Section 2
Population Growth
Book
Version 4
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Sociology
Sociology
by Boundless
5 concepts

Implications of Different Rates of Growth
Different rates of growth can lead to overpopulation or underpopulation, both of which have potential consequences.
Three Demographic Variables
The basics of demographic population growth depend on the rate of natural increase (births versus deaths) and net migration.

Problems in Forecasting Population Growth
Population growth is difficult to predict because unforeseen events can alter birth rates, death rates, migration, or resource limitations.

Malthus' Theory of Population Growth
Malthus believed that if a population is allowed to grow unchecked, people will begin to starve and will go to war over increasingly scarce resources.
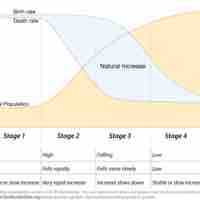
Demographic Transition Theory
Demographic transition theory outlines five stages of change in birth and death rates to predict the growth of populations.