Tomato production: technical guidelines
Practical Action
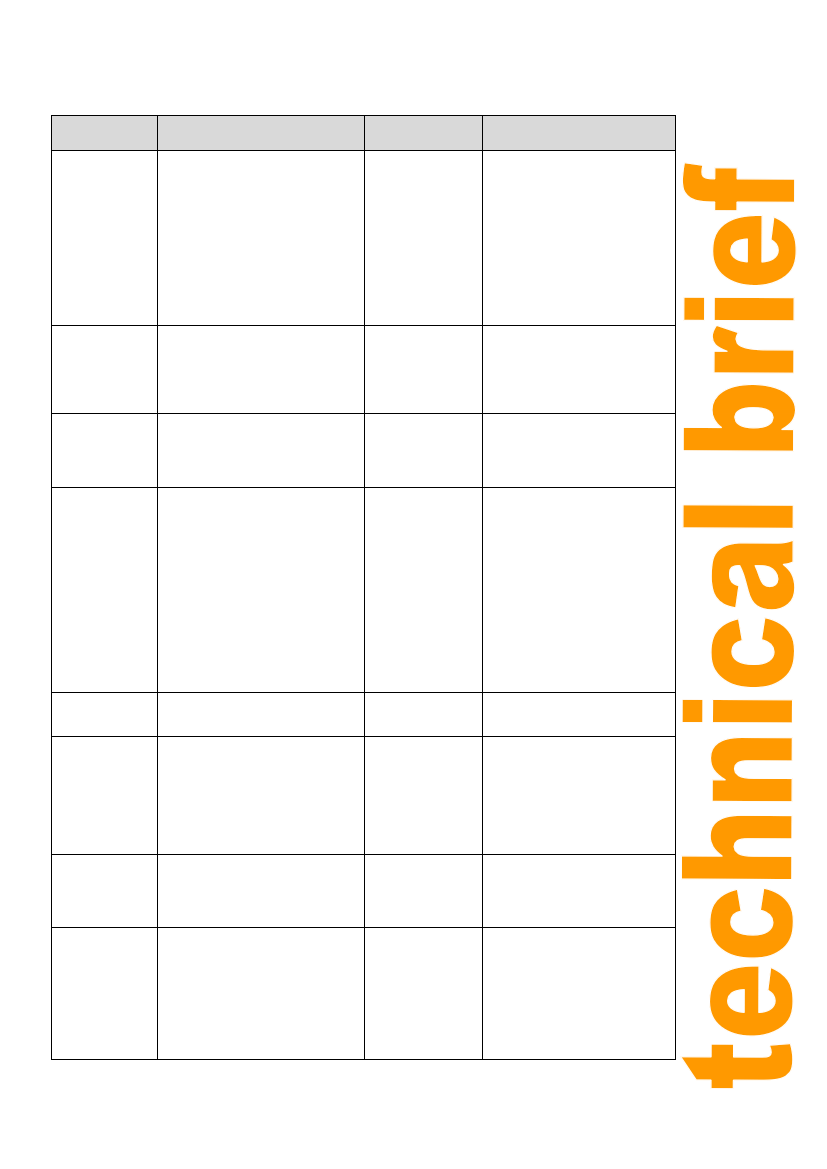
Pest/Disease
Bacterial
Bacterial Canter
Bacterial Spot
Bacterial Wilt
Virus Mosaic
Remarks
Wilting foliage, mealy breakdown
internal tissues of stem with
separation off from pith. Brown
horseshoe-shaped area seen when
leaves are cut off flush with stem
small sports on fruit usually with a
white or yellow halo
Dark brown raised pustules on the
fruit, later becoming slightly sunken
& scabby; leaf spot
Sudden wilting of plant browning of
woody tissues from which bacterial
drained soil slime oozes after cutting
across the
main root & lower part of stem
Mild strains cause a light dark green
mottling of the foliage. Plants
infected early may become stunted,
but infection after the crop has
become established in land normally
has little influence on growth.
Blotchy ripening of the fruit may
occur.
Symptoms
Correct seed and
site selection
should eliminate
the problem
Correct seed
selection copper
oxychloride sprayed
at a rate of
0.4kg/100 litre
water
Plant on well
drained soil
Remove and burn
infected plants.
Plant resistant
cultivar
Control
Soil on whIch a diseased crop has
been grown becomes
contaminated
can transmit Infection to
subsequent crops. Seed borne.
First observed In ZImbabwe in
1960 and now wider spread. If
canter does not occur on the land
the grower should preferably
select seed from his own crop
rather than
buy It.
Seed-borne infection only occurs
during the wet weather
Widespread in Eastern Districts,
but seldom serious
Substantial loss have occurred as
a result of strains
Bunch Top shoot
elongation
Fungal
Botrytis Rot
Collar rot
Early Blight
b) Severe stains cause stunting, leaf
curling,
purpling of the veins; severe brown
markings
sometimes appear on the fruit
Causes a marked reduction in
resulting in leaves at the top of the
plant small and distorted
Green fruit are generally attached.
A small water-soaked spot appears
on the stalk-end or on the side of
the fruit. The spot enlarges,
becomes soft and dirty, light grey to
brown in colour and fruits turn soft.
Also Ghost Spot and Leaf Stem
Rot
Dark-brown sunken lesions on the
stem of seedlings and young
transplant at soil level
Dark reddish-brown leaf spots with
concentric marking appear first on
the lower most leaves; cause
defoliation. Infection of the fruit is
usually around the calyx but may be
associated with cracks and other
skin injuries
Remove and burn
infected plants
Spray with dicloran
50% wp at a rate of
150g/100 litres
water
Outbreaks are sporadic but can
cause failures. As insect vector
may be involved
Spray stem to a height of 450-
600mm and from February,
repeat every 7 days if necessary
Spray with sulphur
mancozeb (48/32%
wp) at a rate of
500-800g/100
litres water
Several chemicals
are available.
Mancozeb 80% wp
at a rate 200/100
litres water can be
used
Full cover spray and repeat at
5/10 day intervals in humid
conditions same fungus as Early
Blight. This disease is common at
all times of the year
7