while the tail whips to and fro. Crocodiles can reach speeds of 10 or 11 km/h (around 7 mph) when they "belly run", and often faster if slipping down muddy riverbanks. Another form of locomotion is the "high walk", where the body is raised clear of the ground.
Crocodiles do not have sweat glands and release heat through their mouths. They often sleep with their mouths open and may even pant like a dog.
The BBC TV reported that a Nile crocodile that has lurked a long time underwater to catch prey builds up a large oxygen debt. When it has caught and eaten that prey, it closes its right aortic arch and uses its left aortic arch to flush blood loaded with carbon dioxide from its muscles directly to its stomach; the resulting excess acidity in its blood supply makes it much easier for the stomach lining to secrete more stomach acid to quickly dissolve bulks of swallowed prey flesh and bone.
Size
Size greatly varies between species, from the dwarf crocodile to the saltwater crocodile. Species of Palaeosuchus and Osteolaemus grew to an adult size of just 1 m (3.3 ft) to 1.5 m (4.9 ft). Larger species can reach over 4.85 m (15.9 ft) long and weigh well over 1,200 kg (2,600 lb). Crocodilians show pronounced sexual dimorphism, with males growing much larger and more rapidly than females. Despite their large adult sizes, crocodiles start their lives at around 20 cm (7.9 in) long. The largest species of crocodile is the saltwater crocodile, found in eastern India, northern Australia, throughout South-east Asia, and in the surrounding waters.
Two larger certifiable records are both of 6.2-metre (20 ft) crocodiles. The first was shot in the Mary River in the Northern Territory of Australia in 1974 by poachers, and measured by wildlife rangers. The second crocodile was killed in 1983 in the Fly River, Papua New Guinea. In the case of the second crocodile, it was actually the skin that was measured by zoologist Jerome Montague, and as skins are known to underestimate the size of the actual animal, it is possible this crocodile was at least another 10 cm longer.
The largest crocodile ever held in captivity is an estuarine–Siamese hybrid named Yai ( Thai: ใหญ่, meaning big) (born 10 June 1972) at the Samutprakarn Crocodile Farm and Zoo, Thailand. This animal measures 6 m (20 ft) in length and weighs 1,114.27 kg (2,456.5 lb).
The longest crocodile captured alive is Lolong, which was measured at 6.17 m (20.24 ft) and weighed at 1,075 kg (2,370 lb) by a National Geographic team in Agusan del Sur Province, Philippines.
Wildlife experts, however, argue the largest crocodile so far found in the Bhitarkanika was almost 7 m (23 ft) long, which could be traced from the skull preserved by the Kanika royal family. The crocodile was shot near Dhamara in 1926 and later its skull was preserved by the then Kanika king. Crocodile experts estimated the animal was between 6.1 m (20 ft) and 7 m (23 ft) long, as the size of the skull was measured one-ninth of the total length of the body.
Age
Measuring crocodile age is unreliable, although several techniques are used to derive a reasonable guess. The most common method is to measure lamellar growth rings in bones and teeth—each ring corresponds to a change in growth rate which typically occurs once a year between dry and wet seasons. Bearing these inaccuracies in mind, the oldest crocodilians appear to be the largest species. C. porosus is estimated to live around 70 years on average, with limited evidence of some individuals exceeding 100 years. One of the oldest crocodiles recorded died in a zoo in Russia. A male freshwater crocodile at the Australia Zoo is estimated to be 130 years old. He was rescued from the wild by Bob Irwin and Steve Irwin after being shot twice by hunters. As a result of the shootings, this crocodile (known affectionately as "Mr. Freshy") has lost his right eye.
Skin
Crocodiles have smooth skin on their bellies and sides, while their dorsal surfaces are armoured with large osteoderms. The armoured skin has scales and is thick and rugged, providing some protection. They are still able to absorb heat through this armour, as a network of small capillaries allow blood through the scales to absorb heat.
Taxonomy of the Crocodylidae
Most species are grouped into the genus Crocodylus. The other extant genus, Osteolaemus, is monotypic (as is Mecistops, if recognized).
- Family Crocodylidae
- Subfamily † Mekosuchinae (extinct)
- Subfamily Crocodylinae
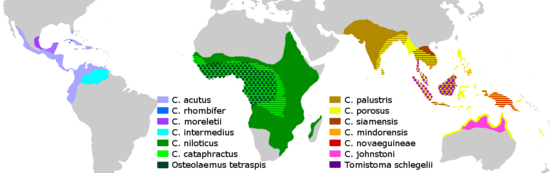
- Genus Crocodylus
- Crocodylus acutus, American crocodile
- Crocodylus cataphractus, slender-snouted crocodile (studies in DNA and morphology suggest this species may be more basal than Crocodylus, so belongs in its own genus, Mecistops).
- Crocodylus intermedius, Orinoco crocodile
- Crocodylus johnsoni, freshwater crocodile, or Johnstone's crocodile
- Crocodylus mindorensis, Philippine crocodile
- Crocodylus moreletii, Morelet's crocodile or Mexican crocodile
- Crocodylus niloticus, Nile crocodile or African crocodile (the subspecies found in Madagascar is sometimes called the black crocodile)
- Crocodylus novaeguineae, New Guinea crocodile
- Crocodylus palustris, mugger, marsh or Indian crocodile
- Crocodylus porosus, saltwater crocodile or estuarine crocodile
- Crocodylus rhombifer, Cuban crocodile
- Crocodylus siamensis, Siamese crocodile (may be extinct in the wild)
- Crocodylus suchus, West African crocodile, desert or sacred crocodile
- Genus Osteolaemus
- Osteolaemus tetraspis, dwarf crocodile (There has been controversy as to whether or not this is actually two species; recent (2010) DNA analysis indicate three distinct species: O. tetraspis, O. osborni and a third, currently unnamed.)
- Genus † Euthecodon
- Genus † Rimasuchus (formerly Crocodylus lloydi)
- Genus † Voay Brochu, 2007 (formerly Crocodylus robustus)
- Genus Crocodylus
Phylogeny
The cladogram below follows the topology from a 2012 analysis of morphological traits by Christopher A. Brochu and Glenn W. Storrs. Many extinct species of Crocodylus might represent different genera. C. suchus was not included, because its morphological codings were identical to these of C. niloticus. However, the authors suggested that it could be explained by their specimen sampling, and considered the two species to be distinct.
Crocodiles and humans
Danger to humans

The larger species of crocodiles are very dangerous to humans, mainly because of their ability to strike before the person can react. The saltwater crocodile and Nile crocodile are the most dangerous, killing hundreds of people each year in parts of Southeast Asia and Africa. The mugger crocodile, American crocodile, American alligator and black caiman are also dangerous to humans.
Crocodile products

Crocodile leather can be made into goods such as wallets, briefcases, purses, handbags, belts, hats, and shoes.
Crocodile meat is consumed in some countries, such as Australia, Ethiopia, Thailand, South Africa and also Cuba (in pickled form); it can also be found in specialty restaurants in some parts of the United States. The meat is white and its nutritional composition compares favourably with that of other meats. It tends to have a slightly higher cholesterol level than other meats. Crocodile meat has a delicate flavour; some describe it as a cross between chicken and crab. Cuts of meat include backstrap and tail fillet.
Crocodile oil has been used for various purposes.