Section 6
Humoral Immune Response
Book
Version 29
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Physiology
by Boundless
5 concepts
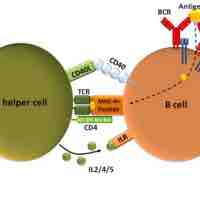
Clonal Selection and B-Cell Differentiation
B cells mature in the bone marrow, where they undergo VDJ recombination to produce unique receptors that do not react to self-antigens.
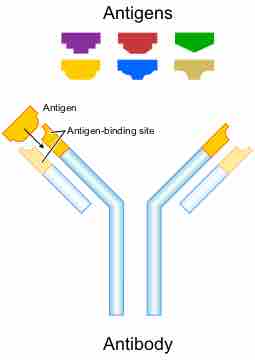
Structure and Function of Antibodies
An antibody is a Y-shaped protein produced by B cells to identify and neutralize antigens in the body.
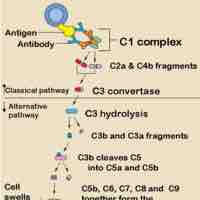
Role of the Complement System in Immunity
The complement system is the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to remove pathogens from an organism.
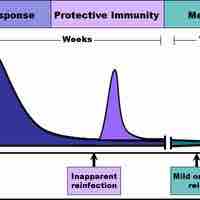
Immunological Memory
Immunological memory refers to the ability of B and T cells to produce long-lived memory cells that defend against specific pathogens.
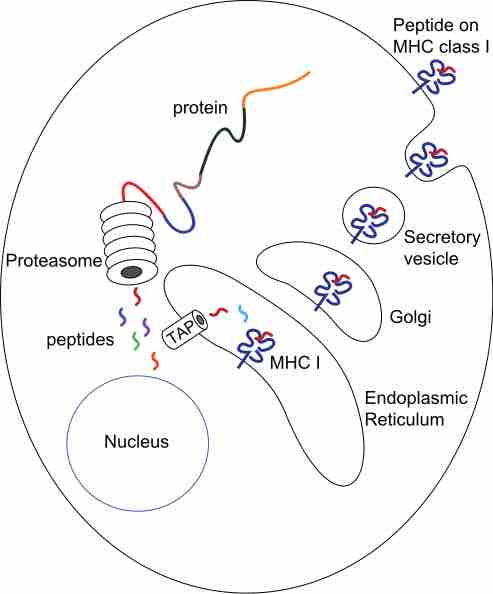
Major Histocompatibility Complex Antigens (Self-Antigens)
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a cell surface molecule that regulates interactions between white blood cells and other cells.