Section 1
Water Balance
Book
Version 29
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Physiology
by Boundless
4 concepts
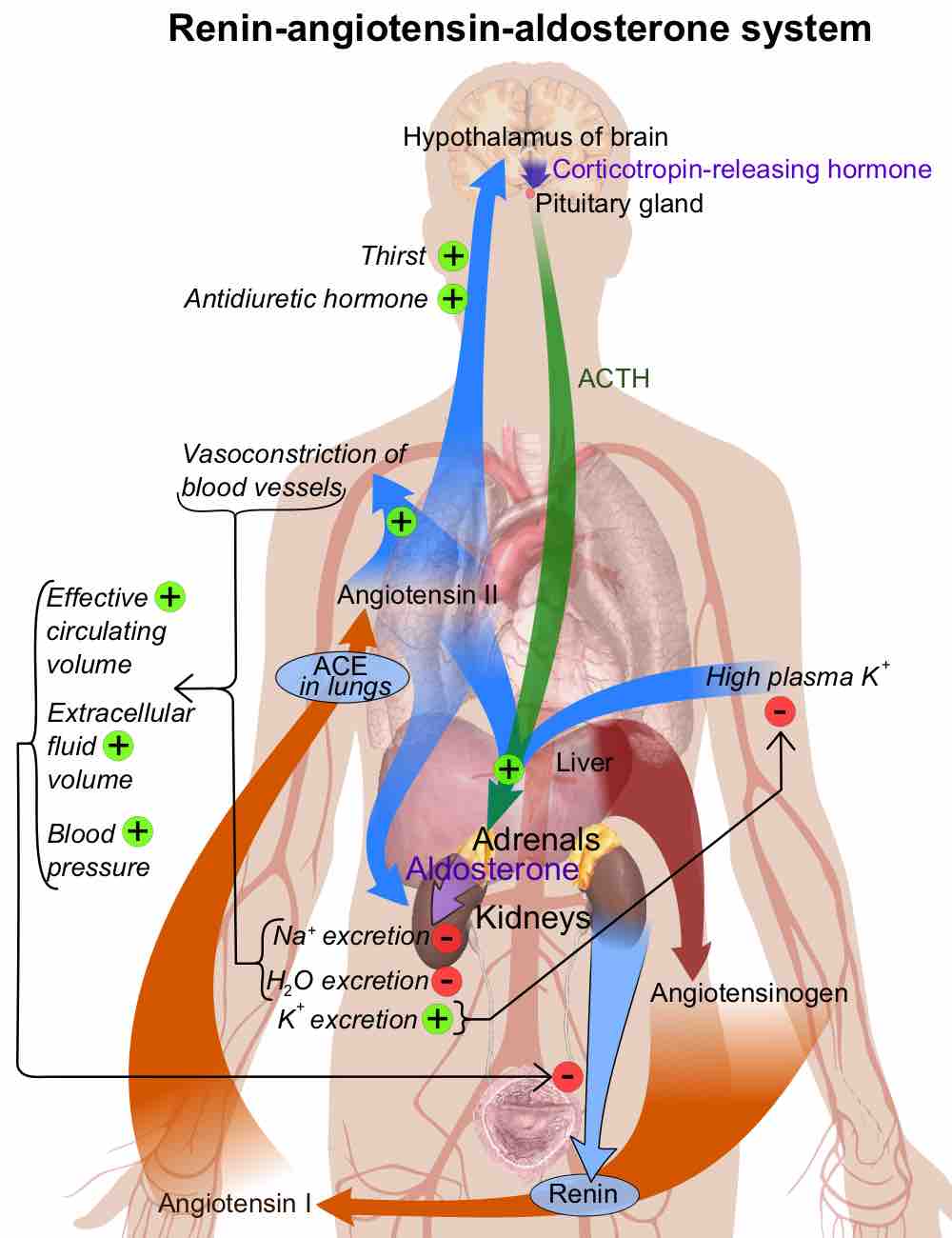
Regulation of Water Intake
Fluid can enter the body as preformed water, ingested food and drink, and to a lesser extent, as metabolic water.
Regulation of Water Output
Fluid can leave the body in several ways: urination, exretion (feces), and perspiration (sweating).
Nitrogenous Waste in Terrestrial Animals: The Urea Cycle
Urea, a nitrogenous waste material, is the end product excreted in urine when ammonia is metabolized by animals, such as mammals.
Water Balance Disorders
Dehydration is the excessive loss of body fluid.