


 |  |  |
| | ||
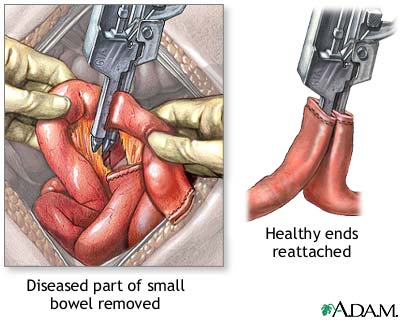
Small bowel resection - series: Procedure
 |
|
The diseased part of the small intestine (ileum) is removed. The two healthy ends are then sewn back together and the incision is closed.
If it is necessary to spare the intestine from its normal digestive work while it heals, a temporary opening (stoma) of the intestine onto the abdomen (ileostomy) may be done. A temporary ileostomy will be closed and repaired later. If a large portion of the bowel is removed, the ileostomy may be permanent.
The ileum absorbs much of the fluid from foods. When the large intestine is bypassed by an ileostomy, the patient should expect liquid stool (feces). The constant or frequent drainage of liquid stool can cause the skin around the ileostomy to become inflamed. Careful skin care and a well-fitting ileostomy bag can reduce this irritation.
Update Date: 7/23/2008 Updated by: Jacob L. Heller, MD, Emergency Medicine, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, Washington, Clinic. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
