Fruit vinegar
Practical Action
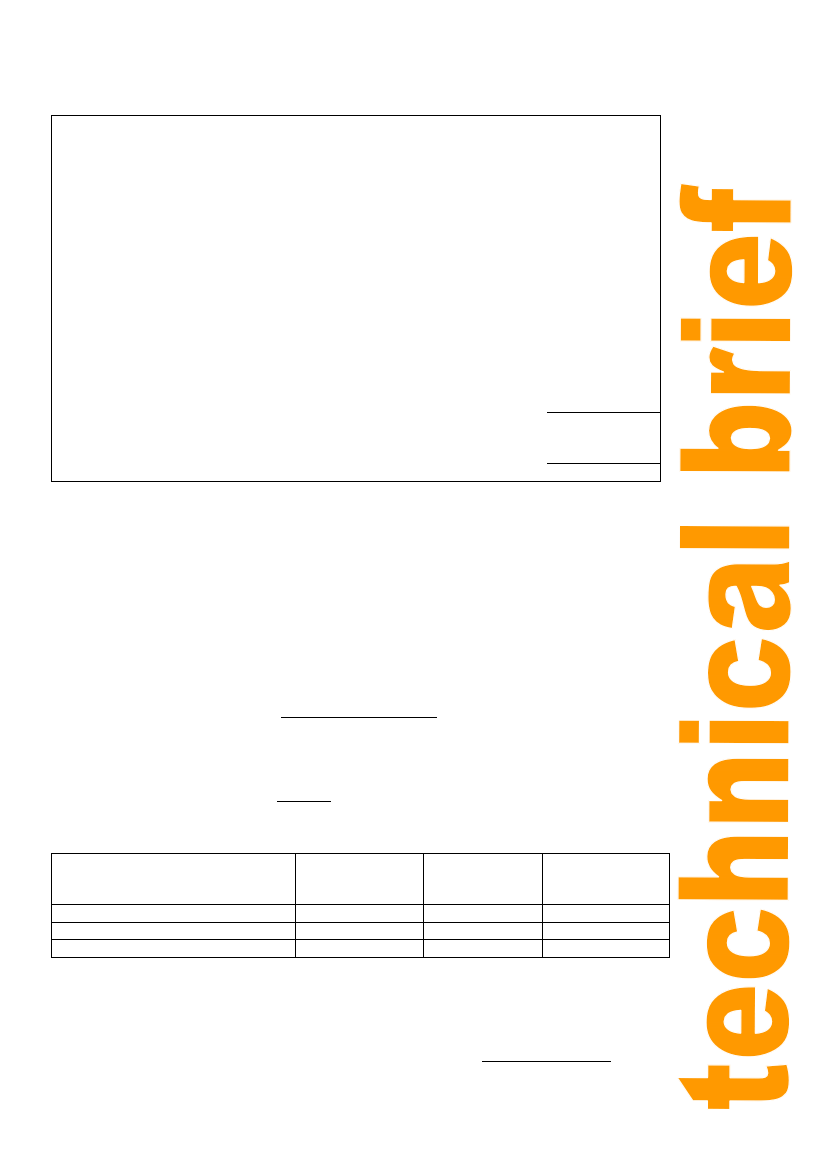
Raw material(banana) (Kg)
Labour (day)
Yeast (g)
Sodium bisulphate (kg)
Vinegar starter (lts)
Sugar (kg)
Citric acid (g)
Bottles (450 cc)
Plastic tops (unit)
Cap sleeves
Labels
kerosene (gal)
cotton (pack) 500 g
Water (lts)
Marketing costs (10%)
Miscellaneous (10%)
expense
($)
0.1420
0.0200
0.4500
0.0001
0.6850
0.0680
0.1000
1.0000
1.0000
1.0000
1.0000
0.0140
0.0080
0.4280
price
per unit
($)
0.120
1.850
0.004
2.500
0.240
0.500
0.003
0.050
0.020
0.030
0.008
1.450
1.300
0.220
total
cost
($)
0.0017
0.0370
0.0020
0.0003
0.1640
0.0340
0.0003
0.0500
0.0200
0.0300
0.0080
0.0200
0.0100
0.0940
$ 0.4866
0.0487
0.0535
$ 0.5888
To produce different quantities eg 778 (450 cc) bottles (or 350 litres of vinegar) we need
- banana
778 x 0.142 = 110 kg of banana
- sugar
778 x 0.068 = 52.90 Kg of sugar
and so on for every ingredient.
Break even production
Knowing the variable costs per bottle ($ 0.59) and the sale price per bottle of vinegar (1.01) we
can calculate the production quantity which will be equal to the total monthly income plus costs
(break even production) i.e. one neither gains or loses money when producing this amount of
vinegar.
Break even production
In our example:
= Total fixed costs of vinegar
Sale price - Variable cost
per bottle per bottle
Break even = $255.62 = 609 bottles of vinegar (450 ml)
1.01 - 0.59
Profitability of the plant
Monthly volume of
production (bottles)
(450 cc)
609 (break even)
778
2000(max. cap.)
Percentage use of
capacity
(%)
31
39
100
Total earnings of
the plant
($ US)
0.00
68.64
581.70
Total income per
person/month
($US)
7.59
9.60
24.67
Total Investment for Plant
A) Setting up costs
B) Costs of equipment and materials
C) Fixed costs
D) Variable costs (4 weeks) + (50 kg. of fruit)
Total
$ 146.47
$ 3109.45
$ 255.62
$ 465.02
$ 4379.58
10