Section 2
Sensory Processes
By Boundless
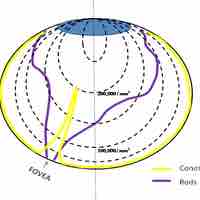
In the human visual system, the eye receives physical stimuli in the form of light and sends those stimuli as electrical signals to the brain, which interprets the signals as images.
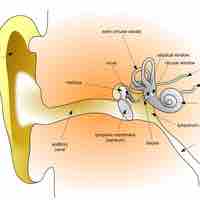
The human auditory system allows us to perceive and localize sounds in our physical environment.
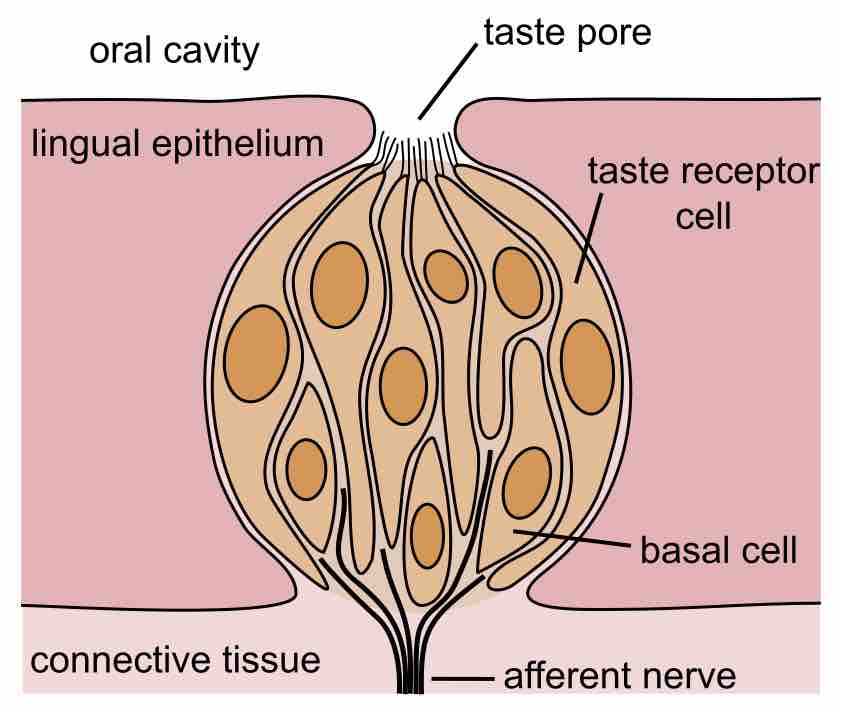
The gustatory system, including the mouth, tongue, and taste buds, allows us to transduce chemical molecules into specific taste sensations.
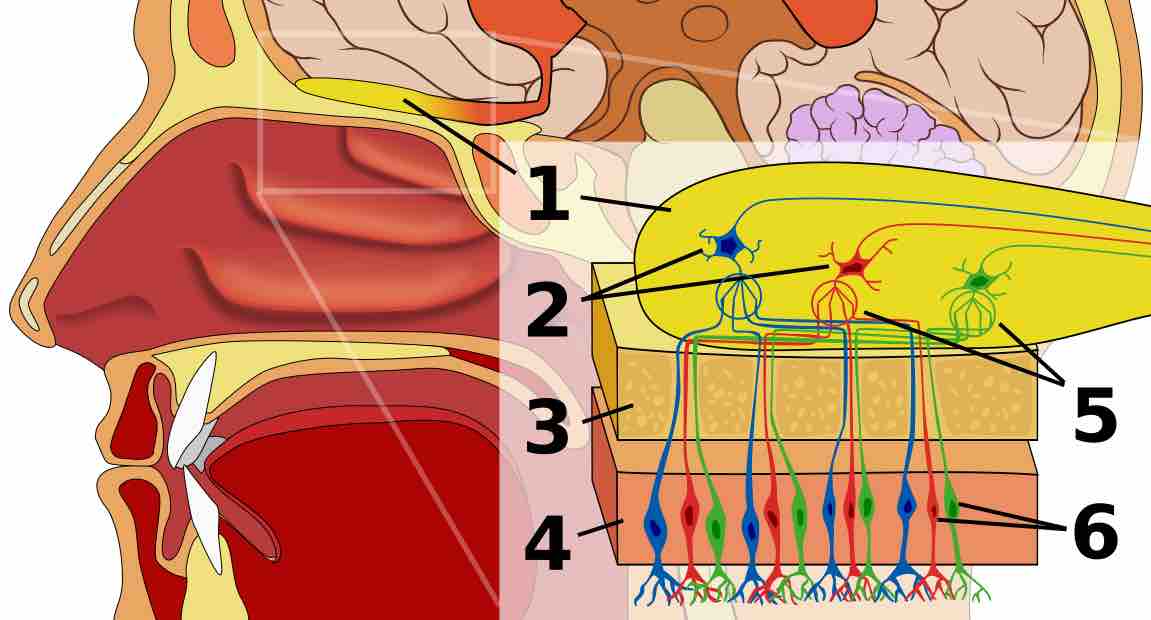
The olfactory system gives humans their sense of smell by collecting odorants from the environment and transducing them into neural signals.
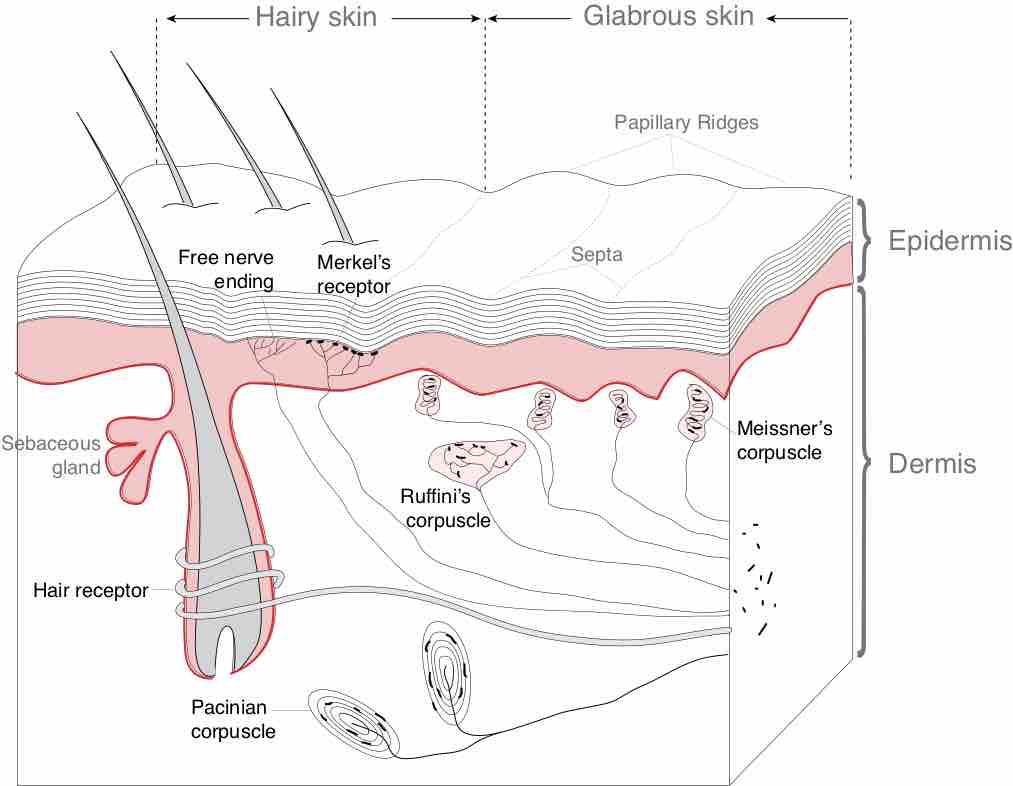
The somatosensory system allows the human body to perceive the physical sensations of pressure, temperature, and pain.
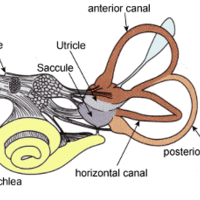
Two additional sensory systems are proprioception (which interprets body position) and the vestibular system (which interprets balance).