Medical Encyclopedia
Exchange transfusion - series: Indication
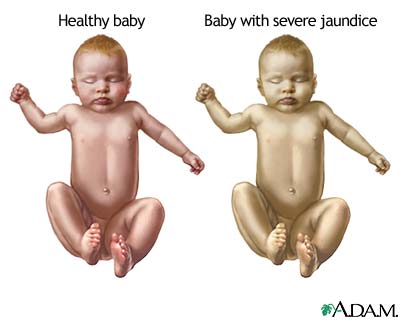
Less frequently, when neonatal jaundice is more severe, and fluorescent light therapy is unable to break down all circulating bilirubin, exchange transfusion is often used. High levels of bilirubin in the blood can lead to brain damage and other serious problems. In these cases, exchange transfusion is a life-saving procedure designed to counteract the effects of serious jaundice, infection, or toxicity. The procedure involves the staged removal of the infant's blood and replacement with fresh donor blood or plasma.
Guidelines for an exchange transfusion include:
-
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (Rh disease)
-
Life-threatening infection
-
Severe disturbances in body chemistry
-
Toxic effects of drugs
-
Polycythemia
Update Date: 4/8/2008
Updated by: Editorial Team: David Zieve, MD, MHA, Greg Juhn, MTPW, David R. Eltz, Kelli A. Stacy, ELS. Previously reviewed by Daniel Rauch, MD, FAAP, Director, Pediatric Hospitalist Program, Associate Professor of Pediatrics, NYU School of Medicine, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network (5/10/2006).
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2009, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.