Section 3
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Book
Version 29
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Physiology
by Boundless
3 concepts
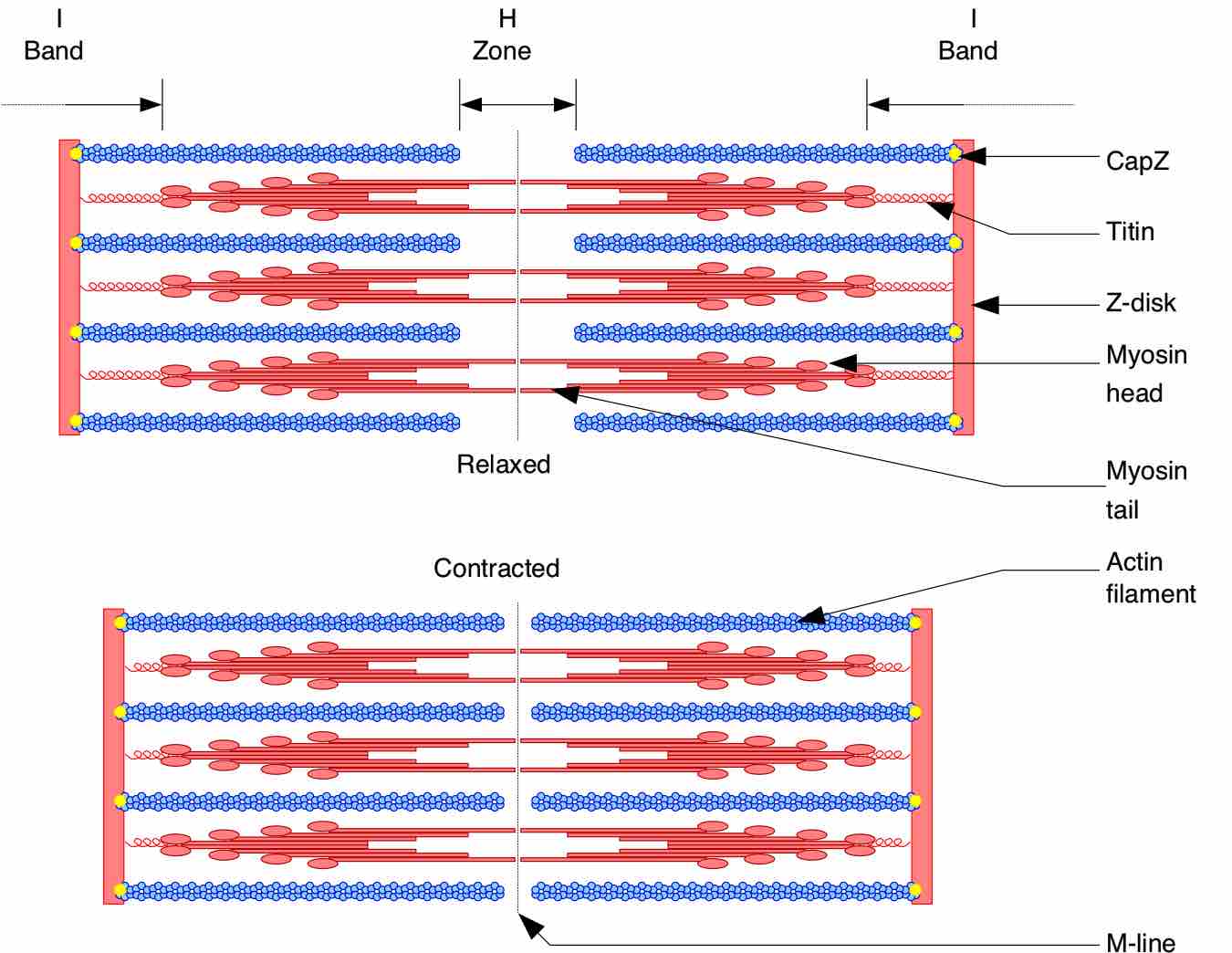
Microscopic Anatomy
Cardiac muscle appears striated due to the presence of sarcomeres, the highly-organized basic functional unit of muscle tissue.
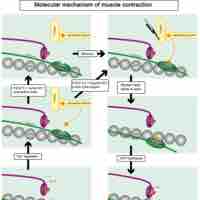
Mechanism and Contraction Events of Cardiac Muscle Fibers
Cardiac muscle fibers undergo coordinated contraction via calcium-induced calcium release conducted through the intercalated discs.
Energy Requirements
Cardiac cells contain numerous mitochondria, which enable continuous aerobic respiration and production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) for cardiac function.