Section 7
The Cerebrum
Book
Version 29
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Physiology
by Boundless
5 concepts
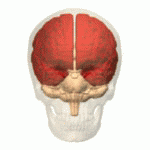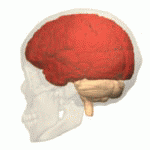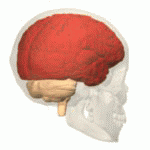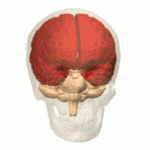
Overview of the Cerebrum
With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the body.
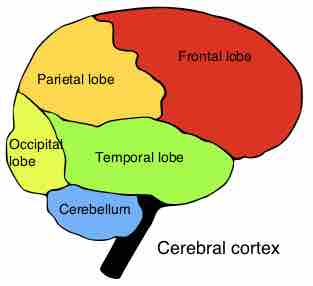
Cerebral Lobes
The cortex is divided into four main lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal.
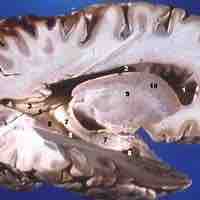
White Matter of the Cerebrum
White matter is composed of myelinated axons and glia and connects distinct areas of the cortex.
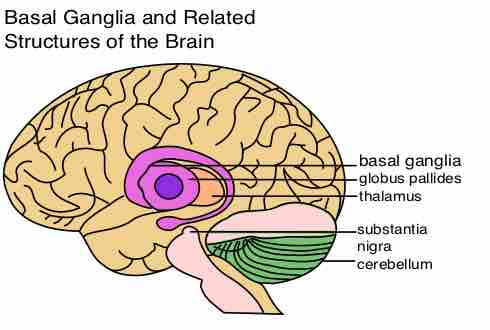
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia is important for initiating planned movements and forming habits, both referred to as 'behavior selection' or 'switching'.
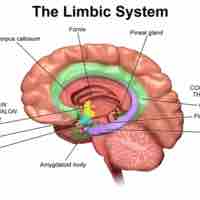
Limbic System
The limbic system makes up the inner border of the cortex and is vital for emotion, motivation, and memory.