MAINSTREAMING CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION IN AGRICULTURAL EXTENSION
SLIDE (Handout)
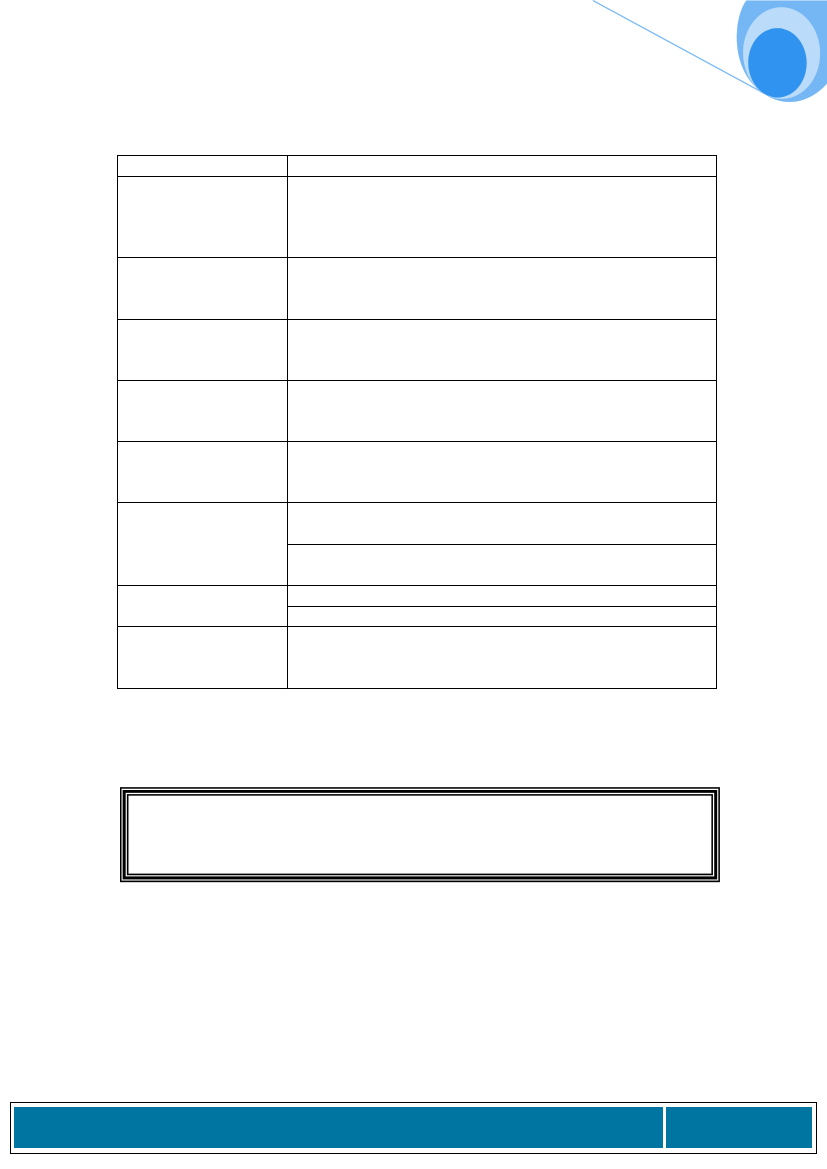
Hazard
History
Frequency / duration
Location
Causes
Warning signs
Who is most
severely affected &
how
How many people
affected
Severity / ability to
recover
Name one hazard type per format
What are the trends in hazard occurrence in living memory
(or beyond if there are records)?
How has the incidence / frequency changed over time?
Draw a TIMELINE to map changes if this helps.
What is the typical frequency of occurrence of this hazard
(annual; occasional)
How long does the hazard itself tend to last?
Which physical areas of the community are affected?
Use the COMMUNITY MAP you developed in Step 1 to add
on areas affected.
Are there underlying causes of the hazard? This may not be
the case for hazards such as earthquakes, however drought
may be caused by deforestation.
Is there local knowledge about signs of an impending
hazard?
Are there any early warning systems established in the area?
1) Farmers in low lying areas, land flooded, crops destroyed,
land eroded
2) Women & children - water supply is contaminated, higher
incidence of illness, more time needed for collecting water
1) 10% of population (poorest)?
2) 50% of population (rich and poor)?
Serious in some years. Lately erratic and very unpredictable.
Crops destroyed. Houses destroyed. Livelihoods threatened.
Food insecurity. Recovery for farmers is difficult and slow.
Task: Groups fill out hazard assessment for their “community”
How will Climate Change affect this table?
A Training Manual on Use of Climate Information and Vulnerability and Capacity Assessment for
Agricultural Extension Staff in Zimbabwe
Page 71