Section 9
Motor Pathways
Book
Version 29
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Physiology
by Boundless
4 concepts
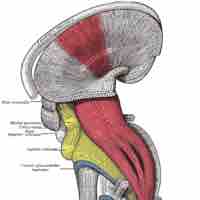
Organization of Motor Neuron Pathways
The motor system is the part of the central nervous system that is involved with movement.
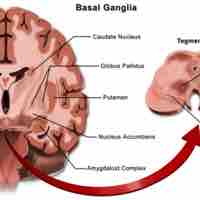
The Role of the Basal Ganglia in Movement
The basal ganglia are responsible for voluntary motor control, procedural learning, and eye movement, as well as cognitive and emotional functions.
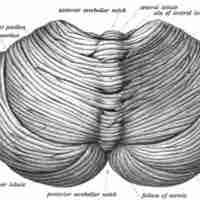
Modulation of Movement by the Cerebellum
The cerebellum is important for motor control—specifically coordination, precision, and timing—as well as some forms of motor learning.
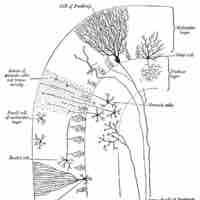
Functions of the Cerebellum in Integrating Movements
The cerebellum uses feedforward processing and modularity to process information.