


 |  |  |
| | ||
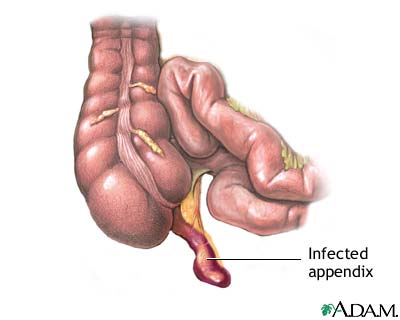
Appendectomy - series: Indications
 |
|
If the appendix becomes infected it must be surgically removed before it ruptures and spreads infection to the entire abdominal space. Symptoms of acute appendicitis include pain in the lower right side of the abdomen, fever, reduced appetite, nausea or vomiting.
Before surgery, the doctor will perform a physical exam. The physician will check the abdomen for tenderness and tightness and check the rectum for tenderness and an enlarged appendix. In women, a pelvic exam is also performed to exclude pain caused by the ovaries or uterus. Additionally, blood tests and X-rays may also be performed.
There is no test to confirm appendicitis and the symptoms may be caused by other illnesses. The doctor must diagnose from the information you report and what he sees. During appendectomy surgery, even if the surgeon finds that the appendix is not infected (which can happen up to 25% of the time), he will thoroughly check the other abdominal organs and remove the appendix anyway.
Update Date: 4/17/2008 Updated by: Jacob L. Heller, M.D., M.H.A., F.A.C.E.P., Section of Emergency Medicine, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
