How to find and keep customers
Practical Action
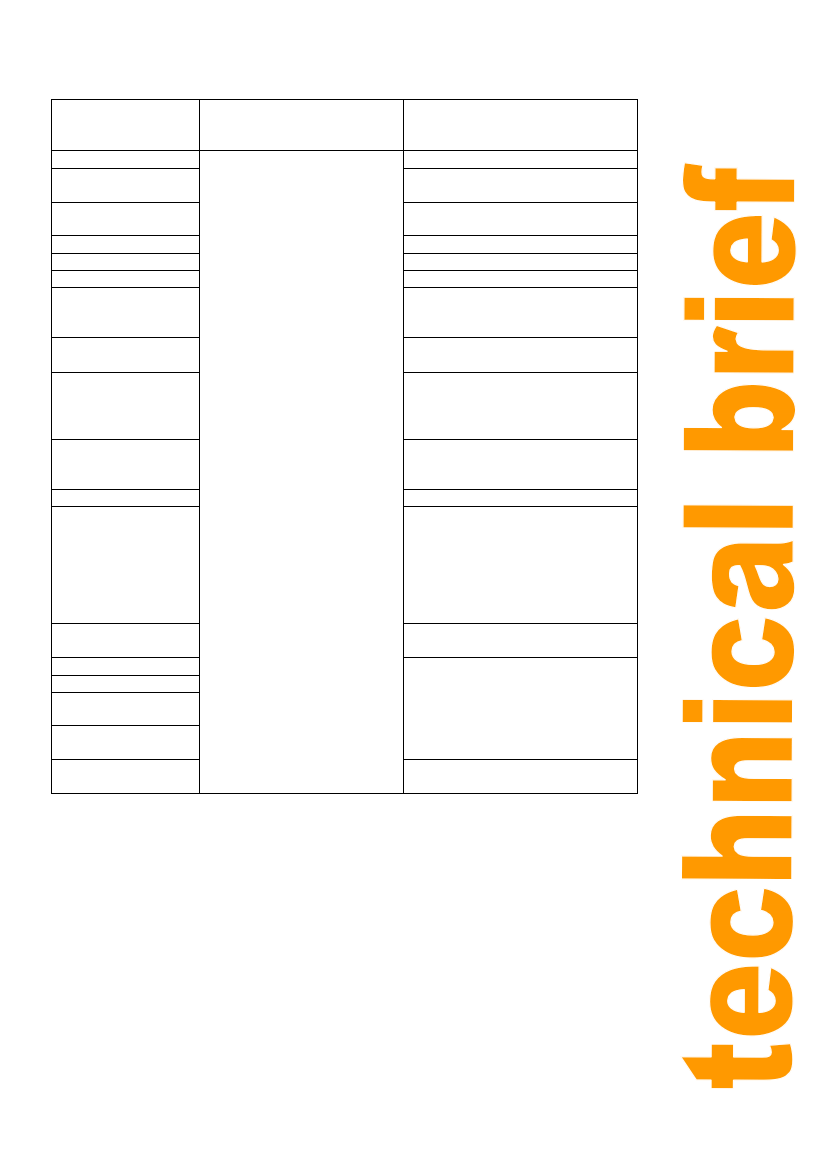
Market segments
Examples of different types of
Examples of foods
retail or food service
consumers
Direct sales
From own ‘factory Men or women
All foods
shop’
Service (or ‘custom’)
milling
Children and young
people
Cereal flours or cooking oils
Retail
Supermarkets
Shops
Rural, peri-urban or
urban households
All foods
All foods
Kiosks or street
vendors
Wealthy or less wealthy
families
Confectionery, dried fruits, roasted
nuts, sandwiches, bread and other
bakery products.
Food service
businesses
Cafes, restaurants,
People interested in
‘healthy’ foods
Cooking oil, bakery products, milk,
‘fast food’ outlets,
take-aways or bars
People with special
dietary needs
butter, cheese, chilled or frozen
meat products, bulk jams or sauces,
alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks.
Hotels/lodges
Portions of butter or jam, packaged
Office or factory workers juices or other drinks, bulk cooking
ingredients and chilled fresh foods.
Street-food vendors
Cooking oils, chilled meats or fish
Wholesalers
All foods
Local wholesale
buyers
Fair trade
organisations
Regional or national
wholesale buyers
Institutional buyers
for:
Schools
Bulk cereal flours, cooking oils,
Hospitals
dried or chilled fruits or vegetables,
Military barracks
chilled or frozen meat and fish.
/police
Local or central
government
Other food businesses
Bulk dairy products, honey, syrups
or jam for bakeries.
Table 1: Examples of market sectors, types of consumer and foods (Note: export markets are
excluded).
Types of markets
One of the first steps is to identify as precisely as possible what are the likely (or ‘target’)
market segments for a product - or more simply, who do processors expect to buy their food.
The types of questions that processors should ask when identifying suitable buyers are shown
in Table 2.
2