Section 3
Operant Conditioning
Book
Version 11
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Psychology
Psychology
by Boundless
5 concepts
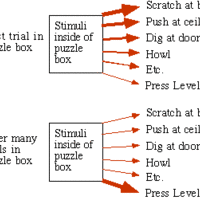
Basic Principles of Operant Conditioning: Thorndike's Law of Effect
Thorndike's law of effect states that behaviors are modified by their positive or negative consequences.

Basic Principles of Operant Conditioning: Skinner
B. F. Skinner was a behavioral psychologist who expanded the field by defining and elaborating on operant conditioning.

Shaping
Shaping is a method of operant conditioning by which successive approximations of a target behavior are reinforced.
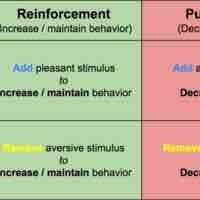
Reinforcement and Punishment
Reinforcement and punishment are principles of operant conditioning that increase or decrease the likelihood of a behavior.
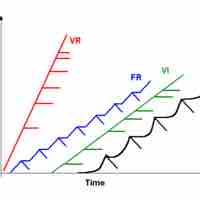
Schedules of Reinforcement
Reinforcement schedules determine how and when a behavior will be followed by a reinforcer.