Section 2
Global Stratification
Book
Version 4
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Sociology
Sociology
by Boundless
5 concepts
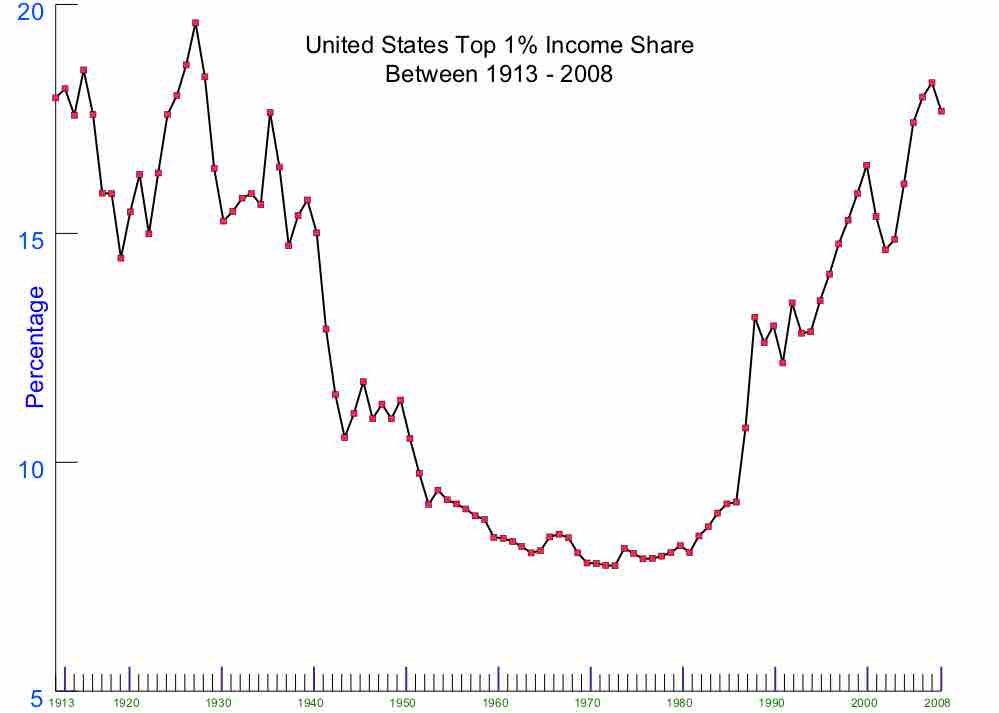
Global Stratification and Inequality
Stratification results in inequality when resources, opportunities, and privileges are distributed based on position in social hierarchy.
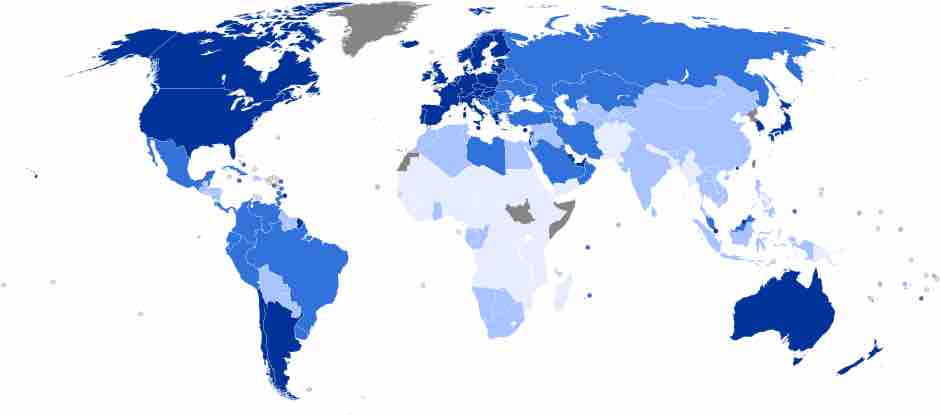
Industrialized Countries
Industrialized countries have greater levels of wealth and economic development than less-industrialized countries.
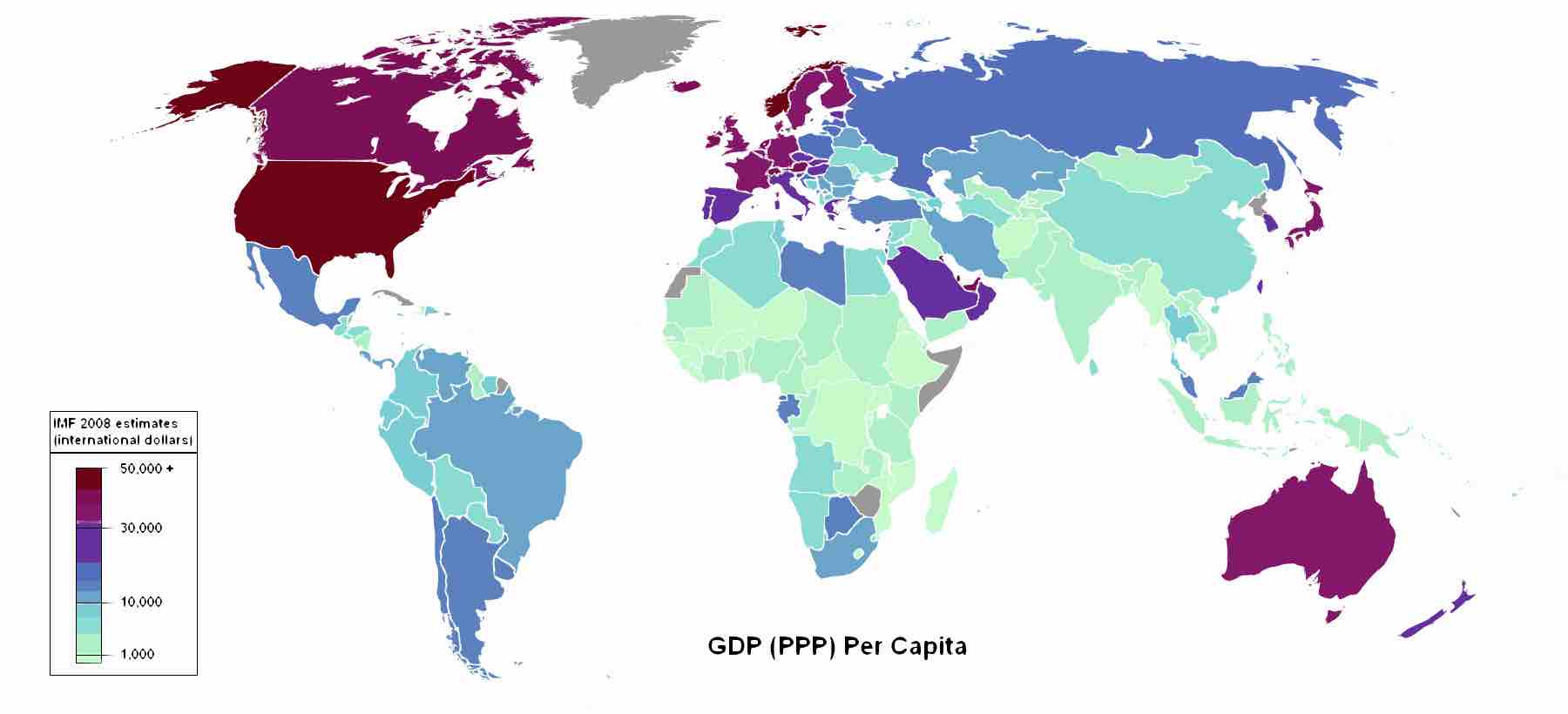
Industrializing Countries
Industrializing countries have low standards of living, undeveloped industry, and low Human Development Indices (HDIs).
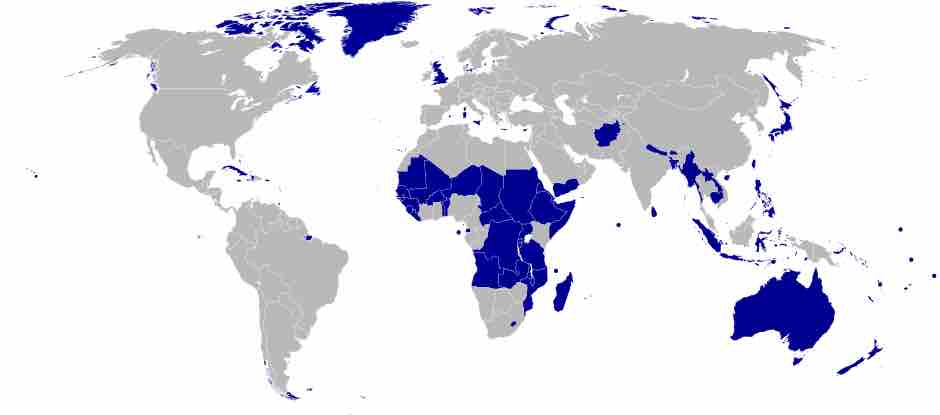
Least Industrialized Countries
The world's least industrialized countries have low income, few human resources, and are economically vulnerable.
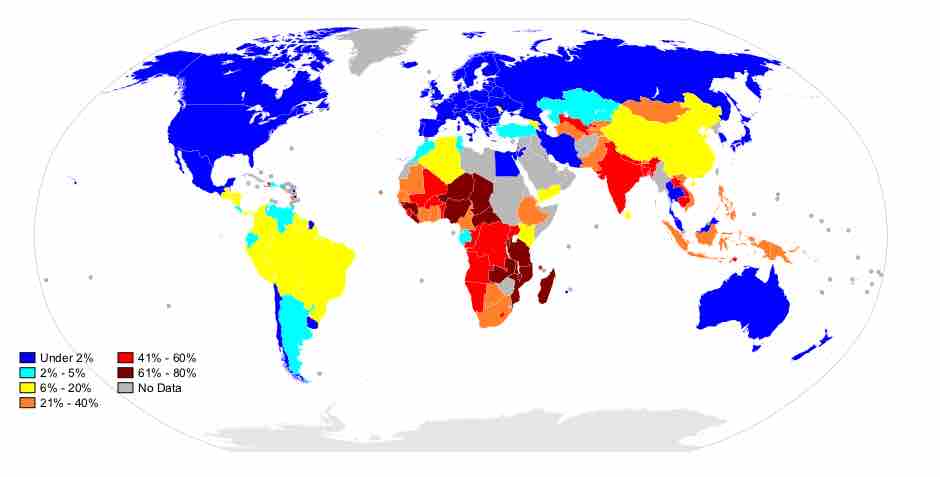
Growing Global Inequality
There is a wide gap between the wealth of the world's richest countries and its poorest.